The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) of China has unveiled draft mandatory national standards for car door handle safety, addressing concerns about electronic and concealed door handle designs. The draft, "Technical Requirements for Automotive Door Handle Safety," was released for public comment on 24/9 and will remain open for feedback until 22/11.
According to the explanatory document, these standards aim to regulate concealed electronic door handles and meet emerging safety needs. The initiative seeks to establish baseline safety criteria while guiding manufacturers to improve door handle design and overall vehicle safety.
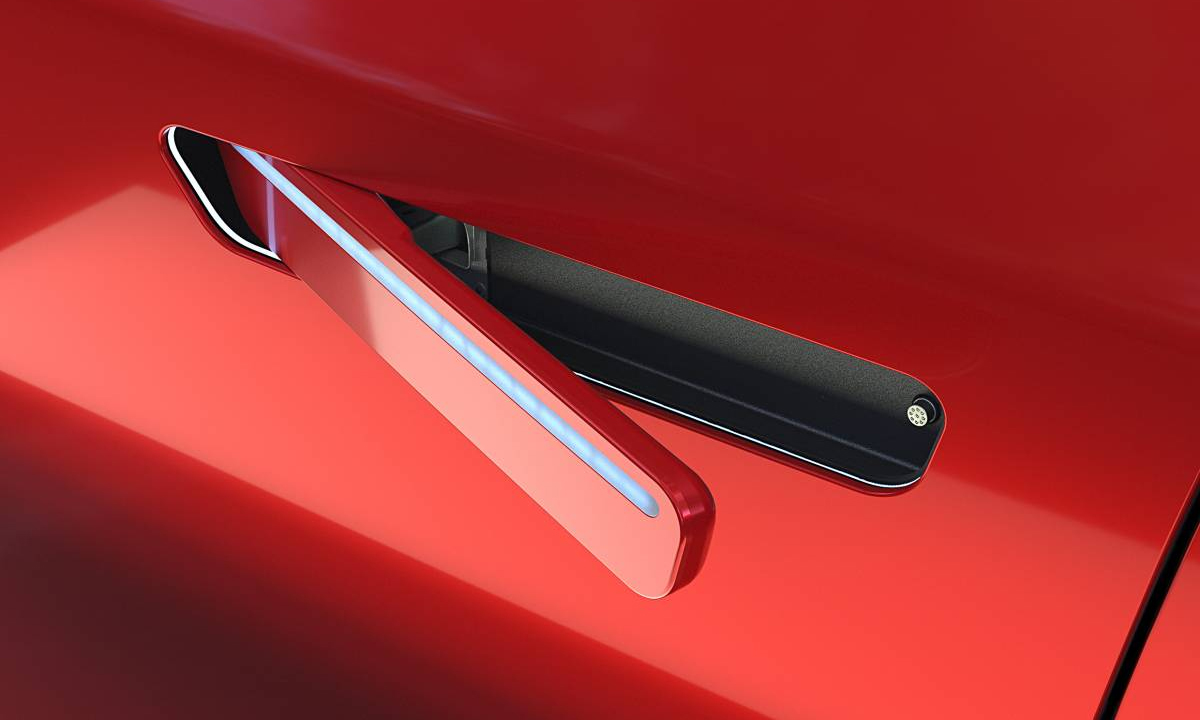 |
A type of concealed car door handle. Photo: Huf |
A type of concealed car door handle. Photo: Huf
Key requirements in the draft standards include: each door (except the trunk lid) must have an external handle with a mechanical unlocking function; in the event of a battery thermal runaway incident, non-impacted side doors must be openable via the external handle without tools; the external door handle must have a minimum hand operating space of 60 x 20 x 25 mm, regardless of the handle's position; each door must have an internal handle with a mechanical unlocking function, capable of opening the door without external tools; if an electric interior handle is installed, a mechanical backup must also be provided; the internal handle must be easily identifiable and visible, located within 300 mm from the door edge and positioned within a specific range from the seating position.
In an interview with CNAutoNews, Rong Hui, vice president of the China Automotive Technology and Research Center, explained that the standards were developed through extensive research involving over 20 companies and 63 vehicle models. The requirements address industry challenges while balancing technological advancements with safety concerns.
"With the development of automotive electrification, electronic door handles have been widely adopted, and the operating methods and structures of door handle products on the market are becoming increasingly diverse," Rong said. "These standards are meant to accommodate new technologies and safety requirements."
The standards focus on three key areas: regulations on door handle structure, ensuring the door release method remains functional in power outages, and standardizing handle placement with clear safety markings.
The MIIT conducted comprehensive research on the door handle configurations of over 230 vehicle models and performed validation tests on over 20 models. Industry experts from over 100 domestic and international automakers, parts suppliers, and testing organizations participated in the standard development process.
In 2012, the Tesla Model S pioneered the electronically controlled pop-out door handle, adding automatic sensing pop-out functionality and a flush design with the car body. This instantly became a symbol of technological sophistication and "futuristic appeal," subsequently emulated by numerous automakers. However, this design is now backfiring on vehicles due to safety and reliability issues. Because the handles rely entirely on electric motors and software control, passengers can be trapped inside during power failures, system malfunctions, or winter freezes. Multiple incidents have led to regulatory investigations. In September, Tesla's design chief, Franz von Holzhausen, publicly acknowledged that the company is redesigning its door handle system to make mechanical opening in emergencies more direct and reliable.
My Anh (CarNewsChina)