One common mistake is immediately cooking crushed garlic or adding it to dipping sauces.
A crucial compound in garlic is allicin, known for its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-boosting properties. Allicin isn't inherently present in garlic but forms when the enzyme alliinase reacts with air after the garlic is crushed or minced.
This reaction requires 10-15 minutes for allicin to fully form. Cooking or using crushed garlic immediately prevents this process. Studies suggest that cooking garlic right after crushing can reduce allicin levels by up to 90%.
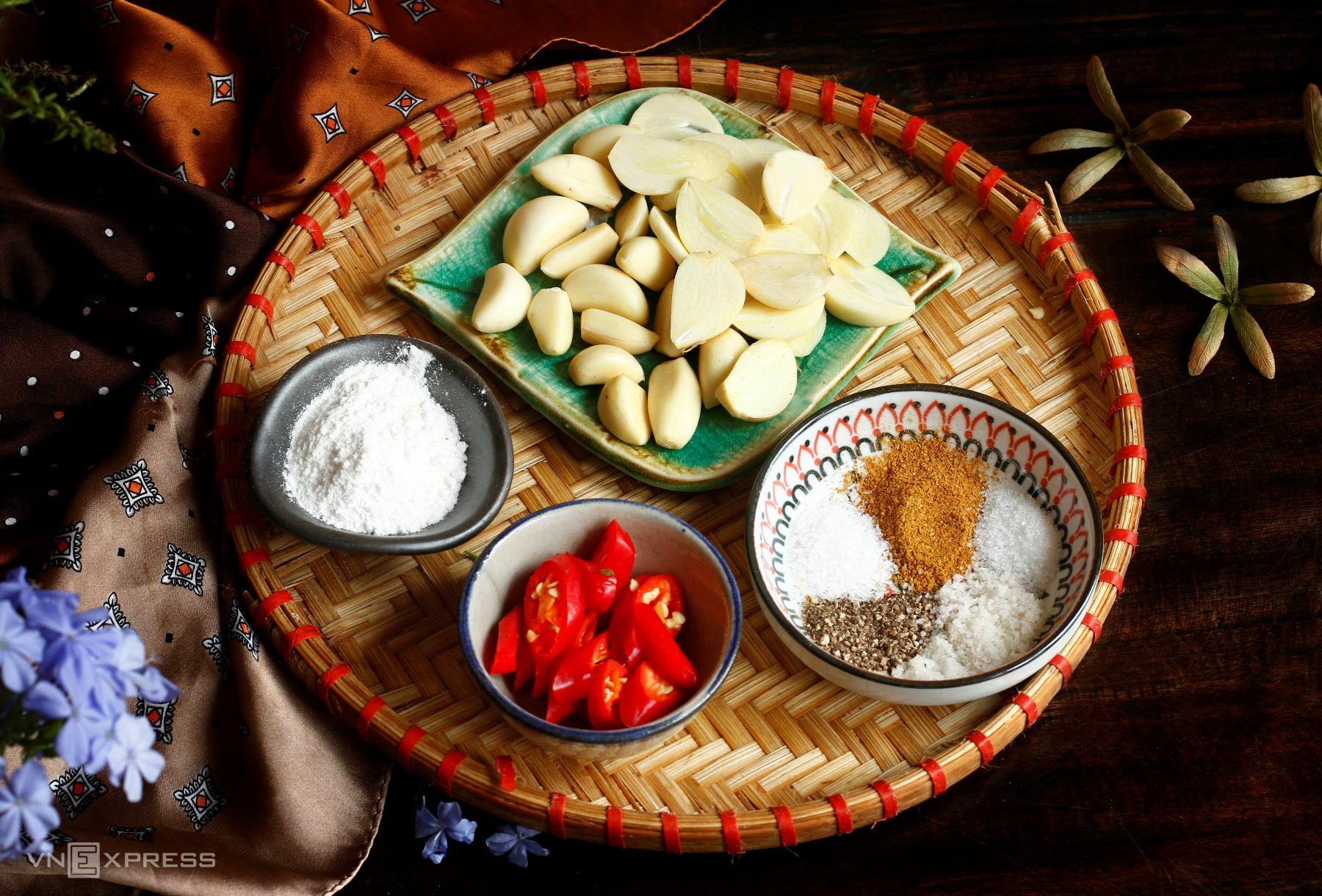 |
Let garlic rest for 10 minutes before cooking. Photo: Bui Thuy |
Let garlic rest for 10 minutes before cooking. Photo: Bui Thuy
Another frequent error is cooking garlic at high temperatures, which destroys its bioactive compounds. Garlic is sensitive to high heat; after just 30-60 seconds at 180°C, most of its active compounds decompose.
Research indicates that allicin is almost entirely lost if garlic is extensively cooked in hot oil. To maximize health benefits, avoid high heat and prolonged cooking times. Nutritionists recommend adding garlic towards the end of cooking or using medium heat and briefly sauteing it.
Preserving garlic also significantly impacts its bioactivity and safety. In Vietnamese cuisine, garlic is often preserved in vinegar or alcohol. The acidic environment of vinegar or the alcohol content can stabilize allicin. Traditional Eastern medicine and modern studies suggest that proper preservation in vinegar or alcohol not only maintains garlic's medicinal properties but also improves absorption.
However, preserving garlic in oil can pose health risks if not done correctly. In oil at room temperature, garlic can become a breeding ground for Clostridium botulinum, a bacterium that produces toxins. Nutritionists advise refrigerating garlic-infused oil and consuming it within a few days.
Pre-peeling and mincing garlic for later refrigeration is another common mistake. This can be counterproductive if stored improperly. Once minced, allicin is susceptible to decomposition from exposure to air, light, and humidity in the refrigerator. Prolonged storage or unsanitary conditions can foster bacterial growth and even the risk of botulinum toxin.
For safety, store minced garlic in a clean, airtight container in the refrigerator for under 10 days, or freeze it in small portions. Discard any discolored or strangely scented garlic.
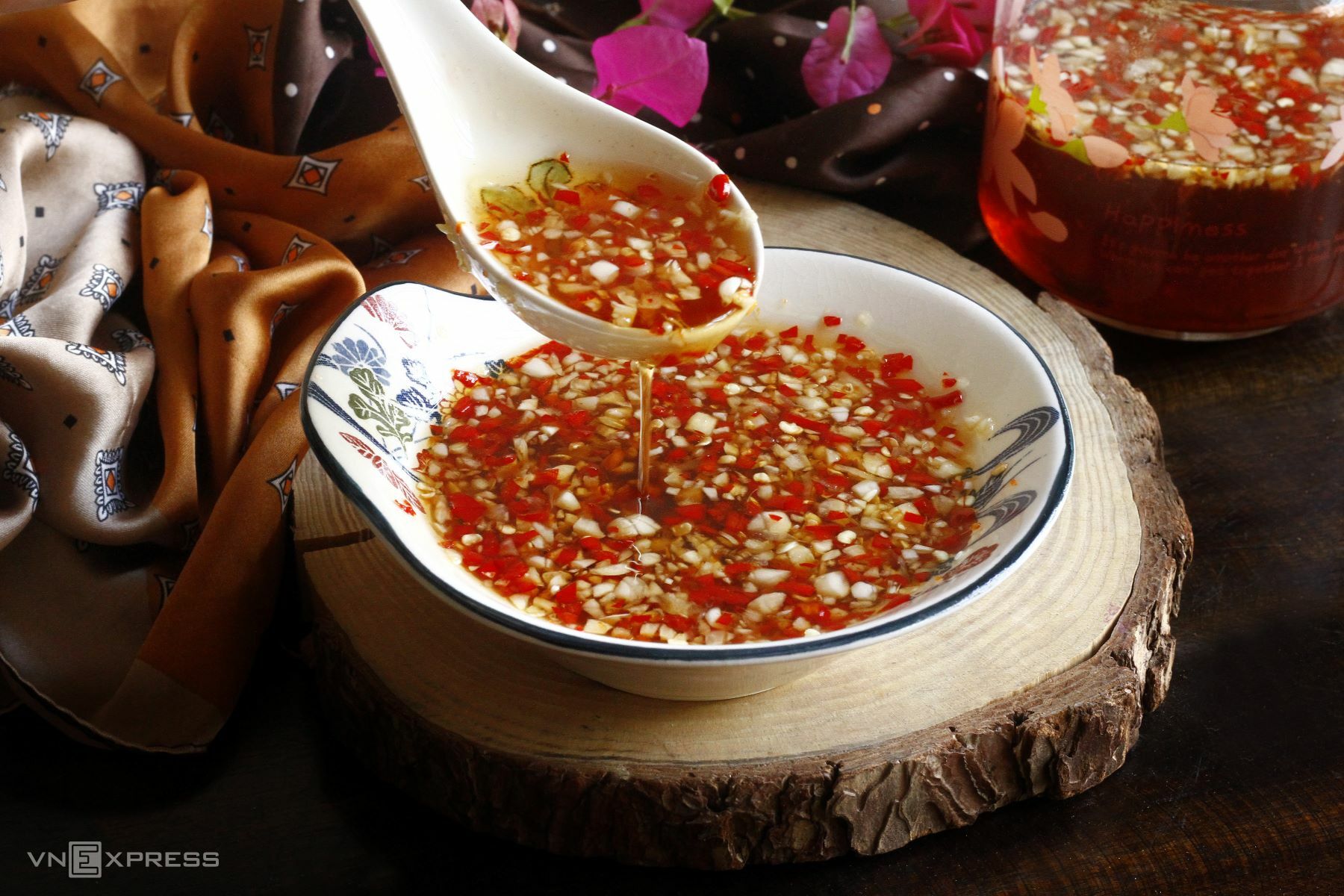 |
Minced garlic is more flavorful after resting for 10 minutes. Photo: Bui Thuy |
Minced garlic is more flavorful after resting for 10 minutes. Photo: Bui Thuy
Even with proper storage and preparation, incorrect timing and dosage can affect health. Garlic has a warm nature, helping regulate blood circulation, dispel cold, and reduce dampness. Excessive consumption in hot weather can cause heat generation, rashes, and indigestion. Therefore, use it in moderation and avoid raw garlic in hot weather or when experiencing heat-related symptoms. Consume garlic during main meals, avoiding it on an empty stomach or late at night to prevent stomach irritation.
Combining garlic with cooling foods like green vegetables, radishes, or cucumbers helps balance its warmth, maintaining yin and yang harmony.
Garlic is more than just a spice; it embodies the subtle harmony of Eastern culinary philosophy. Using garlic correctly enhances the flavor and aroma of dishes while promoting yin-yang balance and long-term health.
Bui Thuy