Dr. Tang Ngoc Anh, Deputy Head of the Ophthalmology Department at Tam Anh General Hospital's High-Tech Eye Center in Ho Chi Minh City, stated that phacoemulsification is a modern method for treating cataracts. According to the National Eye Institute, about 9 out of 10 people experience improved vision after cataract surgery. However, the actual results depend on the pre-operative eye condition, accompanying diseases, and post-operative care.
A thorough pre-operative examination and assessment, including the condition of the lens, overall eye health, and any accompanying diseases, plays a crucial role. This allows doctors to choose the appropriate treatment method and type of artificial lens, and to more accurately assess the post-operative vision results.
According to Dr. Ngoc Anh, blurry vision after phacoemulsification can occur for various reasons. One common cause is corneal edema, mainly due to damage to the endothelium, the cell layer responsible for maintaining corneal clarity by pumping and regulating aqueous humor. This can occur if the endothelium was already weakened before surgery or if it was further damaged by high ultrasonic energy, prolonged manipulation, or mechanical impact during surgery.
Treatment typically involves anti-inflammatory medication combined with eye drops to reduce swelling. In mild cases, corneal edema usually improves within a few days to a few weeks. However, if the endothelial cell count is too low, corneal edema can become chronic, affecting vision long-term, which may require a corneal endothelial transplant.
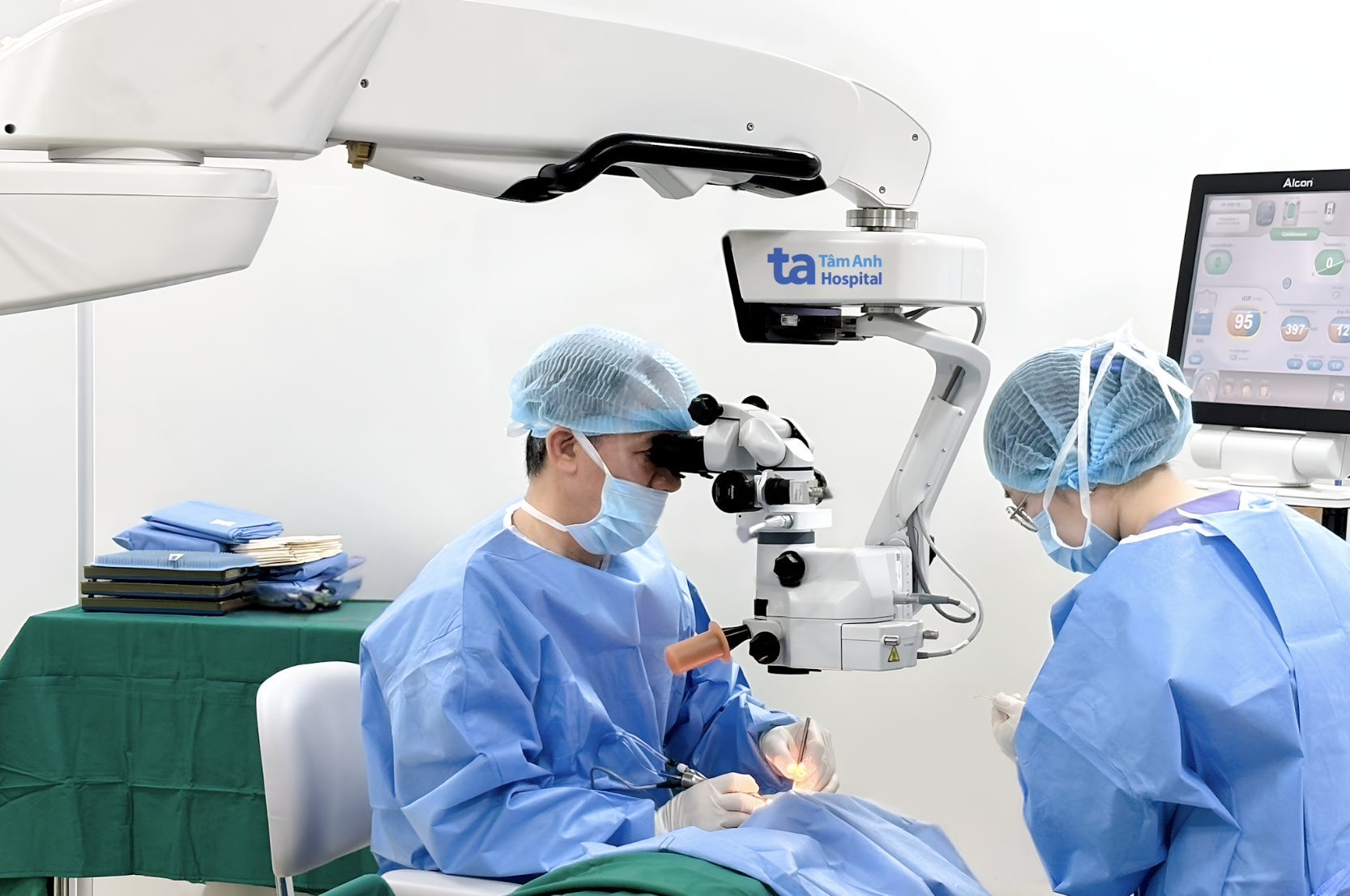 |
A doctor performs cataract surgery. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
A doctor performs cataract surgery. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
Another complication is cystoid macular edema, which usually appears 4-8 weeks after surgery. This occurs due to a disruption of the blood-retinal barrier after surgery, leading to fluid leakage and the formation of small fluid-filled cysts in the macula. Patients may experience blurred vision and distorted images, especially when looking straight ahead or reading small print.
Most cases of post-operative macular edema respond well to medical treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs, and vision recovers within a few weeks to a few months. However, if the patient has high-risk factors such as diabetes, uveitis, complex surgery, or a posterior capsule rupture, macular edema may last longer or recur, requiring close monitoring and more aggressive treatment.
Residual refractive error due to incorrect intraocular lens power or corneal scarring can also prevent post-operative vision from reaching expectations. Less common but noteworthy complications include increased intraocular pressure, retinal detachment, posterior capsule rupture, or IOL (intraocular lens) drop into the vitreous cavity. These complications can seriously affect vision and require prompt specialist intervention.
After cataract surgery, patients need regular follow-up appointments to monitor their vision, receive antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops, and address any abnormalities promptly. In cases of posterior capsule opacification, a later complication occurring after a few months to a few years, causing blurred vision to return, YAG laser capsulotomy is often used to create a new optical pathway, improving vision without requiring further surgery.
Dr. Ngoc Anh advises patients to strictly follow care instructions, take medication as prescribed, and attend follow-up appointments on schedule to ensure optimal vision recovery and long-term results. At the same time, adequate rest and a relaxed state of mind are essential for a smoother recovery process.
Nhat Thanh
| Readers can submit questions about eye diseases here for doctors to answer. |












