Dr. Tra Anh Duy from the Men’s Health center said there's a common belief that abstaining from sex for a long time will improve sperm health, quality, and fertility.
According to research published in Fertility and Sterility, the period of abstinence from ejaculation affects sperm concentration, motility, and viability. Specifically:
Effects of abstinence on sperm health
Sperm concentration is the number of sperm in one milliliter of semen. According to a study published in the Journal of Andrology, abstaining from sex for 2-5 days increases sperm concentration compared to daily ejaculation.
However, if abstinence exceeds 7 days, sperm concentration continues to increase, but this is accompanied by a decrease in motility and quality. Sperm that are retained for a long time tend to become immobile or have reduced swimming ability. At the same time, when remaining in the testes for too long, sperm are at risk of becoming deformed due to the effects of temperature and oxidizing agents.
In addition, according to a study in Human Reproduction, prolonged abstinence (more than 10 days) can increase the risk of sperm DNA damage due to oxidation in the epididymis. When sperm remain in the body for too long without being released, they can be damaged and reduce the chances of conception.
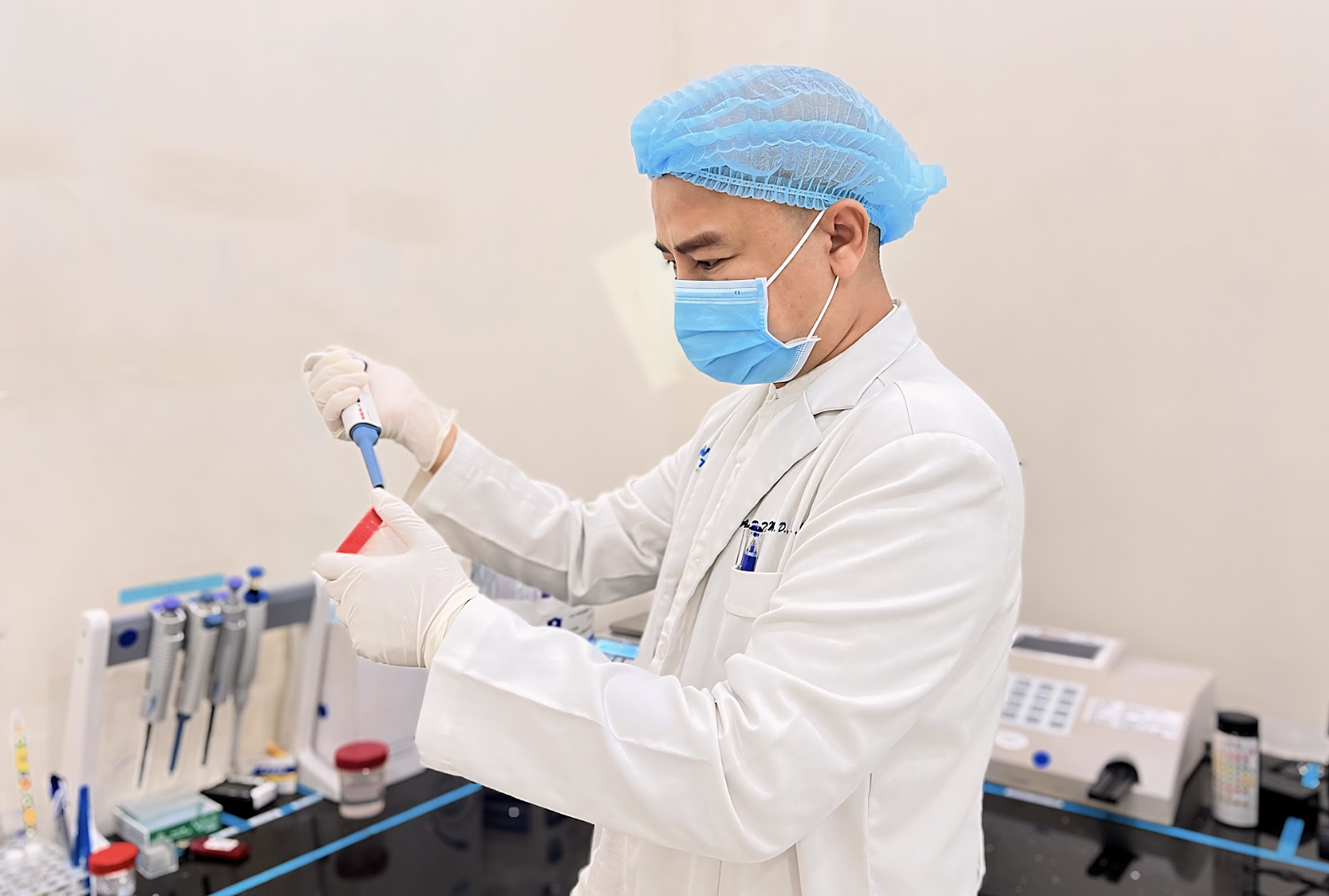 |
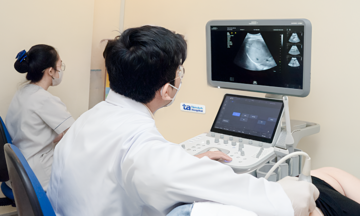
Dr. Duy performing a semen analysis. Photo: Lam Anh |
How to optimize sperm health
Regular ejaculation
Based on numerous studies, experts recommend a frequency of sex or ejaculation of about every 2-3 days to maintain sperm health. According to research in the Journal of Urology, men who ejaculate regularly every 2-3 days have sperm with higher motility and less DNA damage compared to those who abstain for long periods.
Regular ejaculation helps eliminate old sperm, making room for new, healthier sperm. It reduces oxidative stress and limits sperm DNA damage, while maintaining a stable genital environment and reducing the risk of inflammation.
Nutrition
Zinc supplementation helps increase sperm count and quality; vitamins C and E are antioxidants that protect sperm from damage; omega-3 improves sperm motility.
Lifestyle
Limit alcohol and tobacco as nicotine and alcohol reduce testosterone and affect sperm production.
Moderate exercise helps increase blood circulation to the testes. Avoid high temperatures, as hot baths or tight clothing can affect sperm production.
Stress management
Prolonged stress can reduce testosterone production and affect sperm quality. Stress management methods such as meditation, yoga, and adequate sleep can improve fertility.
When to see a doctor
Men should consult a specialist if they experience the following signs:
Irregular ejaculation or difficulty ejaculating.
Abnormal semen quality (color, odor, consistency).
Reduced fertility after more than 12 months of regular intercourse without pregnancy.
A history of diseases related to the gonads.
Semen analysis can help assess the number, concentration, motility, and shape of sperm, from which the doctor will make appropriate recommendations.
My Y