During pregnancy, the umbilical cord transports nutrients from the mother to the fetus and helps eliminate waste. Immediately after birth, the cord is clamped and cut. About three weeks after birth, the umbilical stump dries, blackens, and falls off without intervention. 7-10 days later, the navel area completely heals.
According to Dr. Nguyen Minh Thanh Giang from the Neonatal Center at Tam Anh General Hospital in TP HCM, during this time, parents need to clean the umbilical cord properly and check it regularly for any unusual signs. After the stump falls off, a few drops of blood without other symptoms is normal. Continued monitoring and care are necessary. However, if bleeding is heavy, prolonged, or accompanied by unusual symptoms, parents should take their baby to a medical facility for examination. Here are some common umbilical cord conditions in newborns:
Umbilical cord infection
This is a bacterial infection of the umbilical cord, with symptoms such as redness and swelling around the navel, which can spread to surrounding tissues. The navel may also discharge pus with a foul odor. The infection can be caused by various bacteria, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Escherichia coli.
Umbilical cord infections in newborns can quickly progress to systemic infection and sepsis, which can be fatal. Parents should immediately take their newborn to the hospital if the umbilical cord bleeds uncontrollably (bleeding continues after 10 minutes or recurs more than three times), if redness spreads more than 1 cm around the navel, or if the baby is lethargic, has a high fever, or is feeding poorly or refusing to feed.
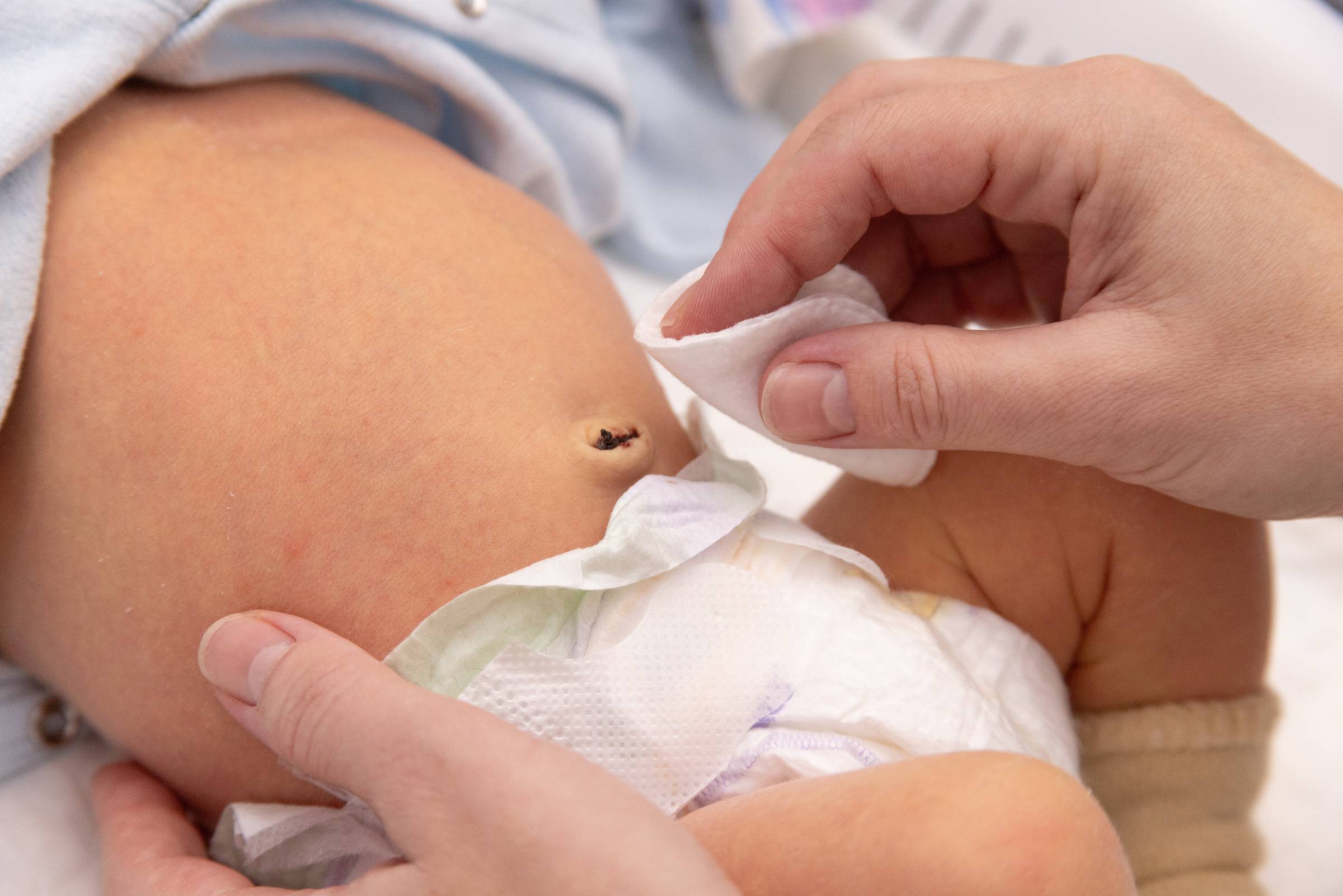 |
Fastening diapers below the navel helps reduce the risk of umbilical cord infection in newborns. Photo illustration: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Umbilical hernia
An umbilical hernia occurs when part of the abdominal wall is weakened, allowing a portion of the intestine to protrude, forming a bulge at the navel. This bulge becomes more prominent when the baby laughs, coughs, cries, or has a bowel movement, and may reduce in size when the baby is lying down.
In some cases, small umbilical hernias can be pushed back into the abdominal cavity. If the hernia causes complications, cannot be pushed back in, or does not disappear by the time the child is 4-5 years old, a specialist consultation is needed for timely intervention. This condition is more common in premature babies and children with Down syndrome (Trisomy 21).
Umbilical bleeding
Newborns may experience slight bleeding from the area between the umbilical stump and the base of the navel. This is known as umbilical bleeding. In most cases, the bleeding can be stopped by gently pressing a sterile gauze pad onto the baby's navel. However, if the bleeding is continuous and uncontrolled, parents should take the baby to a doctor for examination, as it could indicate infection, a blood clotting disorder, or an immune system disorder.
Patent urachus
The urachus is a tube that connects the bladder to the navel, allowing urine to exit the fetus's body. Normally, the urachus closes and degenerates into the median umbilical ligament before birth. However, in some cases, this process does not occur correctly, and the urachus remains partially or fully open, resulting in a patent urachus. This condition can cause the newborn's navel to remain persistently moist, increasing the risk of umbilical cord infection. Signs include discharge from the navel, swelling, redness, and a foul odor.
Umbilical tetanus
Umbilical tetanus occurs when the umbilical cord is infected with the bacterium Clostridium tetani. After an incubation period of about 7 days, symptoms such as high fever, irritability, refusal to feed, jaw stiffness, convulsions, and muscle rigidity may appear.
Single umbilical artery
Typically, a baby's umbilical cord has two arteries and one vein. However, in some cases (about 0.08-1.9% of newborns), the umbilical cord has only one artery, a condition known as single umbilical artery. Babies with this condition may have other birth defects, such as heart or urinary system abnormalities.
Gian Don - Ngoc Chau
| Readers can submit questions about children's health here for doctors to answer |