The shoulder, with its wide range of motion and complex structure, is highly susceptible to injury. Doctor Truong Huu Bao, Head of the Orthopedic Trauma Unit at Tam Anh General Clinic, District 7, explains that while anyone can experience shoulder injuries at the gym, they are most prevalent among beginners and those engaging in high-intensity training.
Sprains and strains are typical shoulder injuries in the gym. Both present similar symptoms: pain, swelling, and reduced mobility in the affected area. However, distinguishing between sprains and strains is crucial for effective treatment.
Tendonitis, the inflammation of tendons around the shoulder joint, causes pain and stiffness, hindering movement. It frequently affects athletes and gym-goers who regularly exert force with their shoulders and arms.
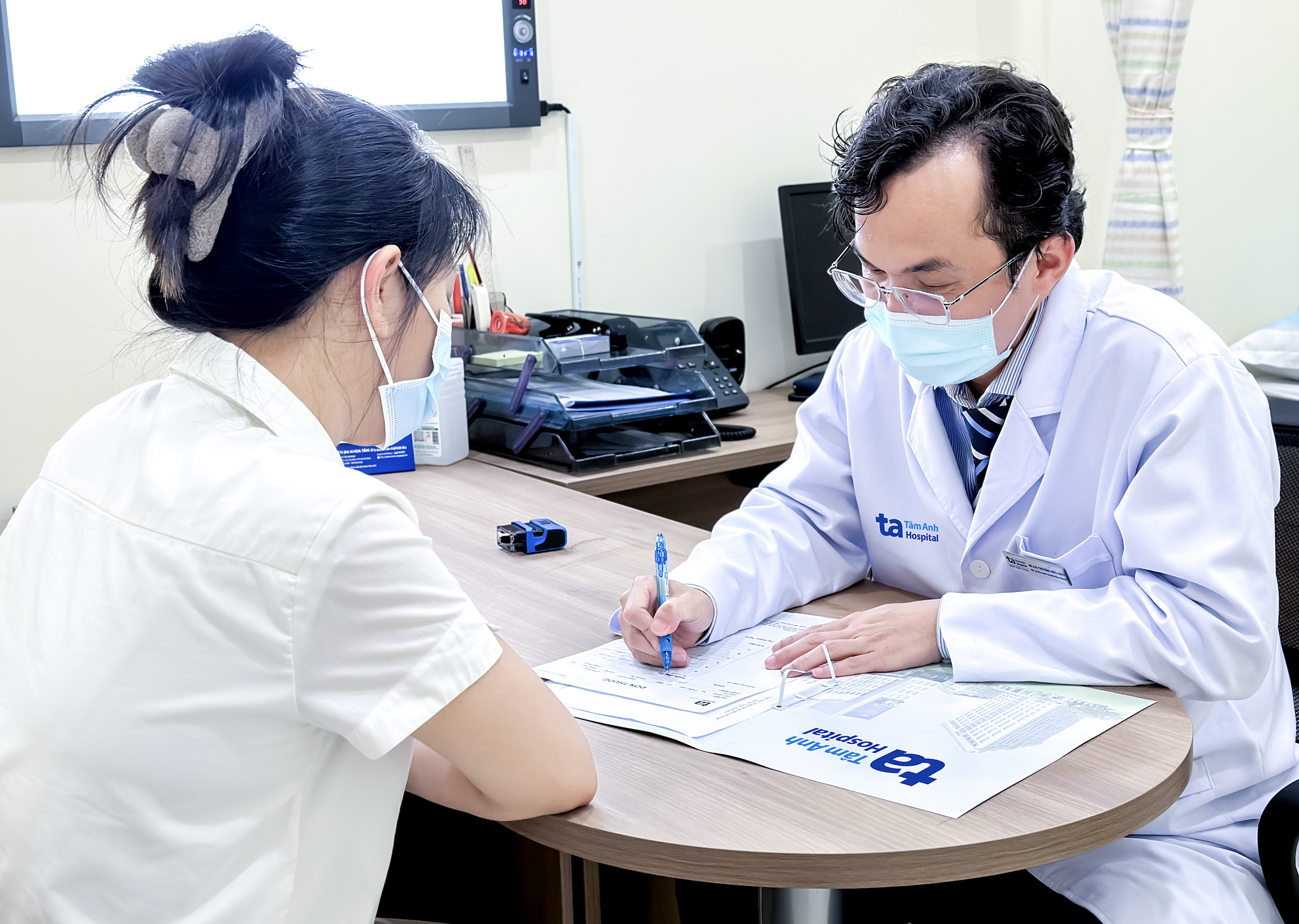 |
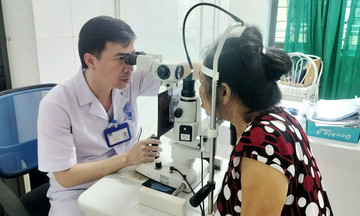
Doctor Bao explaining shoulder joint conditions to a patient. Photo: *Tam Anh General Clinic, District 7* |
Bursitis, the inflammation of the bursa sac cushioning the shoulder joint, can result from impacts, falls, repetitive movements (reaching, twisting the arm), or improper exercise form. Bursitis causes pain, limits shoulder movement, and may lead to swelling and redness around the shoulder.
Rotator cuff tears involve the group of 4 tendons and muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor) surrounding the shoulder joint. Any part of the rotator cuff can be injured, but the supraspinatus muscle is most commonly torn. Tears can occur from sudden trauma or repeated minor injuries over time during gym workouts.
Shoulder dislocations happen when the ligaments holding the shoulder joint in place tear, causing the ball of the upper arm bone to slip out of its socket. During gym workouts, dislocations can occur forward, backward, or downward. Causes include direct impacts to the shoulder, falling and bracing with the hand, or sudden forceful pulling on the shoulder.
Shoulder impingement syndrome occurs when the space between the acromion (part of the shoulder blade) and the rotator cuff tendons narrows. Sufferers often experience fatigue and shoulder pain when lifting, extending, or bringing their arm forward, with pain potentially worsening at night.
Doctor Bao notes that soft tissue injuries like bruises, sprains, and strains are usually not severe and often improve with home care and the body's natural healing mechanisms. Individuals should monitor their condition and seek medical attention if they experience prolonged swelling, redness, and signs of inflammation; pain radiating down the arm or up the neck; persistent pain for 1-2 weeks despite pain relief measures; or sudden unexplained pain.
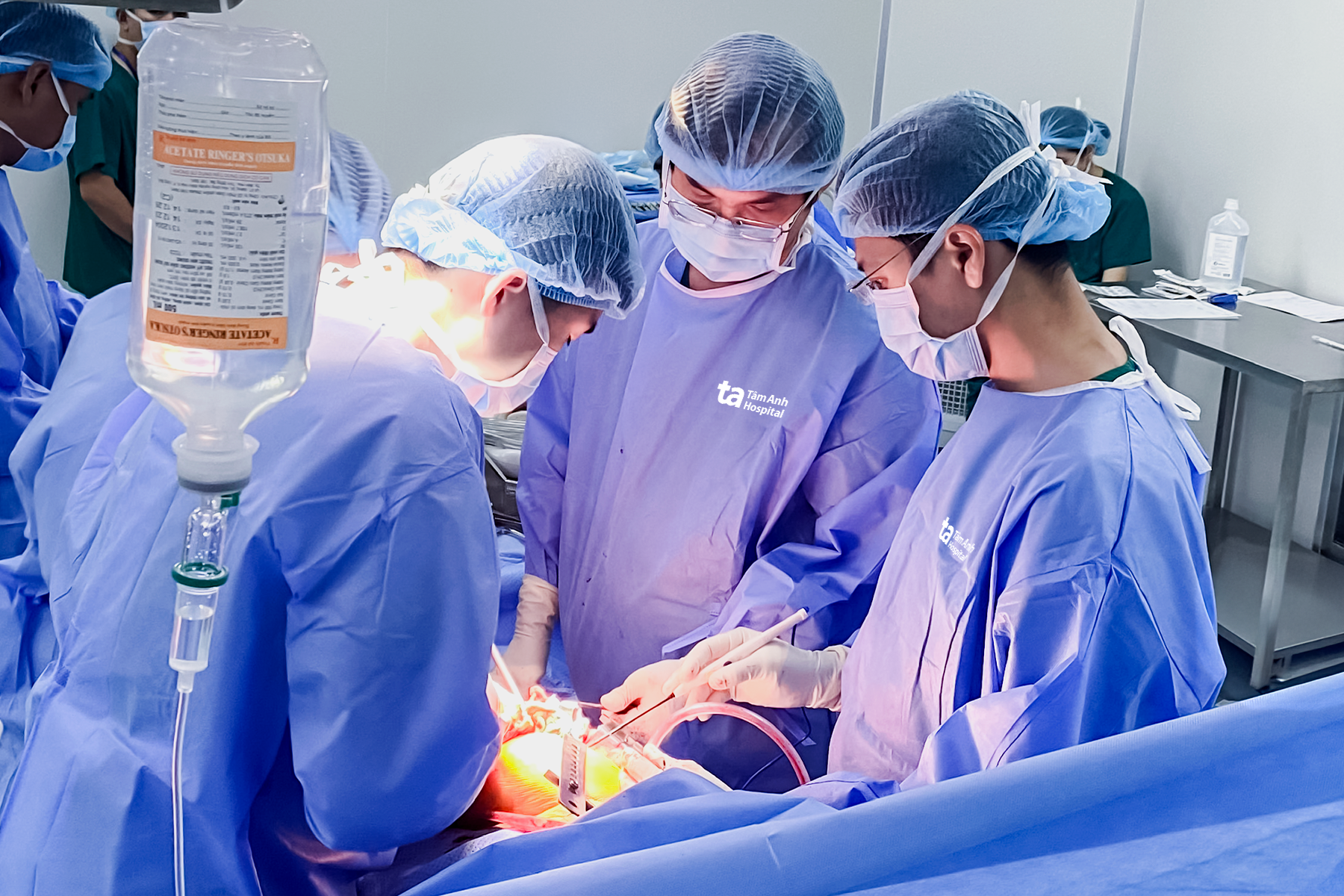 |
Doctor Bao (center) during an orthopedic surgery. Photo: *Hospital provided* |
Doctor Bao emphasizes that shoulder injuries involving fractures or muscle tears require immediate medical intervention. Untreated or improperly managed shoulder injuries can lead to complications such as joint stiffness, muscle atrophy, reduced shoulder function, or joint deformity. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention following the injury. Depending on the specific situation, patients may undergo X-rays, 3 Tesla MRI, 1975-slice CT scans, or 100,000-slice CT scans to assess the damage.
Phi Hong
| Readers can submit questions about musculoskeletal diseases here for doctor's answers. |