Air pollution, unhealthy lifestyles, and smoking significantly impact the respiratory system, placing a substantial burden on the lungs to filter harmful substances. Simple home tests can help individuals monitor their respiratory function and detect potential issues early.
**Check your breath-holding ability**
The breath-holding test assesses lung capacity and breath control. Take a deep breath before attempting to hold it. Individuals with healthy lungs can typically hold their breath for about 25-30 seconds. If you struggle to hold your breath for more than 15 seconds, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
**Blow a balloon**
The balloon blowing test involves inflating a balloon with a single, continuous breath. People with good lung volume can inflate a balloon larger than 20 cm, while those with weaker lung health might only manage 15 cm or less. These simple tests require no special equipment and can be performed anytime. Practicing controlled breathing and balloon blowing can also help strengthen lung muscles.
**The 6-minute walk test**
Walking for 6 minutes on a flat surface can evaluate lung function, heart activity, and muscle strength. Individuals with normal lung function typically walk 400-700 meters during the test. A shorter distance could signal underlying lung or heart problems. This method is particularly useful for assessing lung function in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), tracking changes in exercise performance and blood oxygen levels. Using a blood oxygen monitor during the walk can provide insight into your lungs' oxygen delivery efficiency during physical exertion.
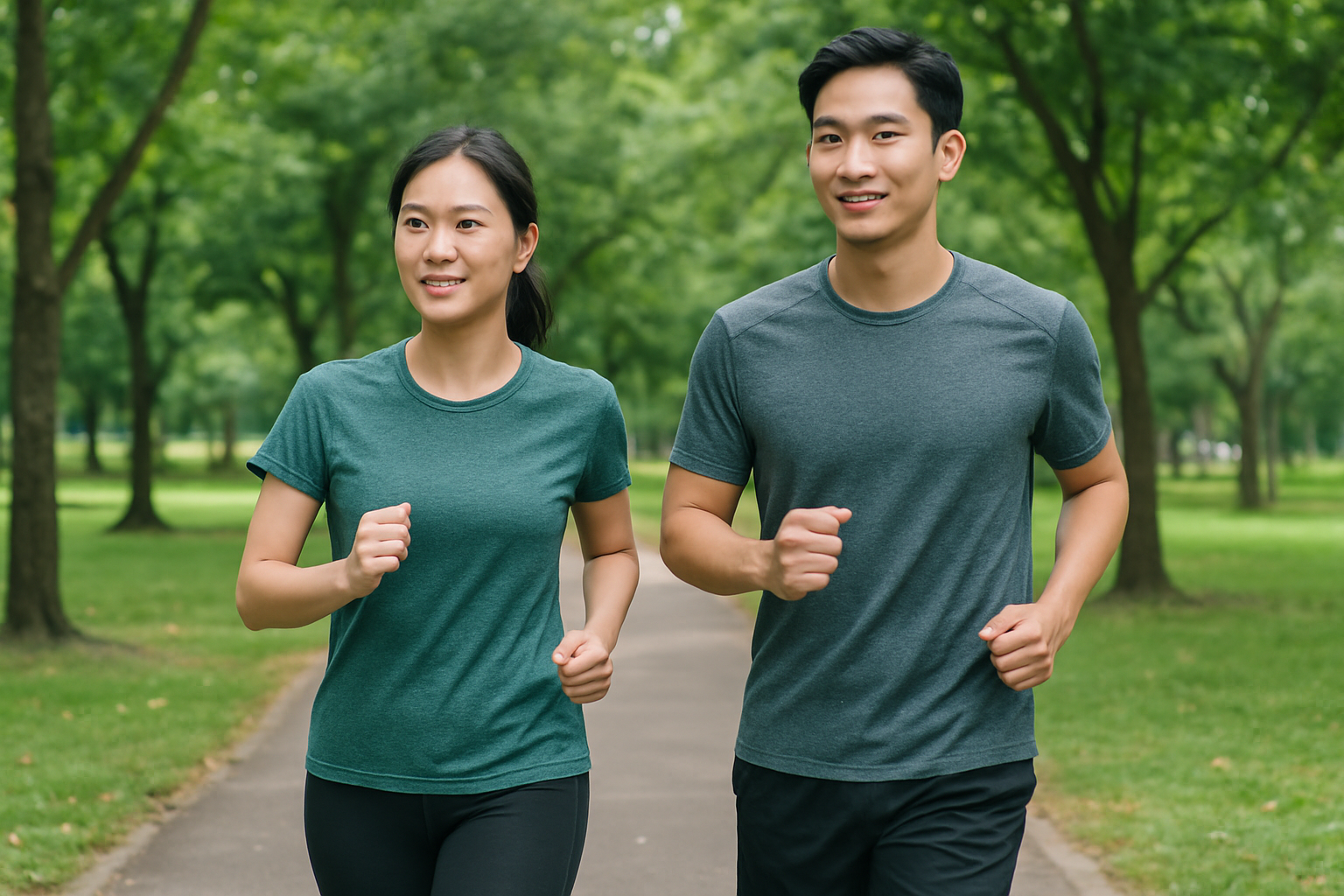 |
Walking for 6 minutes helps assess lung function. *AI-generated image*.
**Stair climbing**
For the stair climbing test, ascend one flight of stairs, then observe how long it takes for your breathing to return to normal. If it takes more than 30 seconds to stabilize your breath, this could indicate suboptimal lung function, reduced lung capacity, or conditions like asthma or bronchitis.
**Assess your breath control ability**
This test focuses on airflow control, a crucial indicator of lung and airway health. Take a deep breath, then slowly and steadily exhale through pursed lips, as if blowing out a candle. Try to maintain a consistent airflow for 8-10 seconds. Difficulty sustaining a steady breath during this period suggests weak breath control, which can be a symptom of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or narrowed airways.
By Le Nguyen (According to Times of India)
Readers can submit questions about respiratory diseases here for doctors to answer.