Testosterone, primarily produced in the testes and to a lesser extent in the adrenal glands, is crucial for developing male sexual characteristics. These include a deeper voice, body hair growth, facial hair, and increased muscle mass. It also plays a vital role in maintaining reproductive health and sperm production. Women also produce small amounts of testosterone in their adrenal glands and ovaries, impacting fertility, libido, red blood cell production, muscle mass, and fat distribution.
Low testosterone occurs when the body produces less testosterone than needed. While causes and symptoms vary between men and women, it increases the risk of certain health issues for both.
In men, insufficient testosterone can lead to bone loss, decreased sperm count, depression, difficulty concentrating, increased body fat, reduced libido, muscle weakness, sleep disturbances, and erectile dysfunction.
In women, low testosterone symptoms can be vague, making diagnosis challenging. Warning signs include difficulty concentrating, hot flashes, low energy and fatigue, reduced libido, muscle weakness, night sweats, thinning hair, and vaginal dryness.
Testosterone is typically measured in the morning when levels are highest. Normal total testosterone in women is 15-70 ng/dL. For men aged 19-49, it's 249-836 ng/dL, and for men 50 and older, it's 193-740 ng/dL. Low levels can cause infertility in both sexes.
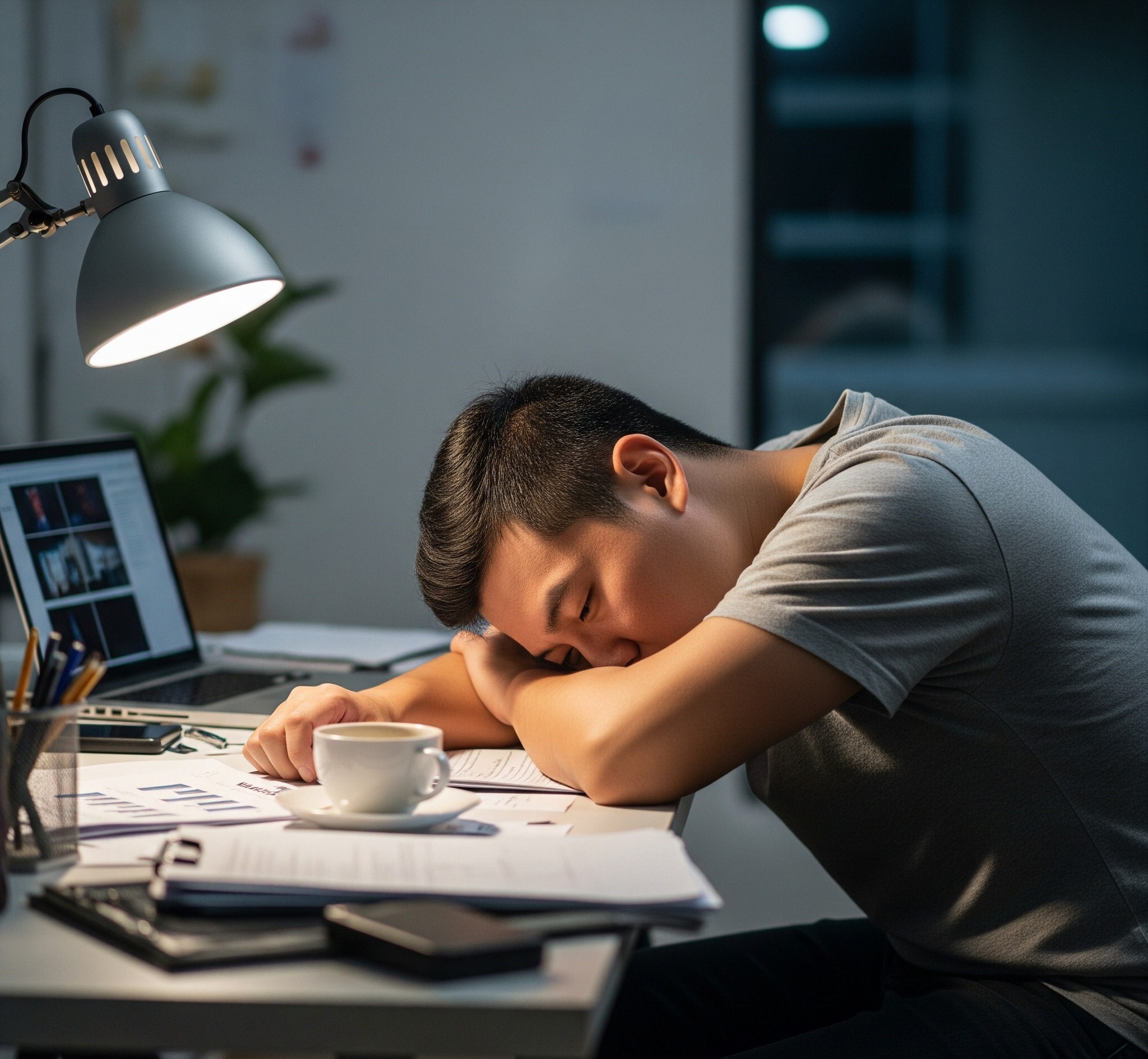 |
Low testosterone can cause difficulty concentrating, fatigue, and reduced libido in men. Image: AI generated |
Low testosterone can cause difficulty concentrating, fatigue, and reduced libido in men. Image: AI generated
Testosterone levels naturally decline with age. However, low testosterone can also result from medical conditions or external factors. Potential causes of hypogonadism in men include chronic stress from overtraining, issues with the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, weight gain, hypothyroidism, testicular damage or cancer, steroid use, iron overload, and certain pain medications.
For women, causes of low testosterone include adrenal insufficiency, prolonged use of estrogen-containing birth control pills, ovary removal surgery, premature ovarian failure (before age 40), and poorly functioning pituitary glands.
Lifestyle adjustments can naturally improve overall health and boost testosterone. These include avoiding tobacco and alcohol, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and getting enough sleep. Avoid medications that interfere with the body's natural testosterone production. If you experience symptoms of hypogonadism, consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Anh Ngoc (According to Verywell Health)
| Readers can submit questions about urological and andrological diseases here for doctors to answer. |