A hospital representative said on 5/9 that this is the heaviest newborn ever recorded in the maternity ward. The mother, in her 41st week of pregnancy, was undergoing her fifth labor and had a history of gestational diabetes. Recognizing potential risks to both mother and child, doctors decided on an emergency C-section.
After birth, the baby boy showed signs of wheezing and slight cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin) around the lips. He was transferred to the pediatric ward for monitoring. Currently, both mother and baby are in stable condition.
The mother's medical history revealed a diagnosis of gestational diabetes, but she hadn't fully complied with the advice, guidance, and monitoring provided by her obstetrician. As a result, the fetus grew excessively large, endangering both mother and baby and increasing the risk of birth complications and future health problems for the child.
The average weight of a full-term newborn is around 2.8-3.5 kg. A fetus weighing more than 4 kg is considered macrosomic (large for gestational age). Heavy babies require close monitoring due to a higher risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) because of their increased energy needs.
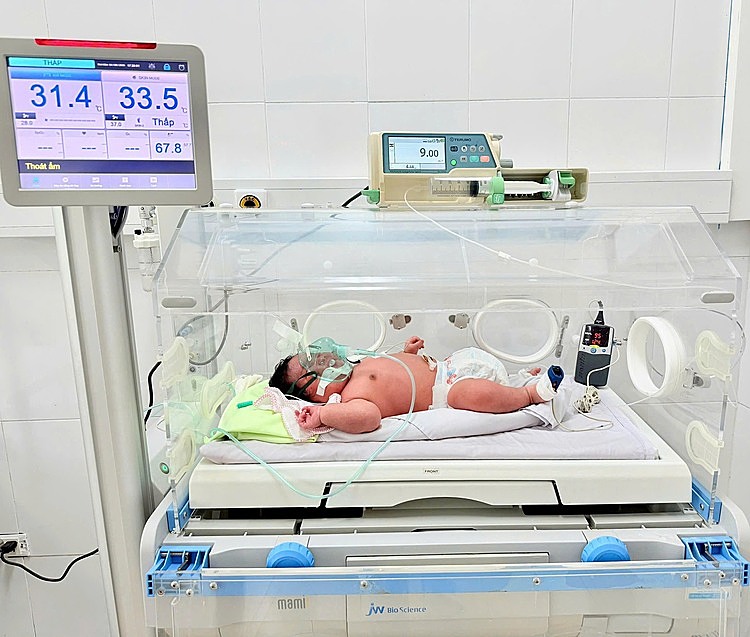 |
The newborn is monitored after birth. Photo: Hospital provided |
The newborn is monitored after birth. Photo: Hospital provided
The record for the heaviest baby born in Vietnam belongs to a 7.1 kg infant born in Vinh Phuc in 2017. A baby girl born in Gia Lai in 2008 weighed nearly 7 kg. In 2014, a mother weighing 102 kg in Quang Nam gave birth to a 6.5 kg baby.
Research suggests three common causes for unusual birth weights: family history, gestational diabetes in the mother, or an excessively rich maternal diet.
Doctors recommend that pregnant women proactively attend regular prenatal checkups. Parents of heavier newborns should monitor them closely and seek immediate medical attention if any unusual signs appear. If the fetus exceeds 3.5 kg, doctors will advise the mother on a suitable diet. Monitoring the mother's weight and pelvic assessments after 37 weeks are essential to minimize potential risks during childbirth.
Thuy Quynh












