Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a condition characterized by inflammation or irritation in the small intestine or large intestine (colon). It is classified into two types: acute (caused by infection) and chronic (as seen in Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis).
Doctor Nguyen Hoang Oanh, a gastroenterologist at Tam Anh General Clinic, District 7, explains that choosing the right foods helps create a healthy biochemical environment in the intestines, providing essential nutrients for the body, thereby reducing symptoms and promoting healing.
Easily digestible starches
Starches are an important nutrient, providing energy for bodily functions. IBD patients should choose easily digestible options like thin rice porridge, soft rice, white bread, mashed potatoes, or rice noodles to provide energy and reduce digestive strain. Avoid whole grains and foods high in insoluble fiber during acute phases, as these can cause bloating, abdominal pain, or worsen diarrhea.
Low-fat proteins
Protein provides essential amino acids that support the repair and recovery of inflamed intestinal lining. Adequate protein intake contributes to overall health improvement and enhances the effectiveness of IBD treatment. Patients should opt for lean chicken, steamed fish, hard-boiled eggs, and soft tofu. Limit red meat, processed meats, or fried foods as they are rich in saturated fats and can be irritating.
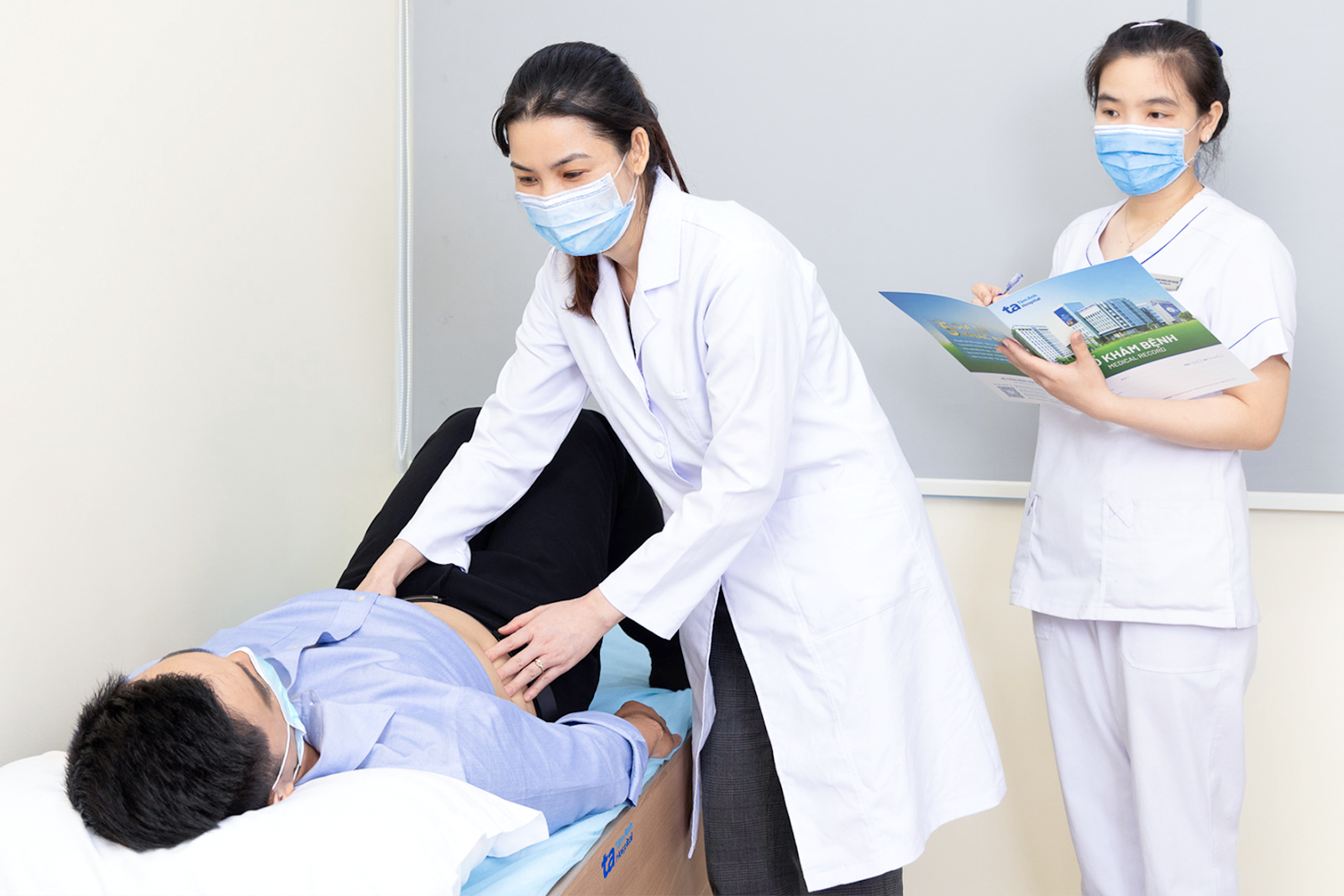 |
Doctor Oanh examines a patient's abdomen. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Doctor Oanh examines a patient's abdomen. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
Soft-cooked vegetables
Vegetables such as carrots, pumpkin, zucchini, and spinach provide fiber (especially soluble fiber), which is beneficial for digestive health. According to Doctor Oanh, soluble fiber binds with water in the intestines to form a soft gel, protecting the intestinal lining and reducing friction as food moves through the digestive tract. This type of fiber also helps nourish beneficial gut bacteria, thereby strengthening immunity and soothing inflammatory symptoms. Patients should avoid raw vegetables, high-fiber vegetables, or undercooked vegetables to prevent symptom flare-ups.
Easily digestible, low-acid fruits
Fruits provide vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and natural fiber beneficial for IBD patients. These components help boost resistance, reduce inflammation, and support intestinal lining recovery. Patients should eat ripe bananas, papaya, steamed apples, or avocados. Avoid acidic, high-fiber fruits like oranges, grapefruits, pineapples, or kiwis, as they can cause irritation and diarrhea.
Foods containing natural probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial microorganisms that help balance gut flora and strengthen immunity. They also inhibit the growth of diarrhea-causing bacteria (a common symptom in IBD patients). Doctor Oanh recommends low-sugar yogurt or kefir (fermented milk) to restore gut flora after diarrhea. Lactose-intolerant individuals can opt for lactose-free yogurt or probiotic tablets as prescribed by their doctor.
Foods rich in healthy fats
Healthy fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats) play a role in maintaining cell membrane structure, absorbing fat-soluble vitamins, and regulating inflammatory responses in the body. As symptoms subside, patients can add small amounts of olive oil, salmon, or avocados – foods containing unsaturated fats beneficial for cell membranes and intestinal lining recovery.
Foods containing anti-inflammatory compounds
IBD patients can supplement with natural foods containing potent anti-inflammatory bioactive compounds to help control inflammation in the body. Examples include garlic, turmeric, ginger, and pure honey. At the same time, limit spicy, oily foods, alcohol, coffee, tea, and processed foods high in additives. Consuming irritating products can exacerbate IBD symptoms and slow down recovery.
Thao Nhi
| Readers can submit questions about digestive diseases here for doctor's answers |