Answer:
Nuchal translucency is a pocket of clear fluid at the back of a developing baby's neck, most visible between 11 and 13 weeks and 6 days of gestation. The amount of fluid changes throughout pregnancy. Ultrasound measurement of NT, combined with maternal age and biochemical markers, screens for fetal abnormalities. Sonographers use software or standardized charts to determine high or low measurements relative to gestational age.
Increased NT can be associated with genetic syndromes, gene abnormalities, congenital heart defects, and structural anomalies. Abdominal or transvaginal ultrasounds yield similar results. Accuracy depends on the sonographer’s skill and experience.
Your 11-week ultrasound showing an NT of 3.8 mm, coupled with absent nasal bone, suggests a potential fetal abnormality, particularly Down syndrome. You should consult a specialist for a first-trimester morphology scan to check for other structural abnormalities, especially in the heart and brain.
Your doctor may recommend chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis to definitively diagnose any genetic abnormalities. CVS involves taking a small tissue sample from the placenta for testing. The placenta originates from the embryo and contains cells with a genetic makeup almost identical to the fetus. CVS is performed between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy, earlier than amniocentesis. This procedure is ultrasound-guided for safety and accuracy. A fine needle is inserted through the abdomen into the uterus to retrieve a sufficient placental sample for diagnostic testing.
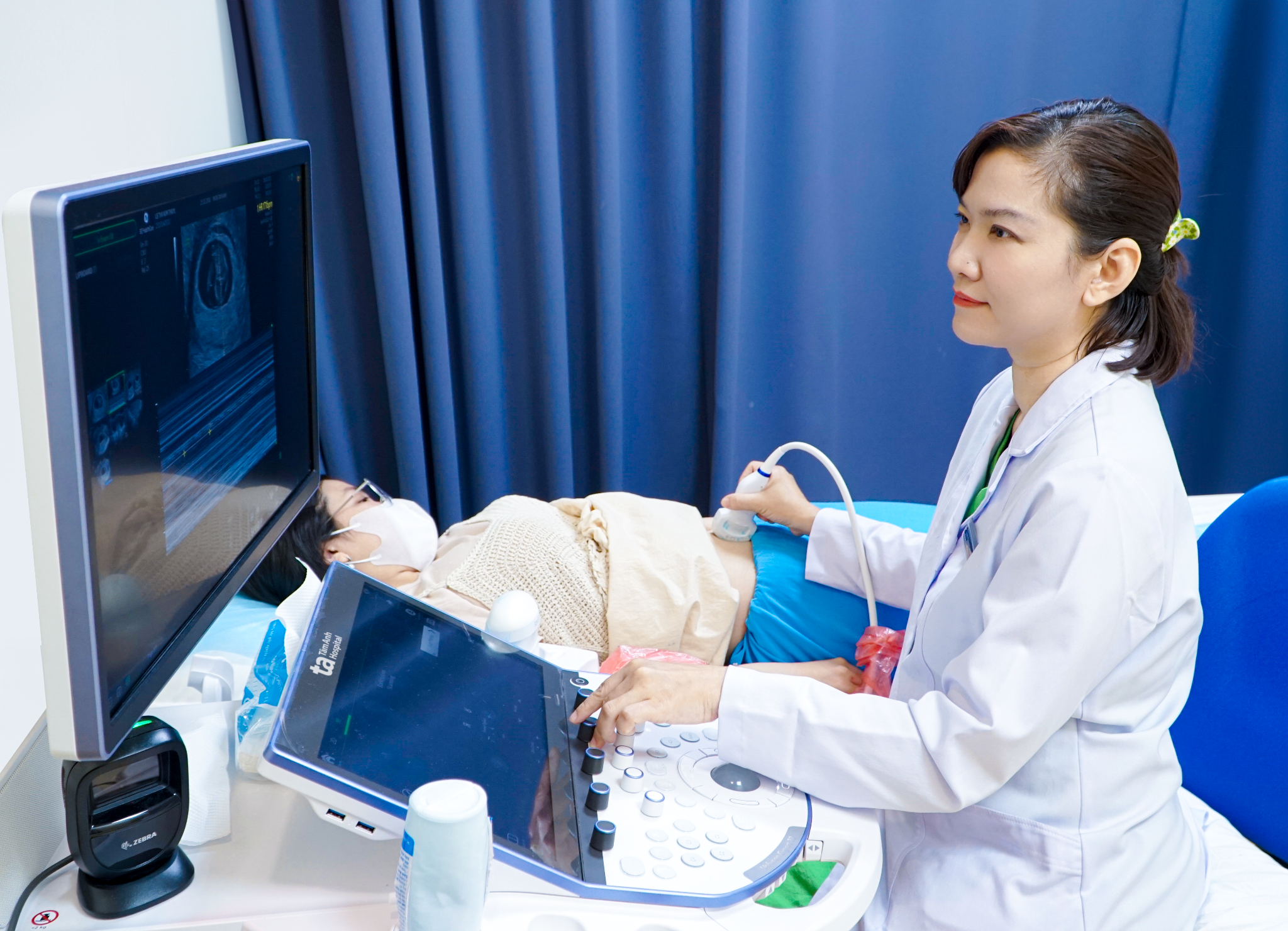 |
Doctor Phuong performs an ultrasound on a pregnant woman. *Photo illustration: Tam Anh General Clinic, District 7* |
Amniocentesis involves extracting a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding the fetus. Amniotic fluid contains fetal skin cells and other cells carrying vital genetic information. About 10-20 ml of fluid is collected under ultrasound guidance, typically at 16 weeks of gestation. Results for both tests are usually available within 1-4 weeks, depending on the specific test (some specialized tests may take longer). After receiving the results, your doctor will discuss the prognosis, future prenatal care, fetal monitoring, and potential pre- and postnatal treatment options.
MSc. Dr. Nguyen Thi Lien Phuong
Fetal Medicine Specialist
Tam Anh General Clinic, District 7
| Readers can submit questions about pregnancy and childbirth here for doctor's answers. |












