|
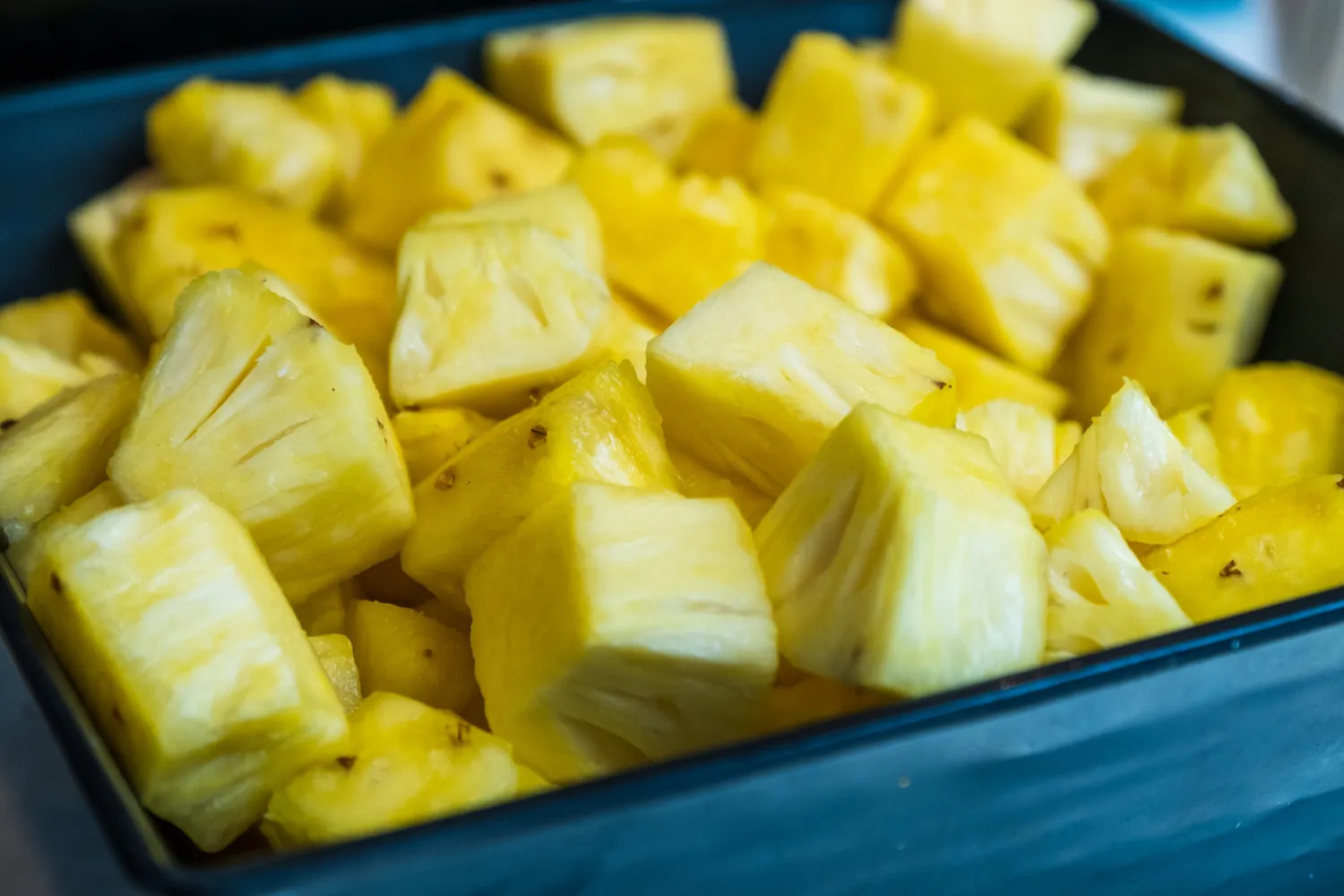
Pineapple contains bromelain, an enzyme that aids protein digestion. Like other digestive enzymes, bromelain is heat-sensitive, so pineapple is best enjoyed raw to maximize its benefits. Blend it into smoothies, add chunks to salads, or incorporate it into salsa for a digestive boost. |
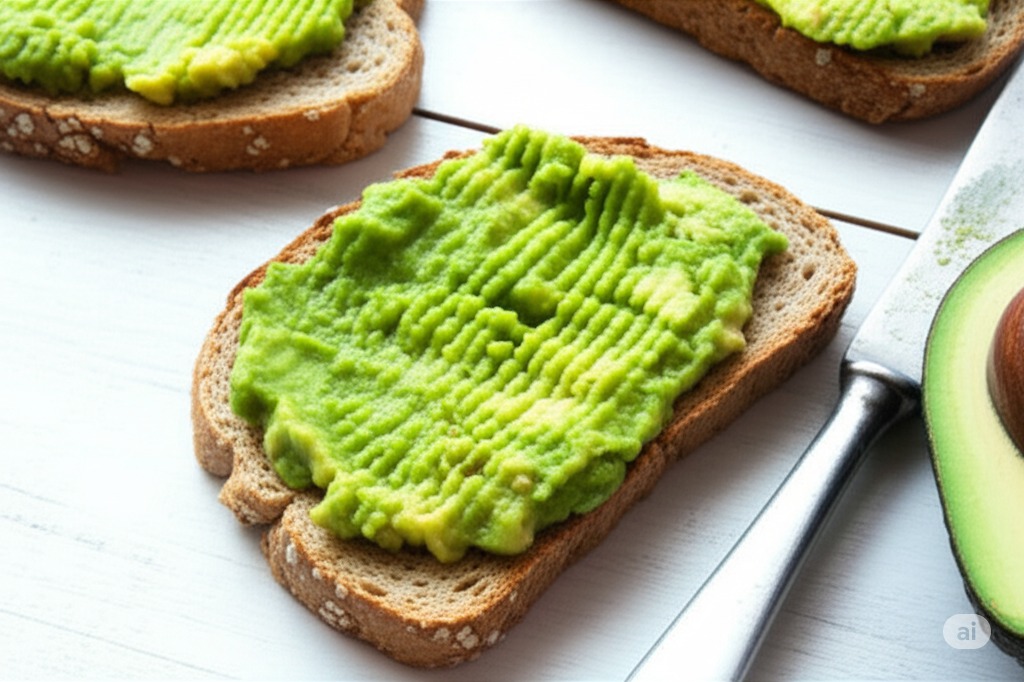 |
Avocado contains lipase, an enzyme essential for fat metabolism and digestion. This fruit is also rich in fiber and nutrients, supporting healthy bowel movements. Avocados are versatile and can be eaten plain, blended into smoothies, added to salads, paired with yogurt, or enjoyed on toast with eggs for a nutritious breakfast. |
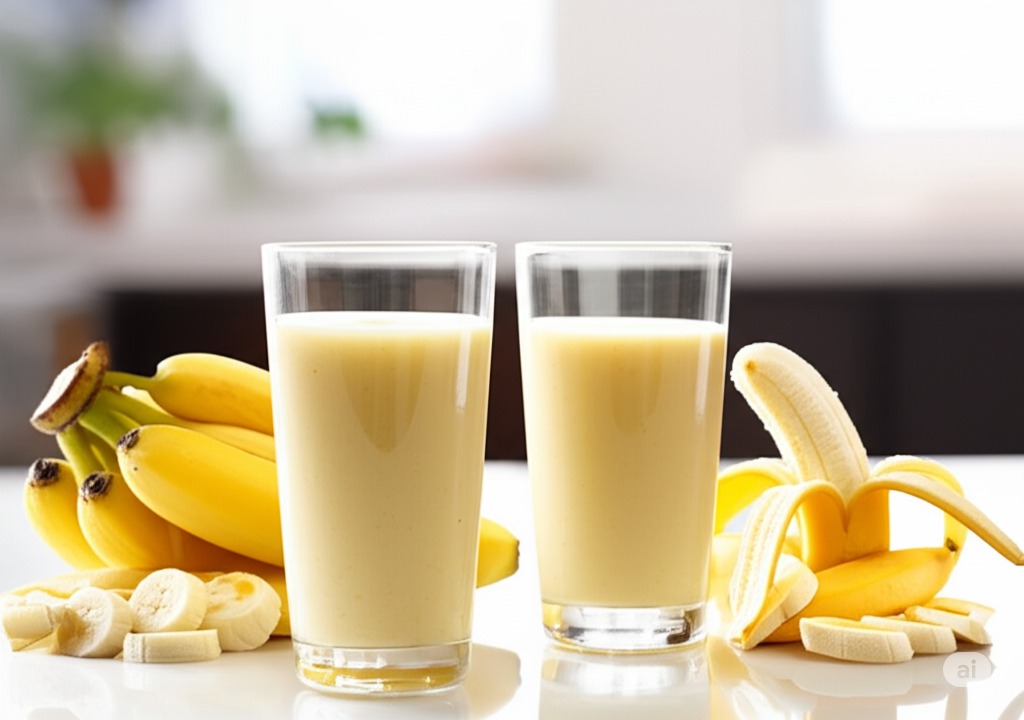 |
Bananas are a good source of potassium and are rich in enzymes like amylase and maltase. Amylase breaks down complex carbohydrates found in bread and cereals, while maltase breaks down maltose, a sugar found in carb-rich foods like starchy grains and vegetables. Incorporate bananas into oatmeal, smoothies, or enjoy one as a standalone dessert. |
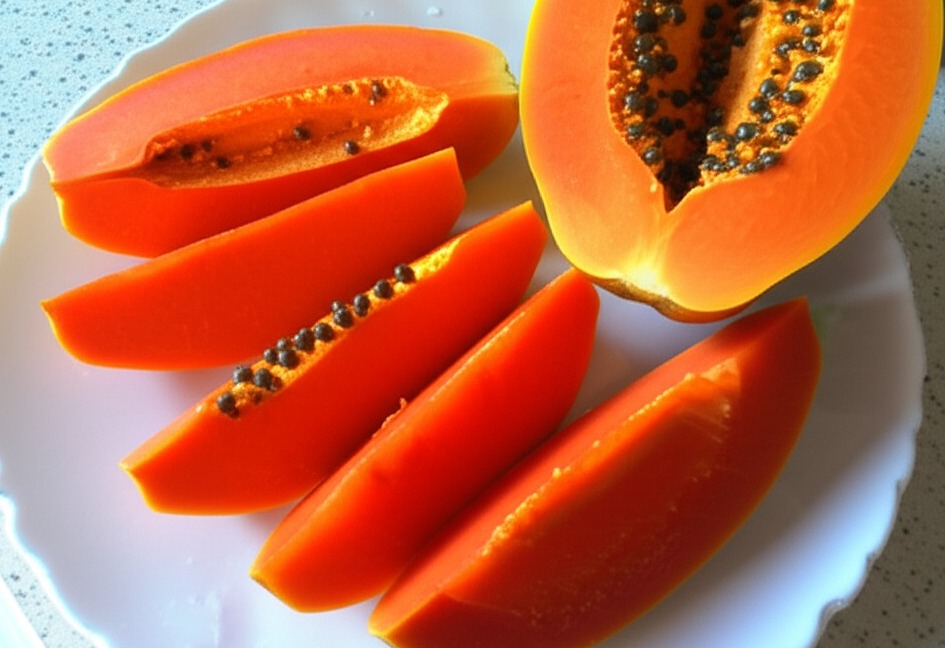 |
Papaya boasts high levels of papain, an enzyme that breaks down proteins. High temperatures can damage papain, so eat ripe papaya raw to aid digestion. Papaya is also rich in fiber and has a low glycemic index, potentially promoting smoother, more stable digestion. Enjoy papaya slices as a side dish or snack to boost enzyme intake. |
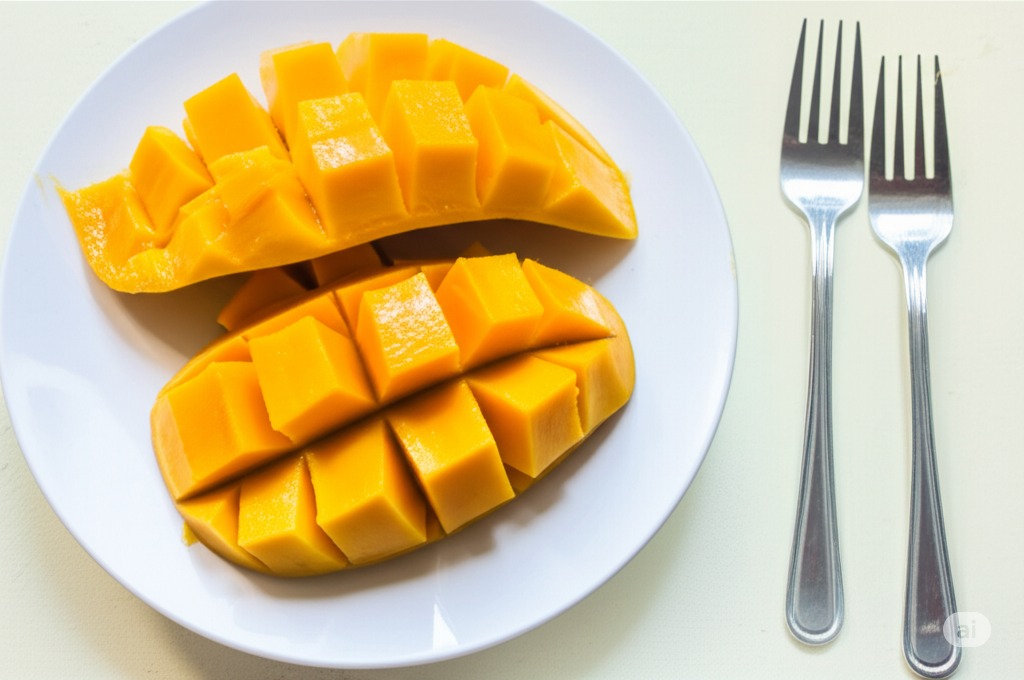 |
Mangoes contain amylase, which helps the body break down starches into smaller carb molecules, aiding absorption. Enjoy sliced or diced mango as a refreshing snack or add it to green salads for a flavorful twist. |
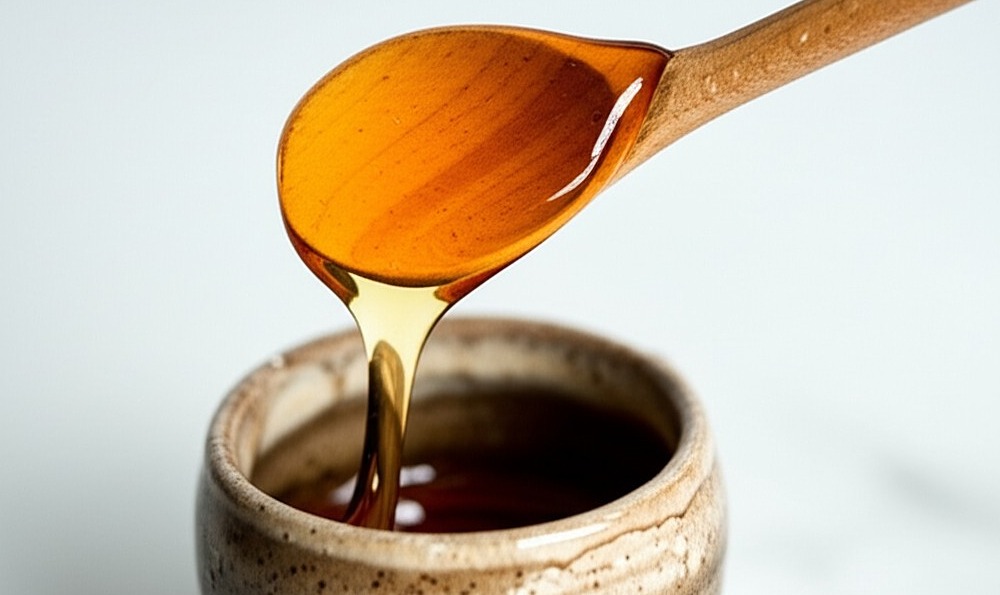 |
Raw honey contains digestive enzymes called diastases, invertase, and protease. Consuming raw honey can support better nutrient absorption, reduce inflammation, and offer antibacterial benefits. A warm cup of honey water in the morning or before bed can promote digestion and overall well-being. |
Anh Chi (According to Eating Well)
Photos: AI, Bui Thuy