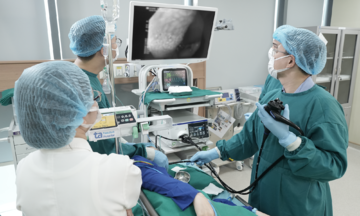
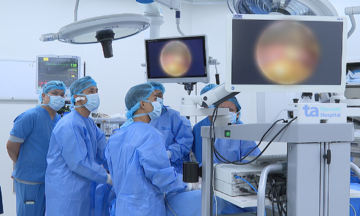
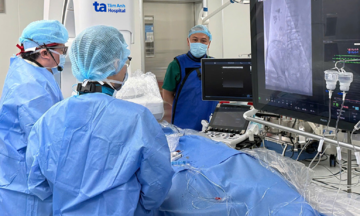
During a gynecological examination and ultrasound at the French-Vietnamese Hospital in Hanoi, doctors discovered a right ovarian tumor measuring approximately 10 cm. The patient was recommended for laparoscopic surgery to remove the tumor, with the goal of preserving healthy ovarian tissue and fertility.
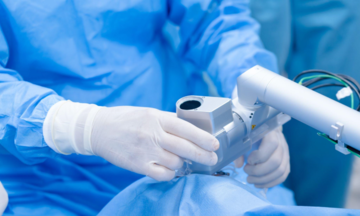
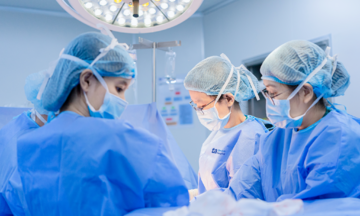
The patient's overweight condition presented challenges during anesthesia and laparoscopic procedures. However, supported by a modern laparoscopic surgical system, doctors meticulously removed the tumor in approximately one hour, avoiding damage to surrounding tissues. This approach allowed the patient to avoid open surgery, ensuring a good cosmetic result and a swift recovery.
On 20/10, Specialist Doctor Level II Cao Thi Thuy Ha, Deputy Head of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology and the lead surgeon for the patient, stated that ovarian tumors are common gynecological conditions in women, particularly those of reproductive age. Many cases of ovarian cysts develop silently with no clear symptoms, leading patients to be complacent. They are often only discovered when the tumor has grown large or caused complications.
"If detected early, patients can be treated with laparoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive method that reduces pain, shortens hospital stays, and ensures a quick recovery. Conversely, when a tumor grows large or complications occur, the risk of needing an oophorectomy (removal of the ovary) is very high," said Dr. Ha.
 |
Doctors performing laparoscopic surgery on the patient. Photo: Provided by the hospital |
Several dangerous complications can arise if ovarian tumors are not detected and managed promptly. These include ovarian cyst torsion, which is common during pregnancy or postpartum and requires emergency surgery. Ovarian torsion cuts off the blood supply to the ovary, leading to necrosis. Tumors can twist due to their large size, weight, or long ovarian ligaments. When a tumor twists, patients may experience sudden abdominal pain, pale skin and mucous membranes, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Other complications include cyst rupture, which can cause internal bleeding in the abdomen and be life-threatening. Infected cysts can adhere to surrounding organs. Large tumors can also cause compression by pressing on the rectum, bladder, or vena cava. The most dangerous complication is malignant transformation, or cancer.
Dr. Ha recommends that women undergo regular gynecological examinations for early detection of any abnormalities. She advises seeking immediate medical attention for symptoms such as: menstrual irregularities, pelvic pain, lower back pain, or abdominal bloating. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and appropriate weight management can also reduce the risk of hormonal disorders and gynecological conditions.
Le Nga