Prostate enlargement is a benign age-related proliferation of the prostate gland, often progressing silently for many years. As the prostate grows, it compresses the urethra, leading to a weak urinary stream, difficulty urinating, and incomplete bladder emptying. According to Master, Doctor Nguyen Ngoc Tan, from the Urology - Andrology Department at Tam Anh General Hospital Hanoi, prolonged obstruction not only causes urinary dysfunction, affecting sleep, psychological well-being, and sexual activity, but also increases the risk of dangerous complications.
Urinary retention
Urinary retention is a common complication, especially in older men. As the prostate gradually enlarges, it compresses the urethra. Patients often feel the urge to urinate but can only pass a small amount or none at all. Prolonged retention of urine in the bladder causes the organ to overstretch, leading to pain in the lower abdomen. Many cases require medical intervention, such as catheterization, to drain urine from the bladder.
Urinary tract infections
When the bladder cannot be fully emptied due to prostate enlargement, residual urine creates a favorable environment for bacteria to grow, leading to urinary tract infections. Recurrent infections significantly impact patient health and make treatment more complex, sometimes requiring surgical intervention.
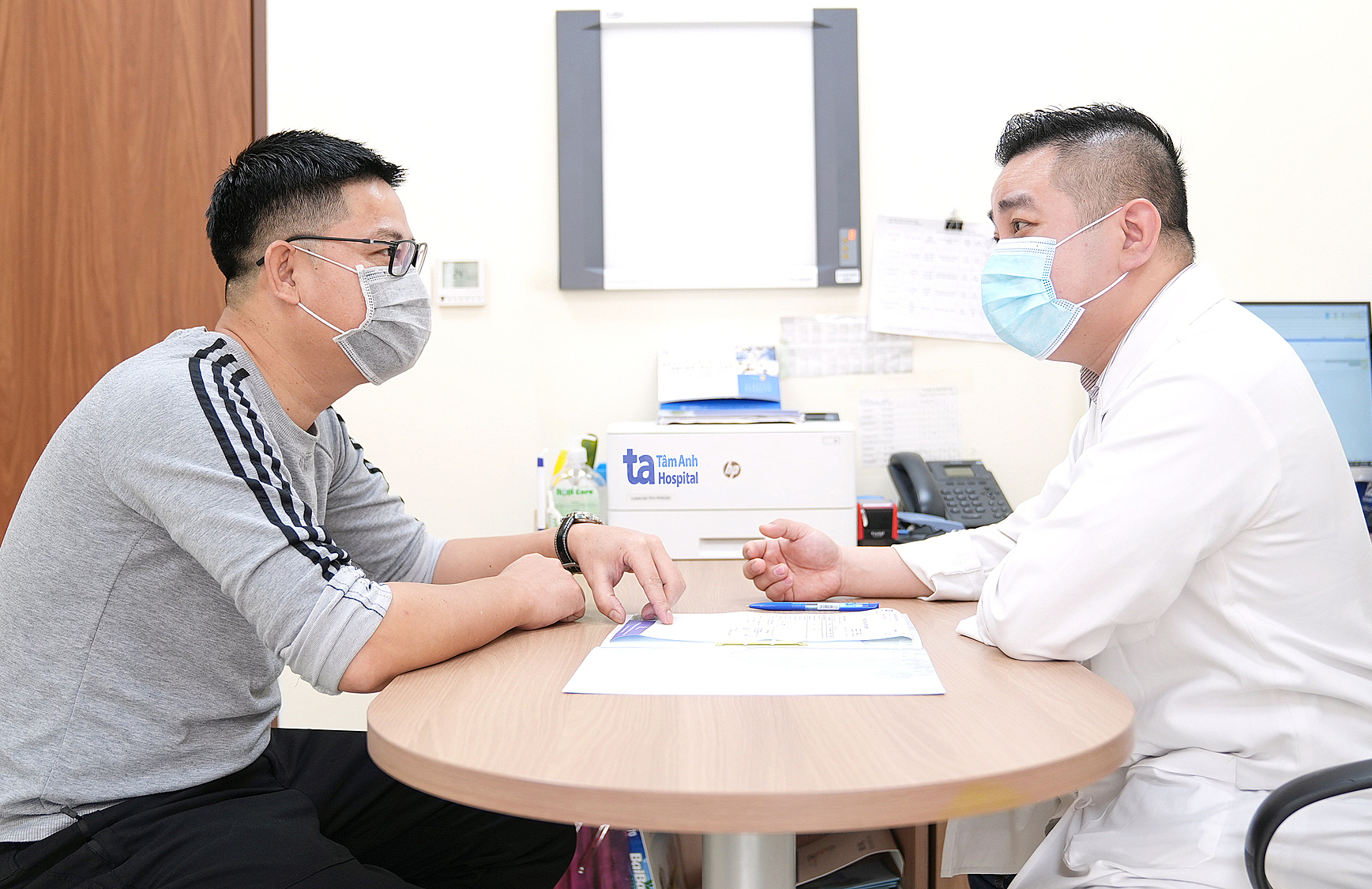 |
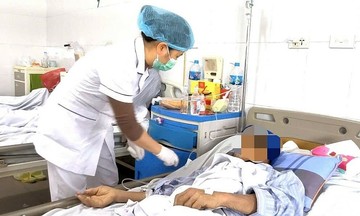
Doctor Tan examining a patient with prostate enlargement. Illustration: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Bladder stones
Prolonged urine stasis also facilitates the formation of bladder stones. Stones can irritate the bladder lining, causing blood in the urine, painful urination, and worsening urinary obstruction. For large stones, doctors may recommend surgical removal combined with addressing the underlying cause of obstruction to prevent recurrence.
Bladder damage
In individuals with prostate enlargement, a bladder that is not completely emptied for an extended period can gradually stretch and weaken. Consequently, the bladder muscle wall no longer contracts effectively to expel urine, making bladder emptying increasingly difficult.
Kidney dysfunction
Prostate enlargement obstructs urine flow, increasing pressure within the bladder, which can lead to kidney damage or facilitate the spread of infection from the bladder to the kidneys.
Doctor Tan advises middle-aged and older men not to disregard urinary dysfunctions such as difficulty urinating, weak stream, or frequent nighttime urination. Early examination at hospitals and specialized medical facilities helps detect prostate enlargement in its early stages, allowing for appropriate treatment and monitoring to minimize complications.
Thu Giang
| Readers can submit questions about urinary diseases here for doctors to answer. |