Answer:
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a sleep-related breathing disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths lasting more than 10 seconds due to a temporary collapse of the upper airway. This occurs when the muscles and soft tissues in the throat relax and reduce the space for airflow. If you experience prolonged sleep apnea, it can severely impact your cardiovascular health, metabolism, neurological function, and overall quality of life.
Regarding cardiovascular health, repeated apnea increases stress on the heart and blood vessels, potentially leading to myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and accelerating atherosclerosis. This prolonged condition also raises the risk of stroke compared to individuals without sleep apnea.
This disorder significantly affects metabolism. Nocturnal breathing interruptions worsen insulin resistance, contributing to blood sugar disorders and increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Neurologically, prolonged oxygen deprivation affects the brain, impairing memory, cognitive abilities, and increasing the risk of Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia.
Oxygen deficiency and chronic sleep disturbance also impact endocrine function, reducing testosterone levels and causing physiological issues in men. Patients often experience fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and anxiety. Daytime sleepiness increases the risk of traffic and workplace accidents.
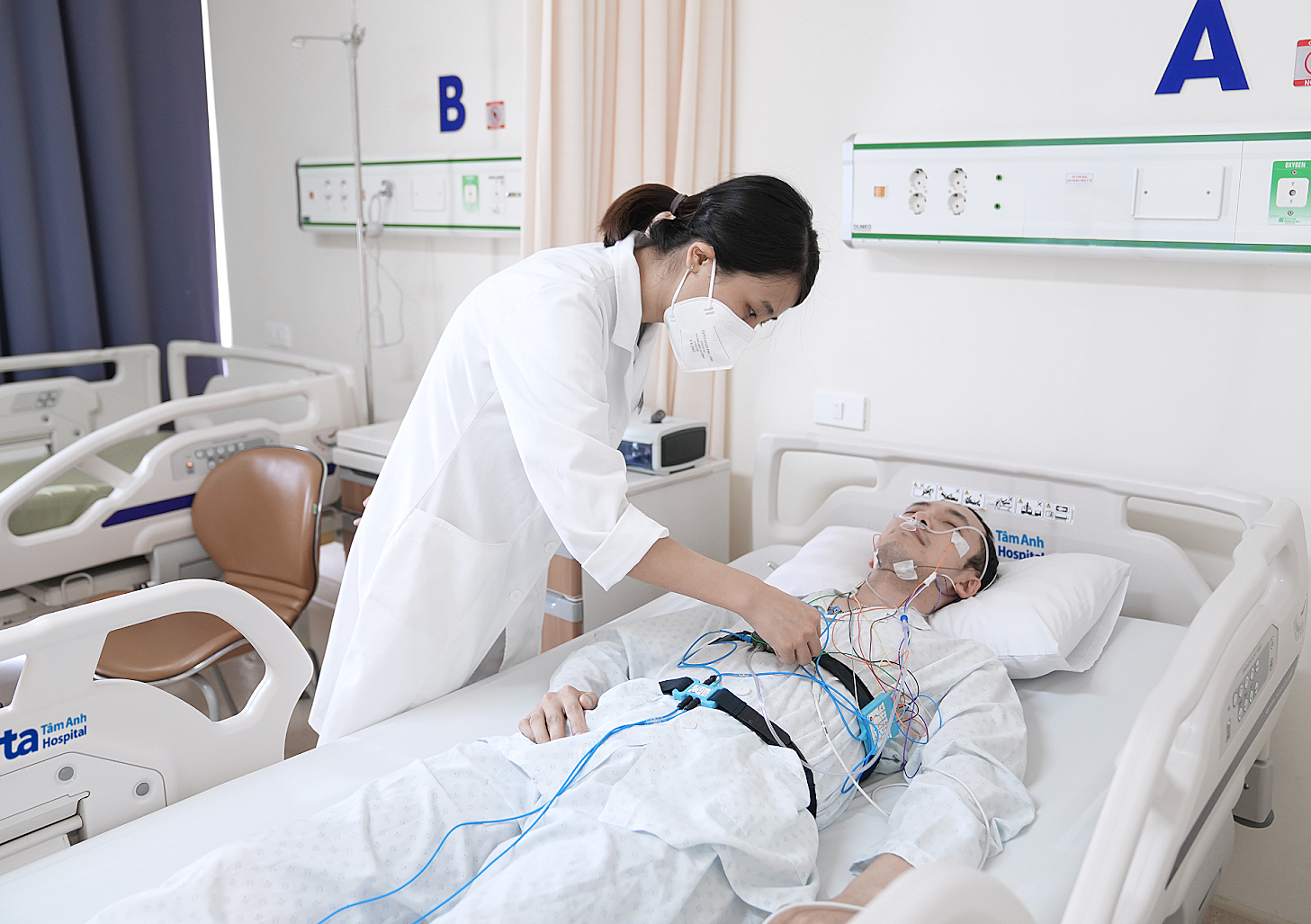 |
A doctor performs a polysomnography on a patient. Illustrative photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
To diagnose sleep apnea, doctors usually recommend a polysomnography, which records breathing patterns, blood oxygen levels, heart rate, brain waves, and airflow during sleep. The results help doctors determine the severity of the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is one effective treatment, helping to keep the airway open during sleep and reduce apnea episodes.
You should consult a doctor for a proper examination and personalized advice. In addition, you should adopt lifestyle changes such as weight loss (if overweight), quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and adjusting your sleeping position. In some cases, surgery to widen the airway may be recommended to improve the condition.
Master, Doctor Dang Thanh Do
Respiratory Department, Tam Anh General Hospital, Hanoi
| Readers can submit questions about respiratory diseases here for doctors to answer. |