Nutritionist Nguyen Thi Quynh from Tam Anh General Hospital in Hanoi explains that pickled eggplant offers small amounts of fiber, B vitamins, and minerals like potassium and magnesium. However, the pickling process, which typically involves submerging eggplant in high concentrations of salt (sodium chloride), can produce nitrites. These nitrites can transform into nitrosamines, which the World Health Organization (WHO) warns are carcinogenic with long-term accumulation. Unsanitary or improper pickling techniques can also lead to uncontrolled fermentation, resulting in mold and bacteria harmful to health.
Quynh advises the following groups to avoid or limit consumption of pickled eggplant:
Individuals with stomach issues: Pickled eggplant's sour and salty nature can irritate the stomach lining, especially when consumed on an empty stomach. Those with stomach ulcers, duodenal ulcers, or gastroesophageal reflux disease may experience discomfort, heartburn, or indigestion after eating it. The acid produced during fermentation can also damage the stomach lining.
Individuals with cardiovascular problems: The high sodium content in pickled eggplant makes it unsuitable for people with high blood pressure, heart failure, or those at risk of stroke. Regular consumption can exacerbate these conditions.
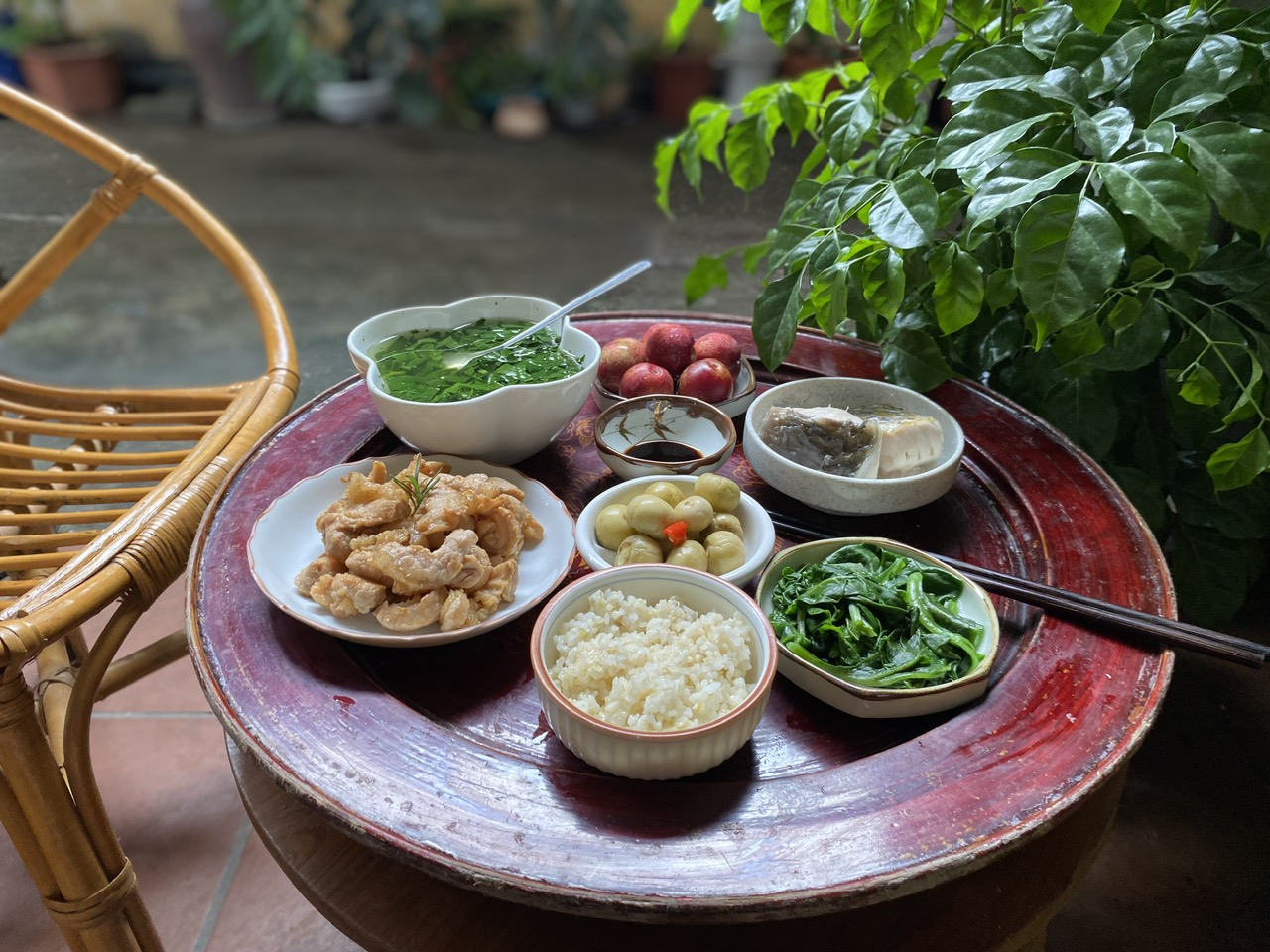 |
Pickled eggplant is a common dish in many households, but excessive consumption is unhealthy. Illustrative photo: Thanh Ba |
Pickled eggplant is a common dish in many households, but excessive consumption is unhealthy. Illustrative photo: Thanh Ba
Individuals with kidney disease: Kidneys play a vital role in sodium excretion and blood pressure regulation. Consuming salty foods or fermented, high-sodium items like pickled eggplant can worsen kidney conditions, increasing the risk of edema, high potassium levels, and electrolyte imbalances.
Pregnant women: During pregnancy, a weakened immune system makes expectant mothers more susceptible to infections from undercooked or improperly stored pickled eggplant. The high salt content can also lead to edema, high blood pressure, and preeclampsia, potentially causing complications for both mother and baby.
Individuals with gout: While pickled eggplant isn't as high in purines as red meat or seafood, it's often consumed with other salty foods, increasing overall purine and salt intake. Long-term consumption can generate plant toxins that affect uric acid metabolism, which is detrimental for those with gout.
Children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems: This group has sensitive digestive systems. The salt and acid in pickled eggplant can cause indigestion, bloating, and diarrhea.
Individuals with allergies or weak digestive systems: Eggplant contains solanine, a compound that can be toxic if consumed in large quantities or not prepared properly. Those with sensitivities may experience allergic reactions to solanine, including hives, nausea, diarrhea, and dizziness. It's advisable to eat only fully fermented pickled eggplant and avoid "quick pickles" (those not fully fermented) due to potential nitrite and bacterial contamination. Even for healthy individuals, pickled eggplant should be a side dish, limited to 1-2 pieces per serving and not consumed daily.
Choose homemade pickled eggplant or those from reputable, safe, and clean sources. Store it in glass jars in a cool, dry place. Discard any eggplant with an unusual odor, slimy film, or mold. Combine pickled eggplant with vegetables and drink plenty of water to balance pH levels and aid salt excretion.
Thanh Ba
| Readers can submit questions about nutrition here for doctors to answer. |