Insomnia, a common sleep disorder, manifests as difficulty falling asleep, restless sleep, or waking up early and being unable to return to sleep. Sufferers often experience fatigue, lethargy, and difficulty concentrating. Causes can include stress, lifestyle habits, medication side effects, or underlying medical conditions.
Doctor Nguyen Anh Duy Tung from the Nutrihome Nutrition Center suggests drinking a glass of warm milk 30-60 minutes before bed. The moderate warmth helps dilate blood vessels, promoting relaxation. Milk also contains tryptophan, an amino acid that helps produce serotonin and melatonin, two hormones that regulate mood and sleep.
Those with insomnia should choose low-sugar or sugar-free milk and avoid condensed milk, chocolate milk, or milk with artificial flavorings. Sugar and caffeine can stimulate the nervous system, leading to restless, light sleep. People with cow's milk protein allergies or lactose intolerance can opt for plant-based milk like almond, walnut, or oat milk. Some nut milks are fortified with natural melatonin or organic magnesium, which can improve sleep in older adults or those with chronic insomnia.
Avoid drinking too much milk before bed, as it can cause bloating, nighttime urination, or indigestion. The recommended amount is 150-200 ml of warm milk, sipped slowly. Avoid drinking it too close to bedtime or lying down immediately after.
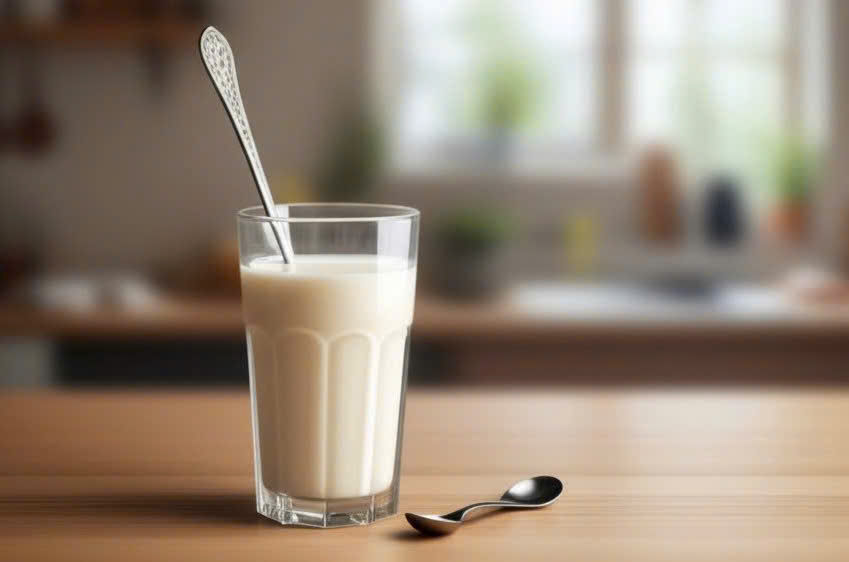 |
Drinking warm milk before bed can promote better sleep. Photo: Trong Nghia |
Besides milk, people with insomnia should eat a light dinner and avoid overly large meals or spicy, fatty, and protein-rich foods. Limiting screen time before bed, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, turning off lights early, and creating a quiet environment can also help the brain relax.
Doctor Duy Tung recommends that individuals experiencing chronic insomnia affecting their daily life and mental well-being consult a neurologist to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Avoid overusing over-the-counter sleep aids or supplements from unknown sources, as these can lead to dependency and worsen insomnia. Depending on the case, doctors may recommend transcranial magnetic stimulation, which uses electromagnetic waves to target specific brain regions, helping treat insomnia, migraines, and anxiety disorders. Supplements containing natural extracts from blueberries and ginkgo biloba can also support increased blood flow to the brain, combat free radicals, enhance neural connections, and improve sleep quality.
Trong Nghia
| Readers can submit nutrition-related questions here for doctor's answers. |