When food is frozen, the water inside its cells turns into ice crystals. These crystals grow, potentially rupturing cell membranes. During thawing, the water and nutrients inside leak out, forming drip loss. This liquid contains not only water but also B vitamins (B1, B2, and B6), minerals like potassium, phosphorus, and iron, along with amino acids and small peptides that contribute to the natural sweetness.
Therefore, thawed meat often loses some of its natural sweetness, and its texture becomes less firm than when fresh. Submerging it directly in water can cause a small loss of water-soluble vitamins and minerals.
 |
According to research published in Meat Science, thawing pork directly in water can reduce its vitamin B1 content by up to 20%. Meanwhile, slow thawing in the refrigerator results in only a 5-7% loss. This percentage increases with longer soaking times, especially in warm water. However, the nutrient loss is not as significant as some people believe.
In red meat, the primary energy-providing components, protein and fat, are minimally affected. For vegetables, especially those rich in water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B vitamins, nutrient loss is more noticeable. With seafood, the loss primarily involves minerals dissolved in the drip loss during thawing, such as potassium, iron, and zinc.
Water thawing isn't inherently wrong, but improper methods can lead to nutrient loss and create a breeding ground for bacteria. Bacteria thrive between 5 and 60 degrees Celsius. Soaking food in water, particularly warm water, quickly raises the surface temperature to this "danger zone" while the inside remains frozen. This results in bacterial contamination on the outer layer before the inner layer thaws. Leaving food exposed to air has a similar effect: the meat or fish softens, but surface microorganisms multiply rapidly.
Therefore, nutritionists and food safety organizations recommend the following for water thawing: Use cold water, place the food in a sealed bag, fully submerge it, and change the water every 30 minutes to maintain a stable temperature. Done correctly, food can thaw in one to three hours depending on size and should be cooked immediately afterward.
Besides nutrition, sensory factors are also crucial. Drip loss contains not only vitamins but also the micro-components that give meat its sweetness. Thus, meat thawed directly in water tends to be blander. Discerning palates can easily distinguish between meat thawed in the refrigerator and meat thawed directly in water.
Water thawing can be a solution for busy individuals, provided they follow these safety guidelines: Seal the food in a bag or vacuum-sealed container before submerging it. Use only cold water, never warm. Change the cold water every 30 minutes to maintain a low temperature. After thawing, dry the food quickly and cook it immediately.
Among current thawing methods, the safest and most nutritionally sound is slow thawing in the refrigerator. The stable temperature of 2-5°C allows for slow thawing, limiting bacterial growth and minimizing vitamin and mineral loss. The only drawback is the longer time required. Due to its balance of safety and nutrition, this method is recommended by the FDA (US) and the National Institute of Nutrition of Vietnam.
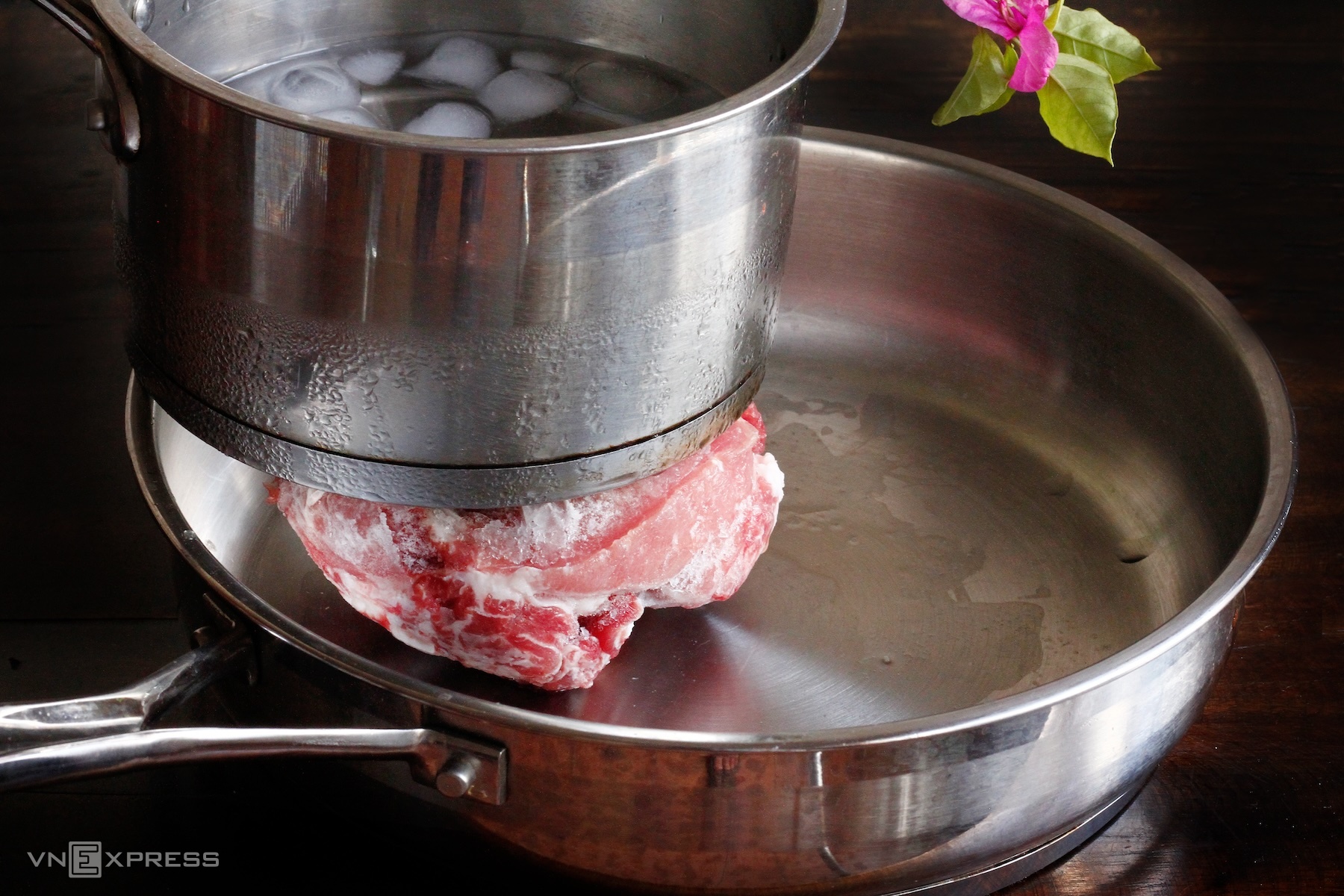 |
Photo: Bui Thuy |
The "reverse ice" thawing technique.
You can quickly thaw food while preserving its flavor using the "reverse ice" technique. Simply sandwich the meat between two metal pans, the top pan filled with cold water and ice. After 20-30 minutes, depending on the meat's thickness, it will be as tender and fresh as if newly purchased.
Metal conducts heat faster than air, creating a temperature difference that thaws the meat evenly without causing water loss or dryness. Adding salt to the ice water increases the effectiveness, but never use hot water. Cook thawed meat immediately and do not refreeze to avoid bacterial contamination.
Microwave thawing is a last resort. In just a few minutes, meat can soften, but microwaves often partially cook the outside while the inside remains cold. This not only affects the meat's texture but also leads to moisture and flavor loss. Therefore, if microwave thawing is unavoidable, cook the meat immediately afterward to ensure safety.
Bui Thuy