Dr. Ha To Nguyen, Director of the Fetal Medicine Center at Tam Anh General Hospital in TP HCM, stated that approximately 20% of fetal abnormalities are related to genetics. These defects often manifest severely in the fetal structure, especially in the brain or heart. Many genetic abnormalities in the fetus appear vague on ultrasound, making them easy to miss.
While some structural fetal defects can be treated after birth, abnormalities caused by gene mutations put children at risk of developmental delays, impacting their lives. Therefore, both the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) recommend genetic screening for healthy individuals before pregnancy to plan for healthy children.
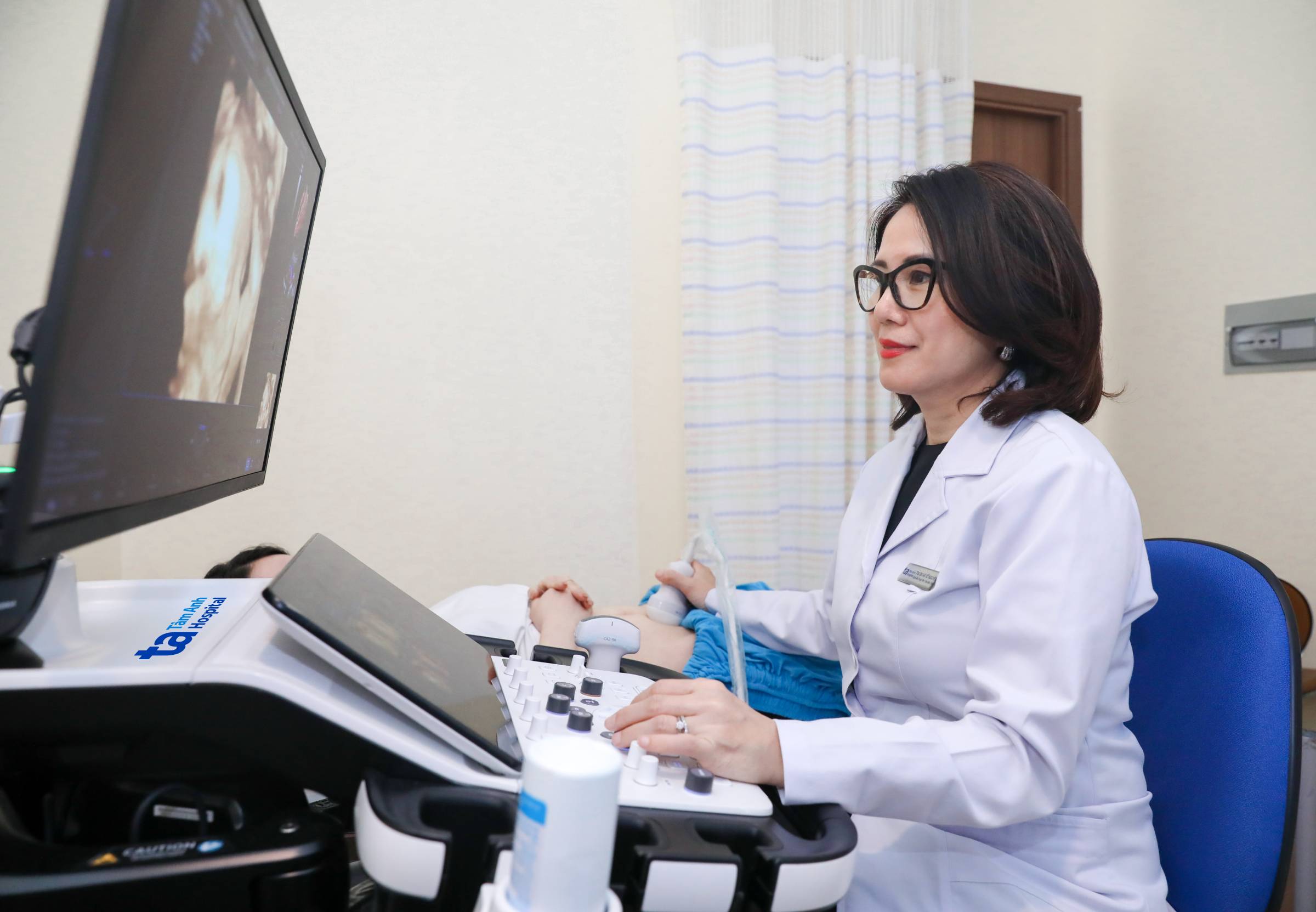 |
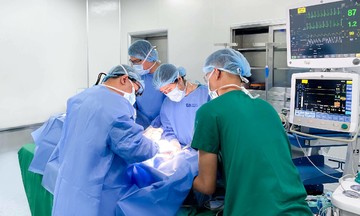
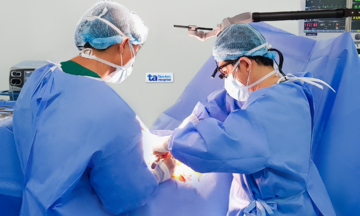
Dr. Nguyen performs an ultrasound on a pregnant woman. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Dr. Nguyen performs an ultrasound on a pregnant woman. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
There are various methods for screening genetic diseases, depending on the target group, timing, and purpose of the screening. Pre-pregnancy or premarital screening is for couples planning to have children to determine if they carry recessive genes that cause genetic diseases. If both partners carry the disease gene, each pregnancy has a 25% risk of the child having the disease, a 50% chance of the child carrying one disease gene, and a 25% chance of the child being normal.
Dr. Nguyen Phuong Thao, from the Fetal Medicine Center, advises couples to undergo screening tests for common genetic diseases that can cause serious birth defects before pregnancy. These include thalassemia, spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), cystic fibrosis, and phenylketonuria (PKU). Couples with a history of miscarriage, stillbirth, infertility, or who have given birth to a child with a birth defect, developmental delay, or genetic disease, should undergo genetic screening to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Pregnant women should undergo prenatal screening in the thu nhat, thu hai, and thu ba trimesters. These common screening methods help detect fetal abnormalities, including those caused by genes. In the thu nhat trimester (11-13 weeks and 6 days), the combined test assesses the mother's age, biochemical indicators in the mother's blood, and nuchal translucency on ultrasound to evaluate the risk of Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Turner syndrome. Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) analyzes free fetal DNA fragments in the mother's blood to determine the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Pregnant women should have regular check-ups to examine fetal morphology. Nearly 1/4 of fetal abnormalities can be detected during the thu nhat trimester ultrasound, with most appearing in the thu hai trimester, and some appearing later in the thu ba trimester or after birth. Structural abnormalities in the fetus can suggest genetic abnormalities, guiding the choice of gene testing for diagnosis.
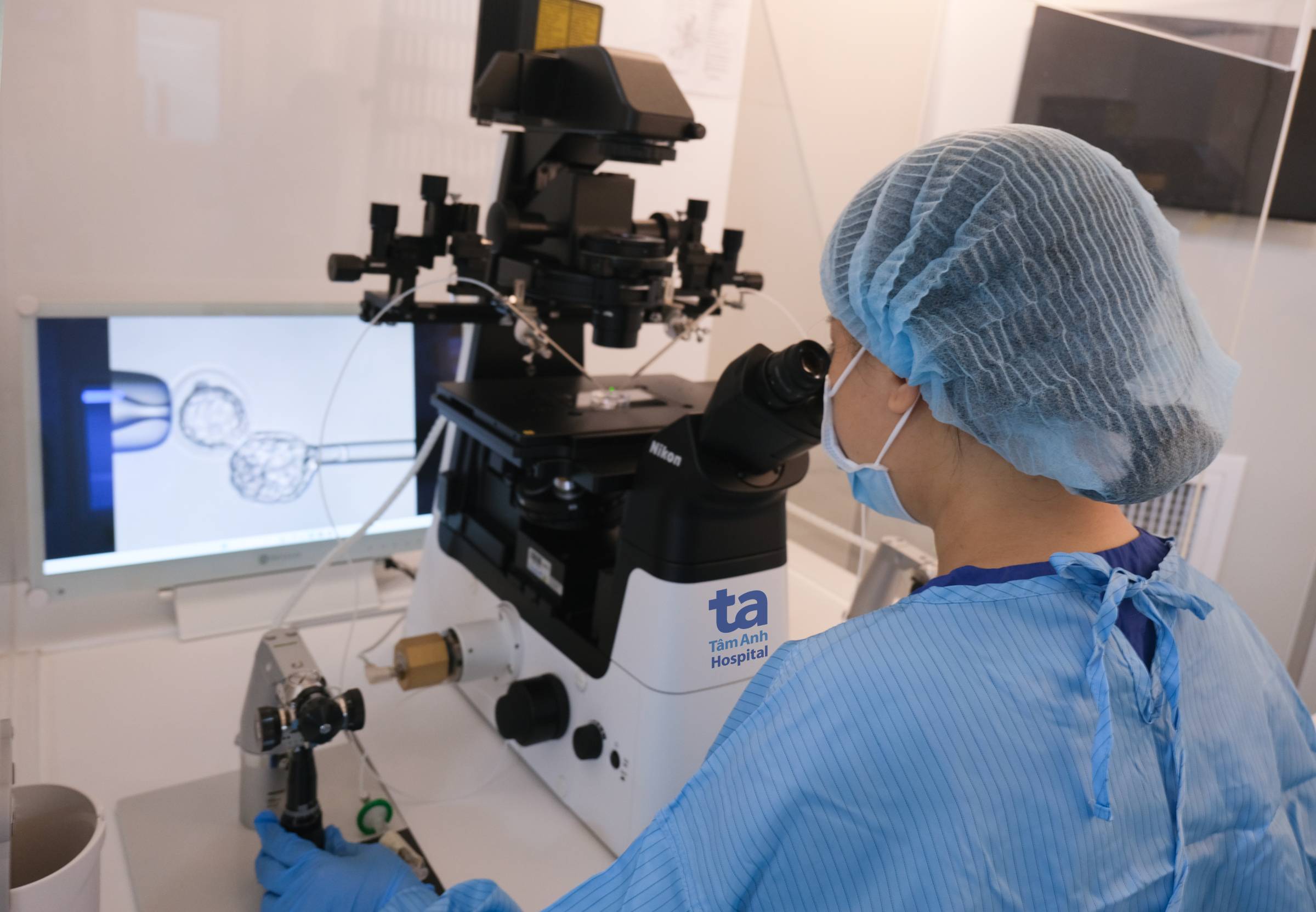 |
Embryo biopsy helps determine if the embryo has genetic abnormalities before transferring it to the mother's uterus. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Embryo biopsy helps determine if the embryo has genetic abnormalities before transferring it to the mother's uterus. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
If prenatal screening indicates a high risk, diagnostic tests such as chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis are necessary. If a couple has a very high risk of having a child with a genetic disease, such as a family history of genetic disease, both parents carrying a recessive disease gene, or one parent having a chromosomal abnormality, they may choose in vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing (PGT). This method helps select healthy embryos without genetic abnormalities for implantation, reducing the risk of the child being born with genetic defects, according to Dr. Thao.
Vietnam records approximately 40,000 children born with birth defects each year. Many single-gene disorders carry a risk of death and illness, placing a significant burden on families and society. Examples include SMA, thalassemia, and cystic fibrosis.
Genetic counseling before or during pregnancy allows doctors to provide information and treatment methods tailored to different genetic disorders, enabling parents to make informed decisions. Depending on each family's choice, doctors provide support and treatment for couples with abnormal pregnancies.
Ngoc Chau
| Readers can submit questions about pregnancy and childbirth here for doctors to answer. |