Ngoc was diagnosed with lung cancer 7 years ago. She underwent surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy, followed by regular check-ups. A month ago, she experienced increased fatigue, fever, and a productive cough, leading her to seek treatment at Tam Anh General Hospital in TP HCM.
On 29/7, Doctor Do Duy Long from the Department of Cardiology at the Heart Center, explained that the patient presented with respiratory failure, pleural effusion, and acute pulmonary embolism. This condition occurs when a blood clot, typically formed in the lower extremities, travels to the lungs and blocks the pulmonary artery. If not promptly diagnosed and treated, pulmonary embolism can lead to respiratory failure and death.
Ngoc received anticoagulants, antibiotics, and pleural drainage, along with intensive care. After 10 days, her cough and respiratory distress significantly improved, her pleural effusion returned to normal levels, and she was discharged.
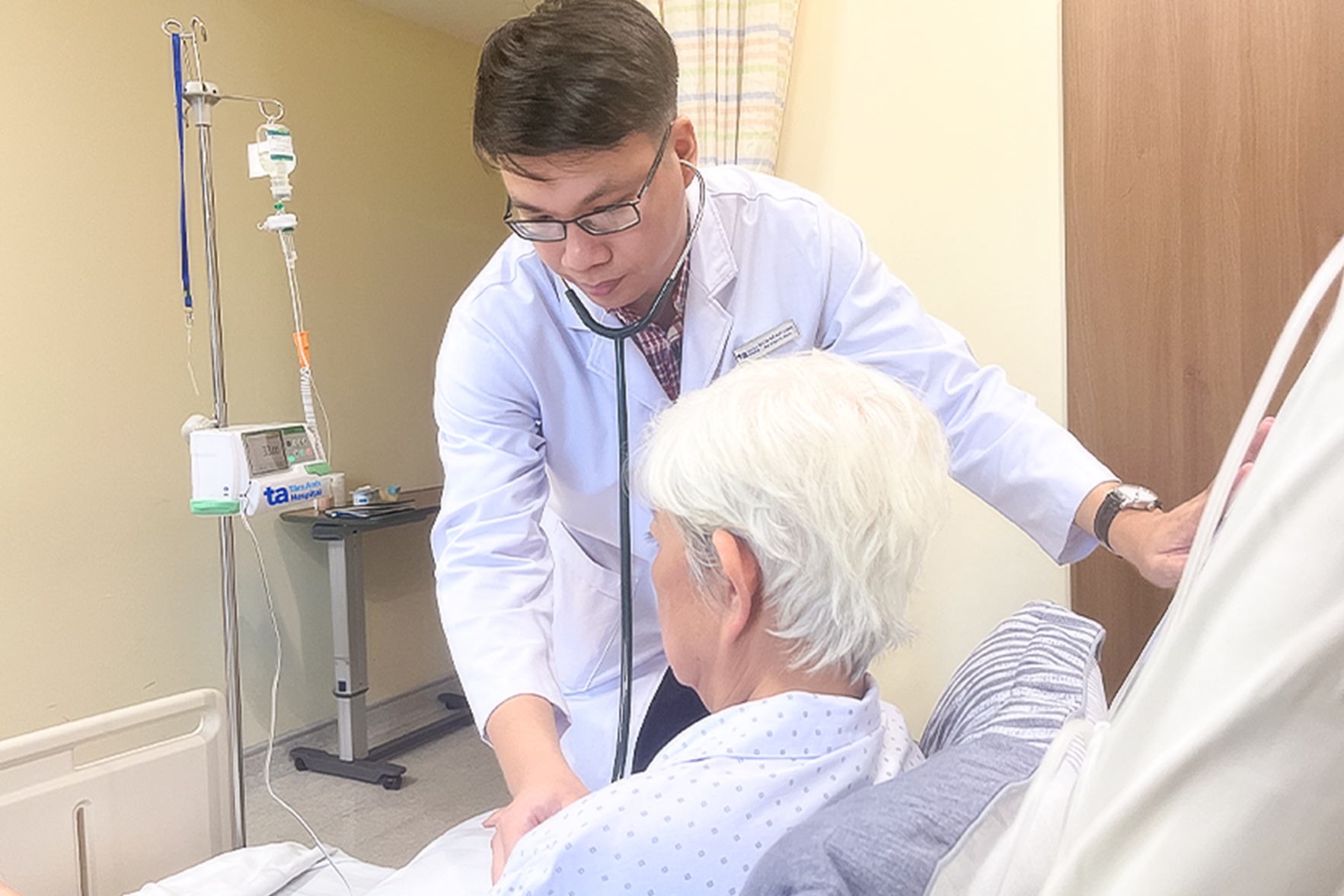 |
Doctor Long examines the patient before discharge. Photo: Ha Vu |
Doctor Long examines the patient before discharge. Photo: Ha Vu
Doctor Tran Vu Minh Thu, Head of the Department of Cardiology 2 at the Heart Center, Tam Anh General Hospital in TP HCM, stated that cancer patients have an increased risk of thrombosis. This is because tumors release substances that promote blood clotting. Additionally, treatments like chemotherapy, antiangiogenic drugs, surgery, and catheter placement can further activate this process. Blood clots often form in the veins of the lower extremities or abdomen and can travel to the lungs, obstructing vital blood vessels.
Factors that increase the risk of thrombosis include older age, obesity, comorbidities (infections, lung disease, chronic venous insufficiency), and prolonged immobility. Advanced cancer stages and tumor locations like the lungs, pancreas, stomach, and brain also pose higher risks.
To prevent this complication, Doctor Long recommends that cancer patients undergo screening and thrombosis risk management from the outset, along with specialized cardiovascular monitoring throughout their treatment. Patients should maintain physical activity, manage their weight, avoid prolonged bed rest, and ensure adequate nutrition.
Thu Ha
*The patient's name has been changed.
| Readers can submit questions about cardiovascular diseases here for doctors to answer. |