Water-soluble B vitamins also disappear quickly if vegetables are soaked for too long. Vitamins A, E, and K are more stable because they are only fat-soluble, but they are difficult for the body to absorb from boiled vegetables, which typically lack fat.
Not only vitamins but also minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium easily leach into the boiling water. This is why many people use the water as a refreshing broth.
Many vegetables contain the enzyme ascorbinase, which is the main culprit behind vitamin C degradation at 20-50°C. When the water is still warm, the enzyme is active, and vitamin loss is high. Conversely, when the boiling water temperature exceeds 90°C, the enzyme is deactivated, and more vitamins are retained. Therefore, adding vegetables to a pot of already boiling water, using high heat and plenty of water, will help the vegetables cook quickly, reducing their exposure to heat and minimizing vitamin loss.
Covering the pot while boiling also helps maintain an even temperature and reduces vitamin evaporation.
 |
According to the National Institute of Nutrition, vegetables should be boiled for a few minutes, depending on the type, and not left on the stove for too long. Properly boiled vegetables retain their color, flavor, and vitamins. Overcooking not only destroys vitamins but also chlorophyll, causing the vegetables to become yellow and dull, losing their flavor.
How vegetables are prepared and washed also contributes to nutrient retention. Leaving vegetables whole often preserves nutrients better than chopping them. Washing vegetables after cutting also causes vitamins to dissolve in water. While soaking vegetables in lightly salted water can eliminate bacteria and pesticides, it can also cause some vitamin loss even before cooking.
Boiling is not the optimal method for vitamin retention. Research published in the Journal of Food Science shows that steaming and microwaving (using minimal water and short cooking times) retain 80-90% of vitamin C, while boiling only retains about 50-60%. However, boiling remains a common practice in Vietnamese cuisine due to its simplicity and convenience, and the vegetable water can be used as a broth.
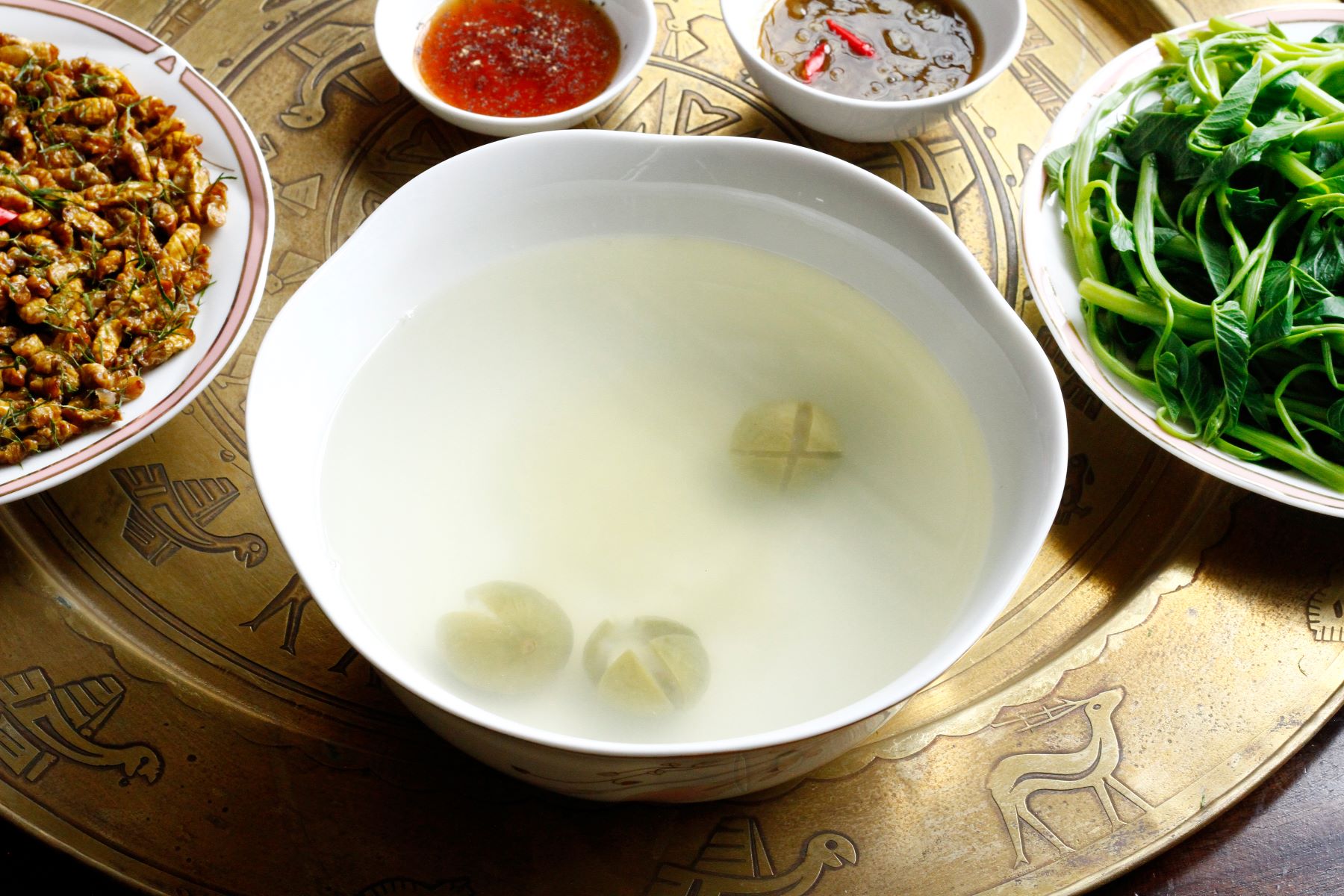 |
Photo: Bui Thuy |
The water used to boil vegetables can be used as broth because it contains dissolved vitamins and minerals.
Boiling vegetables may seem simple, but it involves a combination of culinary experience and nutritional science. By understanding the principles, home cooks can follow these rules: boiling water, high heat, quick cooking, timely removal, and draining in a colander to achieve crisp, sweet, and vitamin-rich vegetables.
Bui Thuy