Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs when high levels of uric acid build up in the blood, causing joint swelling, heat, redness, and pain. This condition often begins in the big toe, but without proper treatment, symptoms can eventually affect various joints throughout the body. Excess uric acid can also damage joints, bones, and other organs.
Joint damage: Chronic gout causes frequent joint swelling and chronic inflammation, which can damage the joints. This can lead to stiffness and deformity. Managing gout flares helps prevent joint damage. The Arthritis Foundation recommends applying ice to the affected area, elevating the joint, drinking plenty of water, avoiding alcohol and sugary drinks, and reducing stress, as stress can exacerbate gout.
Patients should consult a doctor for anti-inflammatory medication to shorten the duration of gout flares. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair joint damage or replace severely damaged joints.
 |
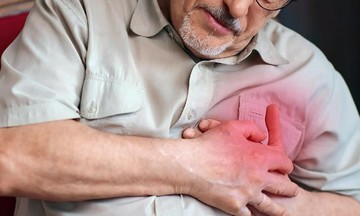
Gout crystals can form and cause pain in many joints of the body such as the knees, hands, and feet. Illustrative photo: Minh Minh |
Gout crystals can form and cause pain in many joints of the body such as the knees, hands, and feet. Illustrative photo: Minh Minh
Tophi formation: Tophi are collections of urate crystals that form lumps of varying sizes on body parts such as fingers, hands, feet, toes, ankles, elbows, and ears. They are a sign of chronic gout and can develop in people with frequent gout attacks. Tophi are usually painless but can damage joints and make movement difficult. Untreated tophi can also lead to complications. If infected or if they press on a nerve, they can cause pain and become dangerous.
To eliminate tophi, doctors may prescribe uric acid-lowering medications to prevent uric acid crystallization. Treating tophi can take time, and their size may decrease after several months of treatment. In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove them.
Kidney stones: People with gout have a higher risk of developing kidney stones. High uric acid levels can cause urate crystals to accumulate in the urinary tract and form stones. Symptoms of kidney stones include severe pain in the back, groin, lower abdomen, or flank below the ribs, painful urination, and brown, red, or pink urine. If kidney stones are caused by gout, doctors may prescribe medication and an alkalizing agent to dissolve the urate stones.
Kidney disease: The kidneys filter waste products, including uric acid, from the body. High uric acid levels can make it difficult for the kidneys to process the excess acid. Uric acid crystals accumulating in the kidneys can impair kidney function and lead to kidney disease or kidney failure. In the early stages of kidney disease, patients may feel tired, weak, or lack energy. As kidney disease progresses, symptoms such as swollen ankles, nausea, fatigue, and loss of appetite can occur.
Eye problems: Eye problems are a rare complication of gout. Uric acid crystals can affect parts of the eye such as the eyelids, cornea, and iris. Tophi can also affect other areas of the eye, such as the upper eyelids.
Cardiovascular disease: Gout is not directly fatal, but it can lead to dangerous complications if not treated properly. According to the American Arthritis Foundation, gout can increase the risk of cardiovascular problems, including heart failure, heart attacks, and strokes, due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals that damage blood vessels.
Gout also increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, especially in women, possibly due to high levels of inflammation. Gout patients are also more prone to being overweight, having high blood pressure, or high cholesterol. Gout can double the risk of sleep apnea, which can lead to serious health problems, including obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, heart attacks, and strokes.
Taking medication to lower uric acid levels, combined with dietary and lifestyle changes, can help control gout and reduce the risk of complications. Patients should limit or avoid purine-rich foods (such as organ meats and shellfish), alcohol, and sugary fruit juices to reduce uric acid buildup and should drink plenty of water. Regular exercise and maintaining a moderate weight are also important, as is managing conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes.
Anh Ngoc (Medical News Today)