Two-year-old Huyen was diagnosed with a ruptured eardrum at Tam Anh General Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City after experiencing recurrent ear and throat infections. An examination revealed a perforated eardrum with yellow pus discharge, nasal secretions, and a swollen throat. Dr. Nguyen Thi Huong, from the hospital’s ENT center, diagnosed her with a ruptured eardrum due to otitis media, acute pharyngitis, and nasal discharge.
The middle ear is a small, air-filled cavity located behind the eardrum. In children, the Eustachian tube is shorter, more horizontal, and narrower than in adults. This makes it easier for bacteria and viruses to travel from the nose and throat to the middle ear, especially during colds or throat infections. Fluid and pus accumulate in the middle ear, increasing pressure on the eardrum, which can then rupture to release the pressure.
Doctors cleaned Huyen’s outer ear canal and prescribed medication. She was scheduled for a follow-up appointment in 3 to 5 days. Her parents were advised on how to care for her ear, including keeping it dry, avoiding swimming, not using any unprescribed ear drops, refraining from ear picking, and limiting forceful nose-blowing. They were also told to keep her away from people with respiratory illnesses, dust, smoke, and allergens.
At the follow-up appointment 5 days later, Huyen’s eardrum was healing well. The perforation had shrunk, and the pus discharge had lessened.
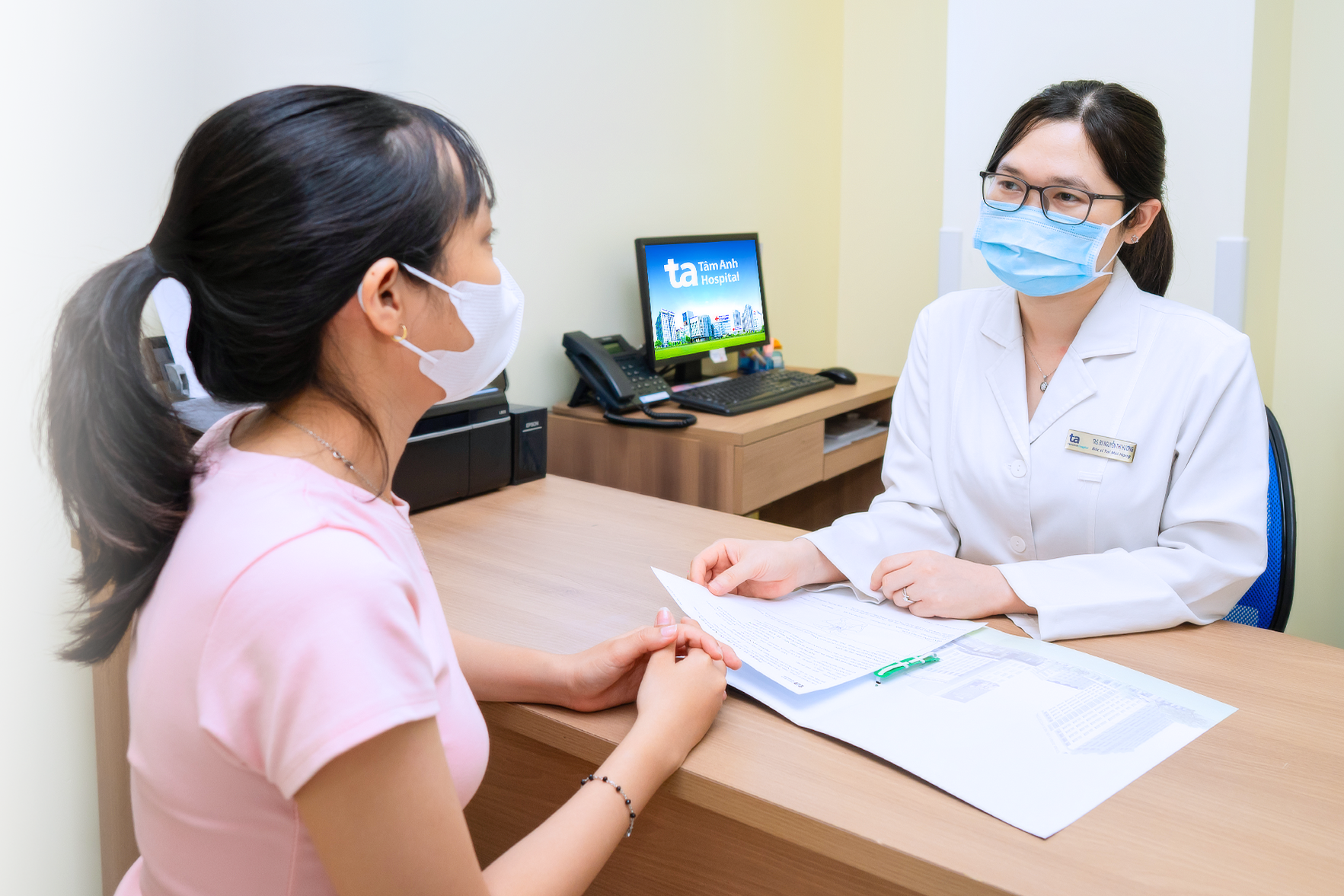 |
Dr. Huong advises Huyen's mother on how to care for her daughter's ear. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Dr. Huong advises Huyen's mother on how to care for her daughter's ear. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
According to Dr. Huong, most ruptured eardrums caused by ear infections heal naturally within a few weeks with proper care. However, recurring or inadequately treated ear infections can prevent healing, potentially leading to hearing loss, mastoiditis, meningitis, or brain abscesses. If the perforation doesn't heal within 3 to 6 months, surgery may be necessary to restore hearing. Before surgery, however, the infection must be completely treated.
Symptoms of a ruptured eardrum in children include earache, fever, ear discharge, tinnitus, and hearing loss. To prevent this condition, children’s throat and ear infections should be treated promptly and completely. Exposure to secondhand smoke should be avoided, and good hand hygiene should be practiced to limit the spread of germs that can cause colds and ear infections. Vaccinations against pneumococcal bacteria and influenza can also help protect children.
Uyen Trinh
*The patient's name has been changed.
| Readers can submit questions about ear, nose, and throat conditions here for doctors to answer. |