Temporary insomnia, characterized by insufficient or poor-quality sleep lasting from one night to several weeks, can develop into chronic insomnia. This can lead to health issues like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hypertension, and chronic stress. Individuals experiencing insomnia can try incorporating these habits to improve their sleep.
Daily physical activity
Regular exercise offers numerous health benefits, including better sleep. Light exercises like cycling, jogging, and swimming for 20-30 minutes daily can promote relaxation, reduce stress, and pave the way for sound sleep. Physical activity stimulates endorphin production, which can alleviate pain and induce a sense of calm, making it easier to fall asleep. However, avoid exercising right before bed as it can be stimulating. Complete workouts at least three hours before bedtime.
15-30 minutes of daily sun exposure
The hormone melatonin regulates sleep. Exposure to sunlight boosts melatonin production, maintaining the body's circadian rhythm and promoting drowsiness at night. Sunlight also aids vitamin D synthesis, positively impacting sleep quality.
Those struggling with insomnia should spend 15-30 minutes daily walking and soaking up the sun to increase serotonin production, another neurotransmitter that contributes to better sleep. Get sunlight soon after waking up to minimize UV exposure. Maintain a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day to regulate the sleep-wake cycle and prevent insomnia.
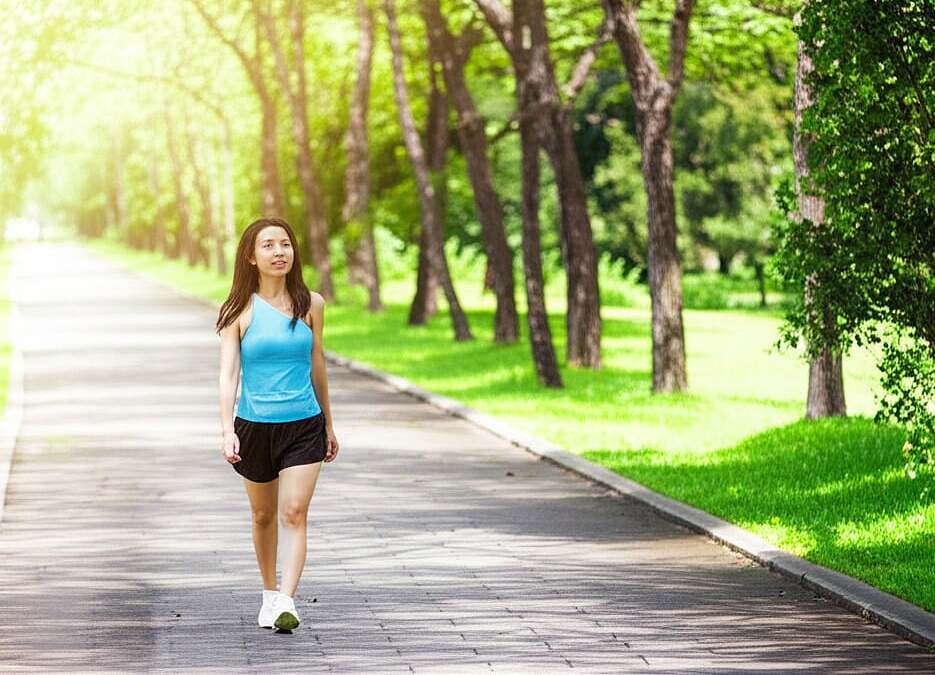 |
Exposure to sunlight during the day can help with sleep at night. Image generated by AI |
Exposure to sunlight during the day can help with sleep at night. Image generated by AI
Using neck and back support while sleeping
Neck and back pain are common culprits of sleep difficulties. To alleviate this, maintain a proper sleep posture using a suitable pillow, ensuring your nose aligns with your body's center and your neck remains in a neutral position. Pillows that are too high or too low can cause neck curvature, leading to pain, nerve compression, and insomnia.
If back pain disrupts sleep, try sleeping on your side with a pillow between your knees to keep your hips aligned, reducing pressure on your lower back. Take a few minutes each night to adjust your pillows and find the most comfortable position.
10-20 minute naps
Short naps are beneficial for those with insomnia, even on weekends or while traveling. Napping offers a good way to rest when fatigued, boosting alertness, mood, and work performance. However, avoid long naps, as they can interfere with nighttime sleep. Ideally, naps should be under 20 minutes, taken in a cool, dimly lit room in a comfortable position. Excessive napping can lead to grogginess and disorientation lasting for several minutes up to 30 minutes after waking.
Anh Chi (According to WebMD, MedicineNet)
| Readers can submit questions about neurological diseases here for answers from doctors. |