Answer:
Guava is rich in vitamin C, beta carotene, and several minerals like potassium, magnesium, iron, and calcium, along with many essential nutrients. It contains a high level of lycopene, an antioxidant twice as potent as beta carotene and 100 times more potent than vitamin E. Lycopene can prevent the formation of free radicals and lower bad cholesterol.
One guava contains up to 229 mg of potassium, which helps maintain heart function, stabilize blood pressure, prevent various cardiovascular diseases, and reduce the risk of stroke. Guava has a very low glycemic index (GI), ranging from 12 to 24, and its natural sugar content is also lower than many other fruits. This makes it a good energy source for people with diabetes, while also helping to maintain stable blood pressure and promoting heart health. It is recommended to eat one to two guavas daily to stabilize blood sugar, reduce cardiovascular risks, and help manage cholesterol.
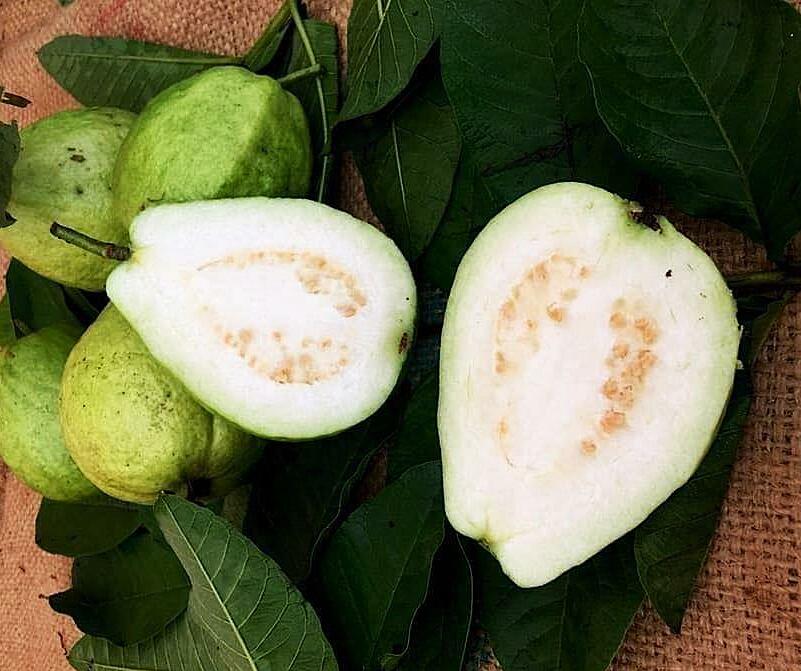 |
Eating one to two guavas a day can help manage cholesterol, blood pressure, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Photo: Dinh Dieu |
Eating one to two guavas a day can help manage cholesterol, blood pressure, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Photo: Dinh Dieu
For optimal nutrient absorption, eat guava one to two hours after a main meal. Avoid eating it on an empty stomach, as it can cause stomach pain and digestive issues. It's best to eat the whole fruit, including the skin (after washing it thoroughly). Guava skin is rich in fiber and antioxidants that aid in cholesterol elimination. Limit consumption of guava juice, as it lacks fiber, reducing its cholesterol-managing benefits. Avoid eating guava with salt or sugar, which can negatively impact blood pressure and fat metabolism. Individuals with digestive issues should eat guava in small amounts and chew it thoroughly to avoid indigestion.
In addition to eating guava, adopting healthy eating habits and regular exercise can improve cholesterol levels. Supplementing with natural active ingredients like policosanol (GDL-5) from South American sugarcane can reduce LDL cholesterol and increase HDL cholesterol, thereby regulating blood lipids, supporting blood pressure management, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Master of Science, Doctor Doan Vinh Binh
Medical Information Center
Tam Anh General Hospital, TP HCM
| Readers can submit nutrition-related questions here for doctors to answer. |