An endoscopic examination of Thuong's ear, nose, and throat revealed nasal discharge, pharyngeal congestion, swollen vocal cords, and swollen arytenoids, with suspected nodules on both vocal cords. Dr. Tran Thi Thuy Hang, Head of the Otolaryngology Department at the ENT Center, diagnosed Thuong with congested laryngopharyngitis, suspected vocal cord nodules, and nasal discharge.
Vocal cord nodules are small, typically symmetrical growths located on both vocal cords. They often have a broad base and appear in the middle third of the vocal cords. The condition is common among individuals who use their voices extensively, such as singers, teachers, and presenters.
Thuong received medication and was advised to rest her voice. However, due to her profession as a teacher, her symptoms didn't improve significantly after 4 weeks. The nodules showed minimal response to medication and voice therapy. Dr. Hang then decided to perform endoscopic microsurgery to remove the nodules.
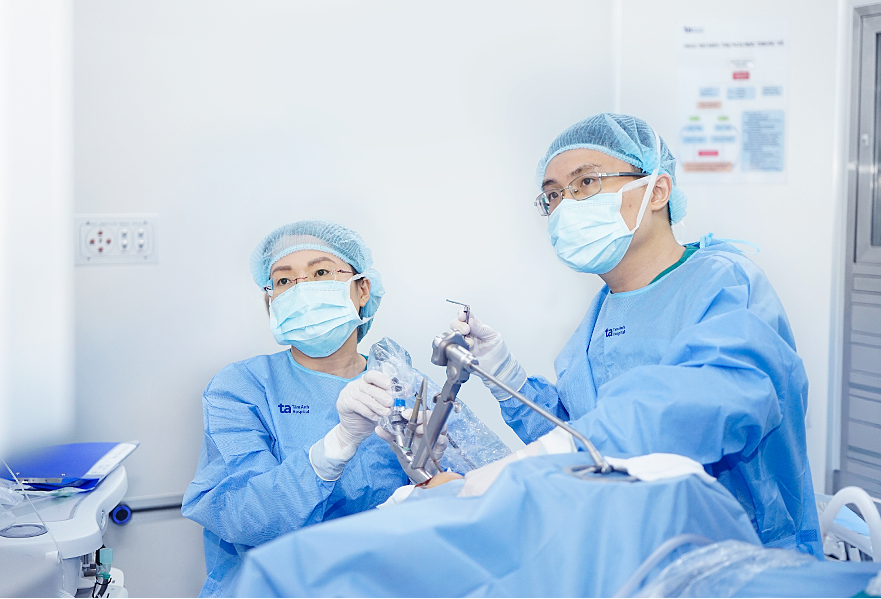 |
Dr. Hang (seated) performing surgery on Thuong. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Dr. Hang (seated) performing surgery on Thuong. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
Using a rigid endoscope and laryngeal suspension, Dr. Hang visualized the vocal cords and surrounding areas on a monitor. Specialized instruments were used to remove the nodules and control bleeding. This minimally invasive procedure doesn't require sutures, promoting rapid healing, minimizing scarring, and preserving the patient's voice.
Thuong recovered well and was discharged the next day. She was advised to limit speaking for the first three days, avoid clearing her throat, stay away from dust and smoke, and drink plenty of water. A week later, her surgical site had healed. After two weeks, her vocal cords and voice had recovered well.
Excessive and continuous voice use can overstretch the vocal cords, diminishing their elasticity. Over time, tissue growth can lead to the formation of nodules. Other contributing factors include untreated laryngitis, chronic pharyngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Symptoms include hoarseness, shortness of breath, difficulty communicating, and throat pain. Long-standing nodules can increase the risk of acute laryngitis, and in severe cases, may cause vocal cord hemorrhage and breathing difficulties.
To prevent vocal cord nodules, Dr. Hang recommends avoiding excessive talking, especially loud talking and shouting. Maintaining good throat hygiene, abstaining from alcohol and tobacco, minimizing exposure to dust and smoke, and wearing a mask outdoors are also beneficial. A healthy diet, adequate hydration, and regular exercise are essential for boosting overall health. Treating GERD and laryngopharyngeal reflux is crucial if present.
Uyen Trinh
| Readers can submit questions about ear, nose, and throat conditions here for doctors to answer. |












