The 7th Expanded Vietnam Hypertension Conference, held in Ho Chi Minh City on 23/11, brought together nearly 1,000 doctors, pharmacists, and experts from across the country. They presented over 200 of the latest specialized reports on hypertension diagnosis and treatment. At the conference, experts emphasized the theme "As One - a disease management solution aimed at comprehensive blood pressure control for public health" as a new approach to improve disease control rates in Vietnam.
 |
The 7th Expanded Vietnam Hypertension Conference took place in Ho Chi Minh City. Photo: LeAn Media |
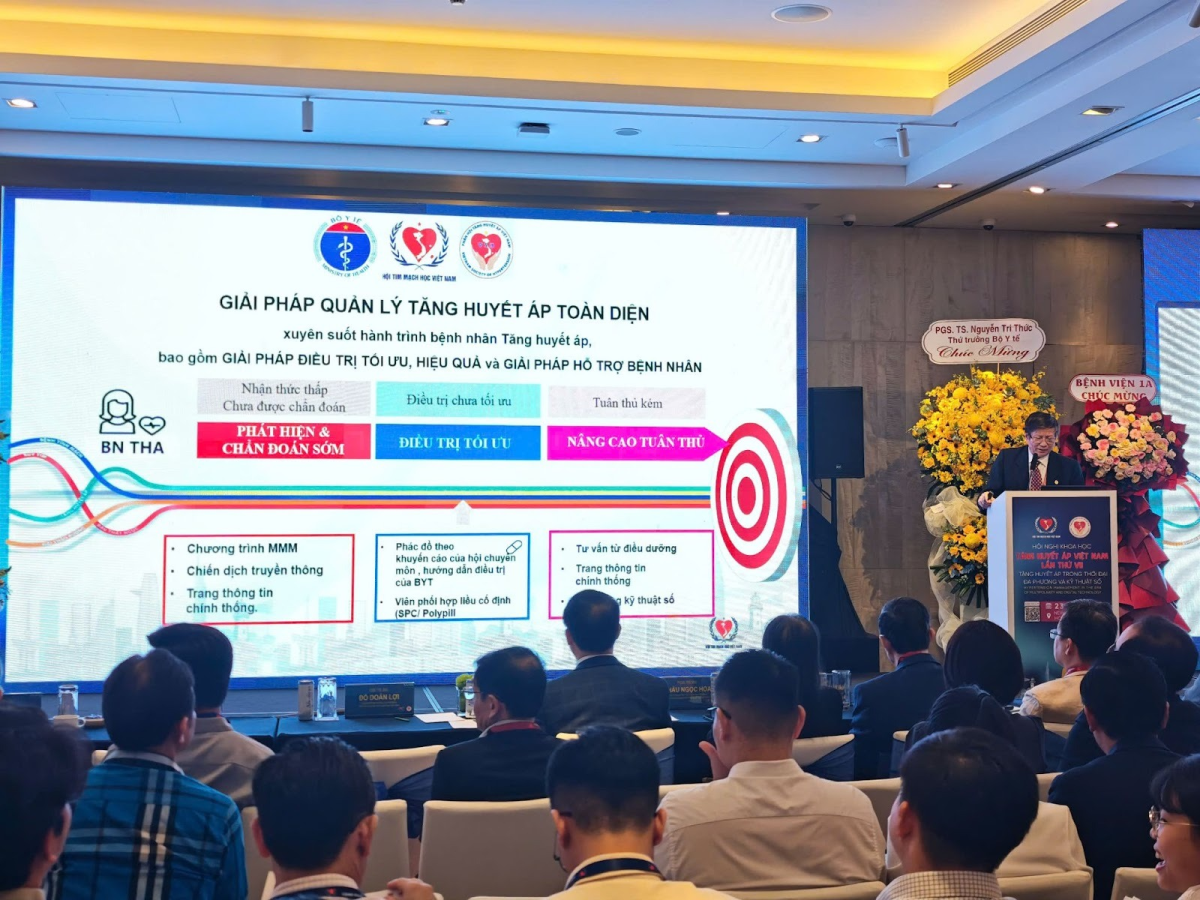
Opening the conference, Professor Dr. Huynh Van Minh shared important data from the May Measurement Month (MMM) program (2017-2023), reflecting the current state of blood pressure screening and control. Given the low control rates, the professor outlined directions for hypertension management in Vietnam. These include promoting early detection in the community, enhancing treatment adherence with fixed-dose combination pills to help patients reach targets quickly, and simplifying treatment regimens. In parallel, there is a need to improve the capacity of grassroots healthcare facilities in counseling, health education, public awareness, and regular screening. Concurrently, a continuous chronic disease management model must be established through the As One solution package to enhance the effectiveness of blood pressure control for Vietnamese patients.
 |
Professor Dr. Huynh Van Minh shared important data from MMM 2017-2023, reflecting the current state of blood pressure screening and control. Photo: LeAn Media |
The As One model, introduced at the conference, is a comprehensive solution that integrates advanced treatment with a multi-tiered patient support system. It prioritizes high-quality treatment based on the latest recommendations from the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) 2025 and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2025, with a particular emphasis on early fixed-dose combination therapy to optimize effectiveness, reduce the burden of multiple pills, and increase adherence. Alongside medication, communication and health education activities are implemented through both direct and online platforms, such as the "First Day" ecosystem. These efforts aim to raise public awareness about cardiovascular disease and underscore the patient's proactive role in managing their health.
The Elfie digital application serves as a companion tool, helping patients monitor their health metrics, receive treatment reminders, and connect with their medical team. The model also emphasizes the importance of multi-disciplinary cooperation among doctors, pharmacists, nurses, health managers, and patients, all working towards the common goal of increasing control rates for blood pressure, blood sugar, blood lipid, and heart rate readings.
During the MMM 2025 discussion session, a highlight of the conference involving representatives from over 20 provincial health departments nationwide, participants shared their experiences in implementing MMM in 2025. They stressed that a hypertension management model is effective only with synchronized efforts from leadership down to doctors and nurses. The discussion also clarified that managing hypertension patients requires attention to each touchpoint along the patient's journey. Upon diagnosis, medical teams and official information channels play a crucial role in communication and counseling, helping patients understand their health status and foster positive changes early on.
During the examination and treatment phase, doctors are central in selecting appropriate, effective, and economically viable treatment methods for patients, ensuring they access optimal care as early as possible. As patients enter the long-term treatment phase, support activities like patient clubs, online communication, and digital tools become companions, providing reminders and motivation to help patients maintain sustainable treatment. Experts concluded that As One focuses not only on medication but also on changing awareness and behavior, empowering patients to be more proactive in managing their own health.
A representative from the Department of Medical Examination and Treatment - Ministry of Health, also emphasized at the conference that improving blood pressure control is a top priority in the national program for non-communicable disease prevention. Building a continuous, patient-centered chronic disease management model with seamless coordination among various agencies is a key strategy to reduce the burden of disease.
The specialized sessions of the conference also updated attendees with new information from international conferences, including the European Society of Hypertension 2025 and the European Society of Cardiology 2025. Key takeaways highlighted the "5D" (Track Plan) model for comprehensive patient diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring; recommendations for early combination therapy; and the pivotal role of fixed-dose combination pills in simplifying and optimizing treatment effectiveness.
Hypertension remains one of the chronic diseases with the highest prevalence and complication rates in Vietnam. Statistics from the May Measurement Month (MMM) program, implemented by Servier Vietnam from 2017-2023, show that only 75% of surveyed individuals knew they had the condition, and the proportion of treated patients achieving target blood pressure was still less than 50%. While the latest recommendations have tightened treatment targets to below 130/80 mmHg, blood pressure control presents many challenges, necessitating a more comprehensive and sustainable disease management model.
The Dan