Cam experienced difficulty swallowing, acid reflux, and digestive upset. An X-ray at Tam Anh General Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City revealed an enlarged esophagus with fluid buildup, a semi-obstruction caused by spasms, and a bird's beak appearance at the lower end. High-resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) further revealed dysfunctional esophageal motility and issues with both the upper and lower esophageal sphincters.
Doctor Do Minh Hung, Director of the Center for Endoscopy and Minimally Invasive Digestive Surgery, diagnosed Cam with reflux esophagitis, erosive gastritis, a superficial duodenal ulcer, and type 2 achalasia.
Achalasia is an esophageal motility disorder characterized by the esophagus's inability to open its lower sphincter to allow food to pass into the stomach, causing difficulty swallowing and reflux. When food and liquids cannot move into the stomach, they accumulate in the esophagus and reflux into the trachea and lungs, which can lead to aspiration pneumonia. Chronic inflammation in the esophagus can also create an environment conducive to cellular changes in the esophageal lining, potentially leading to cancer.
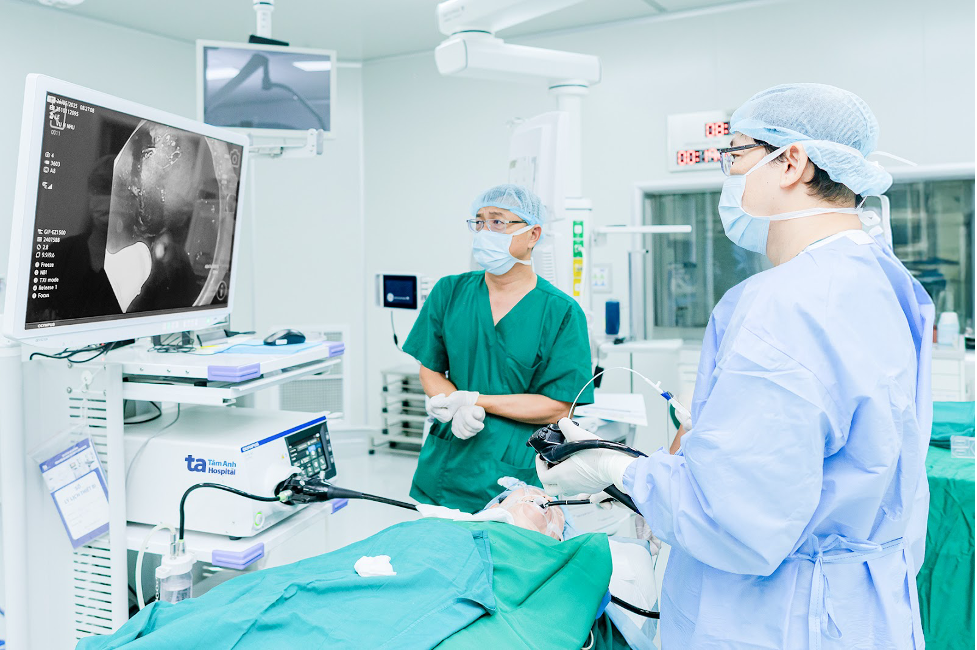 |
Doctor Hung (far right) performs endoscopic surgery on Cam. Photo: *Tam Anh General Hospital* |
Because Cam had previously undergone balloon dilation with severe complications, Doctor Hung recommended peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) to cut the lower esophageal sphincter. This minimally invasive procedure widens the esophageal-gastric junction, allowing food to pass more easily into the stomach. The procedure offers long-term effectiveness, leaves no scars, minimizes pain, and promotes quick recovery. After the surgery, Cam reported no pain and no difficulty swallowing. Upon discharge, she was instructed to consume liquids for the first week, gradually transitioning to softer, well-chewed solid foods, and to follow up with scheduled check-ups.
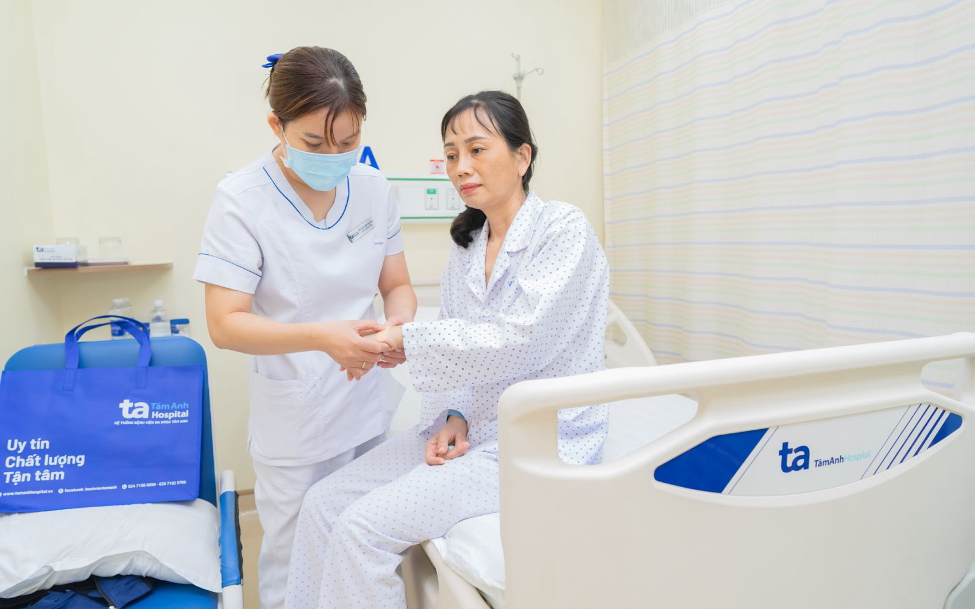 |
Cam receives post-operative care. Photo: *Tam Anh General Hospital* |
The exact cause of achalasia remains unknown, making specific preventive measures unavailable. Doctor Hung advises individuals experiencing symptoms like difficulty swallowing, vomiting undigested food, chest pain, or unexplained weight loss to seek gastroenterological consultation for timely diagnosis and treatment. Depending on the severity of the condition and the patient's overall health, treatment options include medication, botulinum toxin injections, esophageal dilation, or surgical intervention such as laparoscopic Heller myotomy or POEM.
Quyen Phan
| Readers can submit questions about digestive health here for doctor's responses. |