The liver performs many vital functions, including bile production, aiding digestion, filtering blood, metabolizing proteins and lipids, and storing energy, vitamins, and minerals. Damage or weakening of this organ can lead to serious health issues such as fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, increased blood sugar levels, and fatigue. Here are some habits that can boost liver function.
Maintain a healthy diet. A Mediterranean diet, rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and complex carbohydrates, can help reduce liver fat. Prioritized foods in this diet include leafy green vegetables, fish and seafood, omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil and vegetable oils, and nuts (especially walnuts). Monounsaturated fats found in plant sources like olives, nuts, and avocados also contribute to liver health. Some fats in the Mediterranean diet help the body use insulin more effectively, allowing cells to absorb glucose easily, so the liver doesn't need to produce and store as much fat.
Consume coffee and green tea, raw garlic, and berries to increase your antioxidant intake. These help protect cells from fat accumulation and reduce inflammation. Foods high in saturated fats, which can increase the risk of fatty liver disease, include red meat, poultry skin, pastries, and fried foods. Foods high in sugar, such as candy and soft drinks, should also be limited.
Avoid alcohol. Abstaining from alcohol is paramount in preventing alcoholic fatty liver disease. The liver removes toxins from alcohol, and excessive drinking overworks the organ, reducing its ability to detoxify other substances. This leads to fat accumulation in the liver, causing fatty liver disease and damage such as hepatitis and cirrhosis. Alcohol also weakens the immune system, negatively impacting overall health.
Limit alcohol intake and drink 1.5-2 liters of water daily. You can also supplement with pure fruit juice, smoothies, nut milk, or lemon water to support liver health.
Maintain a stable weight. Maintaining a normal body mass index (BMI) between 18.5 and 24.9 helps prevent obesity, which can lead to fat accumulation in the liver. Losing 7-10% of body weight can help reduce liver cell damage and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in overweight individuals. To maintain a stable weight, adults should eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and ensure calorie intake is less than or equal to calories burned.
Exercise regularly. Both aerobic and high-intensity exercise are beneficial for overall health and can limit liver fat accumulation and reduce inflammation. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting, can also help improve fatty liver disease. Adults should aim for 30-60 minutes of exercise daily, at least 5 days a week.
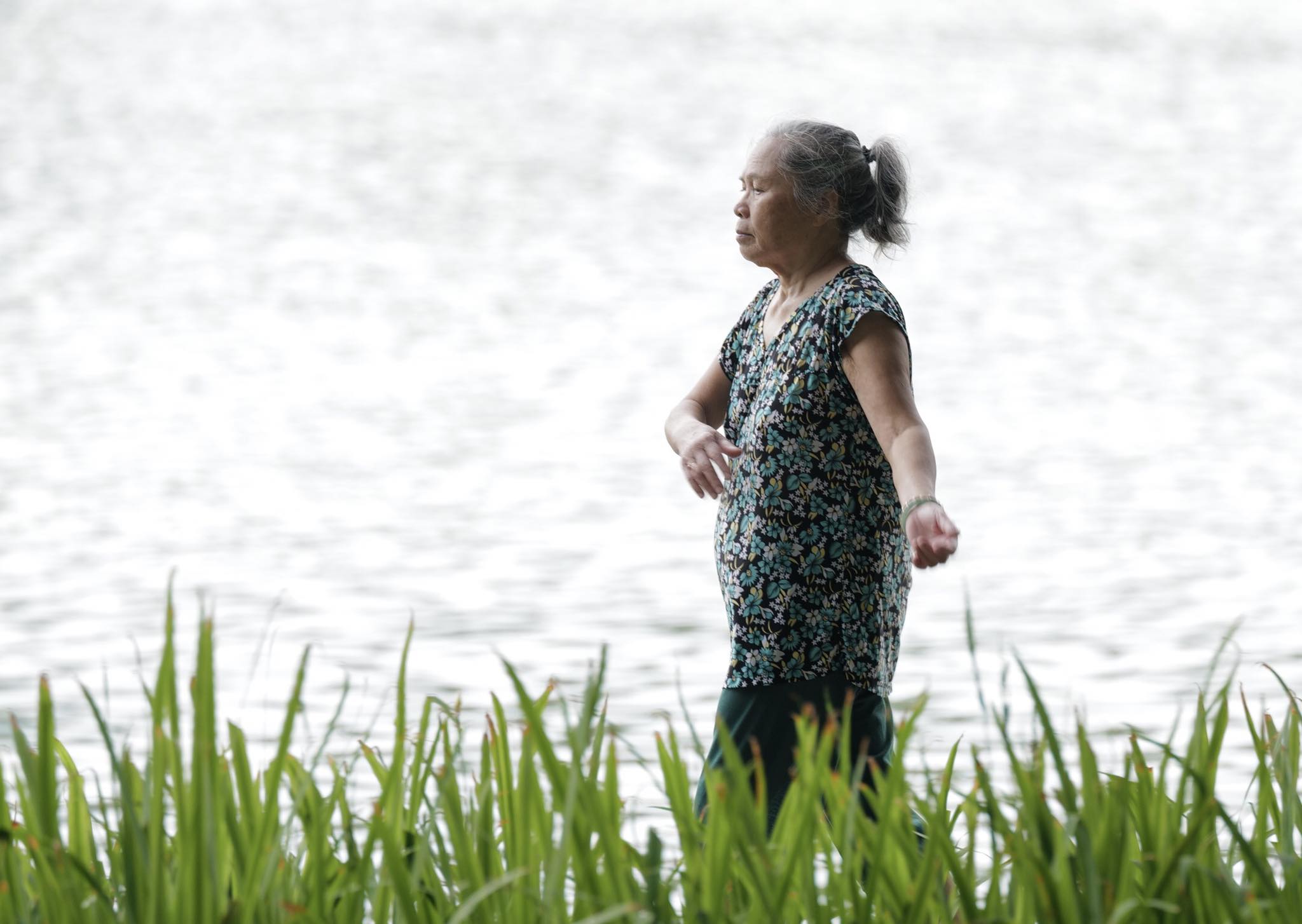 |
Daily exercise contributes to a healthy liver. Photo: Giang Huy |
Manage diabetes. The liver stores and releases glucose as needed, helping maintain stable blood sugar levels. High blood sugar can damage the liver, leading to hepatitis, fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is common in people with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, individuals with diabetes should take medication as prescribed by their doctor, monitor their blood sugar levels, and adjust their diet accordingly.
Maintain healthy cholesterol levels. A healthy liver helps maintain healthy cholesterol and triglyceride (blood fat) levels. A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, regular exercise, and medication as prescribed by a doctor can contribute to controlling cholesterol and triglycerides.
Anh Chi (According to WebMD, Healthline)
| Readers can submit questions about digestive diseases here for doctors to answer. |