Answer:
Lung nodules are small lesions in the lung tissue, often discovered incidentally during chest X-rays or low-dose CT scans. Based on various characteristics of the nodules according to the Lung-RADS (Lung Reporting and Data System) classification, doctors assess the risk of cancer.
Most lung nodules are benign, especially those that are small, have well-defined borders, and don't grow over time. Benign nodules are often caused by infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, fungal infections, the non-infectious inflammatory disease sarcoidosis, or granulomatous disease. For nodules with a low risk of cancer, patients need monitoring and periodic checkups with CT scans. Continuous monitoring over a few years ensures that any unusual changes in the nodules are not missed. If the nodule doesn't change within two years, cancer is less likely, and the doctor may extend the interval between checkups.
A small percentage of lung nodules are malignant. Factors that increase the risk of malignancy include smoking, older age, family or personal history of cancer, and living in a polluted environment. When the characteristics of a lung nodule suggest malignancy, the doctor may order a biopsy. This involves using a needle inserted through the chest wall, guided by CT, to collect a small tissue sample from the nodule. Patients may undergo thoracoscopic surgery if the nodule has a high risk of malignancy. If the lesion is difficult to identify during surgery, the doctor will mark it under CT guidance before the procedure. The tissue sample undergoes an immediate frozen section biopsy, and if cancerous, the doctor determines the treatment based on the stage.
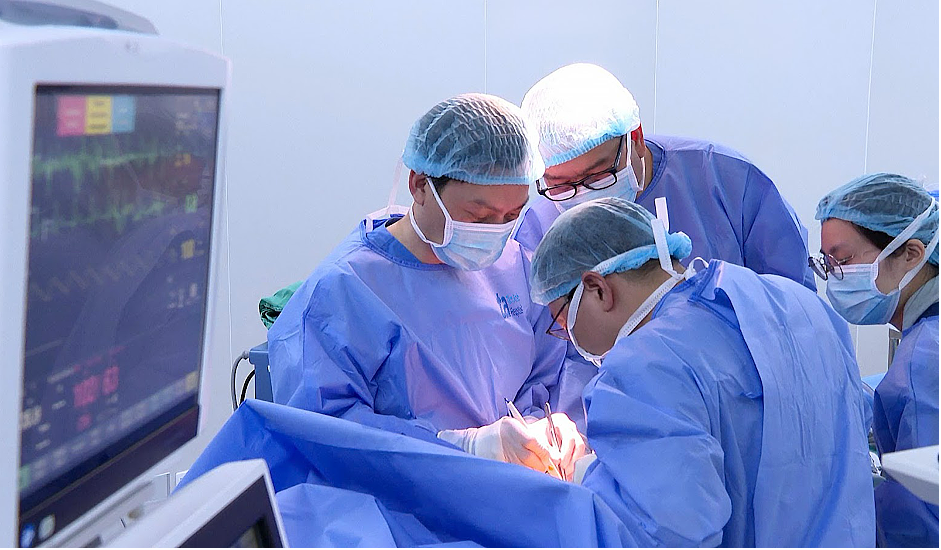 |
A doctor performs lung cancer surgery. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Quitting smoking is the most important factor in reducing the risk of lung cancer, especially for those who already have lung nodules. You should quit as soon as possible using support methods such as nicotine replacement therapy, counseling, or medication prescribed by a doctor.
Limiting exposure to secondhand smoke and airborne toxins like dust and exhaust fumes is also crucial for lung health. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and antioxidant-rich foods strengthens the immune system and promotes lung health. Regular exercise improves respiratory function and overall health. People with a family history of lung cancer or other high-risk factors should have regular checkups for early detection of respiratory diseases.
MSc. MD Nguyen The Thu
Oncology Department
Tam Anh General Hospital Hanoi
| Readers can submit questions about cancer here for doctors to answer. |