Answer:
Women who are overweight or obese before and during pregnancy have an increased risk of high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and gestational diabetes. Obese pregnant women are also at risk for preeclampsia, a serious complication involving high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Maternal obesity can also lead to birth defects and excessive fat in the baby, which can cause childhood overweight or obesity.
For newborns, a predictive factor for obesity later in life is the mother's pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI). Overweight mothers may carry genes that predispose their children to obesity, and family history can also influence this risk. Excessive weight gain during pregnancy is also linked to fetal macrosomia (large birth weight) and the development of childhood obesity. Infants with macrosomia have a higher risk of becoming obese as they grow older than infants with normal birth weight.
You should consult a nutritionist or endocrinologist for appropriate weight management advice. Maintaining an optimal weight helps pregnant women reduce the risk of pregnancy complications and prevent overweight and obesity in their children.
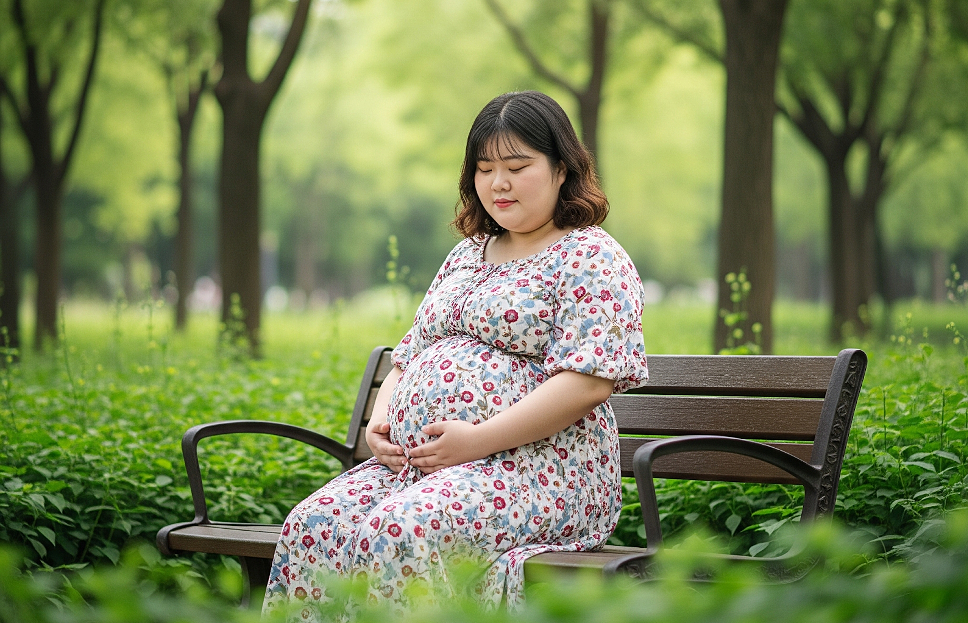 |
Maintaining an optimal weight ensures the health of both mother and baby. *Image generated by AI* |
You should eat a healthy diet during pregnancy and adopt a healthy lifestyle, including getting enough vitamin D and limiting fried foods and caffeine. Eating three main meals and two snacks with adequate nutrients can help prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and reduce the risk of insulin resistance. Regular exercise such as walking, swimming, or yoga during pregnancy can regulate weight and limit insulin production.
Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Kim Tuyen
Center for Weight Control and Obesity Treatment
Tam Anh General Hospital, TP HCM
| Readers can submit questions about endocrine diseases here for doctors to answer. |