Many cases of weakened kidneys begin without obvious signs, or symptoms mimic dehydration, as both disrupt fluid balance. Many people simply assume they need to drink more water. However, correctly identifying the difference between kidney issues and other conditions like dehydration allows for early detection and timely treatment.
Persistent fatigue: Feeling tired even after drinking plenty of water may indicate kidneys are not properly filtering toxins. As waste accumulates in the blood, individuals experience a significant drop in energy.
Muscle cramps and body aches: Cramps can occur with dehydration or impaired kidney function. Dehydration-related cramps typically resolve with increased fluid intake. Kidney-related cramps happen when kidneys fail to balance electrolytes such as calcium and potassium. These often accompany other symptoms like fatigue, swelling, and abnormal urination.
Nausea or vomiting: When kidneys do not filter waste, toxins accumulate, leading to feelings of nausea.
Persistent dry mouth and a metallic taste: If your mouth remains dry even after adequate hydration, it may signal impaired kidney function. Accumulating toxins can cause bad breath and a metallic taste.
Dark or foamy urine: Dark urine often results from insufficient fluid intake. However, if kidney issues are the cause, urine will be dark and excessively foamy or bubbly, indicating too much protein. This serves as a sign of kidney damage.
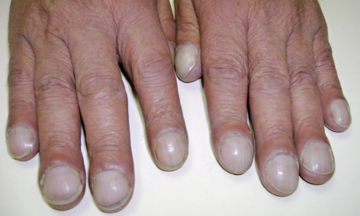
Swelling in feet, ankles, or face: Kidney problems often cause swelling in certain body parts because the body cannot properly eliminate excess fluid and sodium. Swelling around the eyes is a common early sign.
Difficulty concentrating: When kidneys fail to function properly and remove waste effectively, toxins accumulate in the blood. This impacts brain activity, making concentration and clear thinking difficult.
Persistent itching: While drinking water can alleviate dehydration-related itching, it does not help with kidney-related itching. This occurs when toxins build up or mineral balance is disrupted due to impaired kidney function.
Lower back or flank pain: Unrelieved pain in the lower back may signal infection, kidney stones, or swelling. If this symptom persists, even after adequate hydration, you should seek a kidney examination. Early diagnosis of kidney disease can significantly benefit long-term health.
By Bao Bao (Source: *Times of India*)