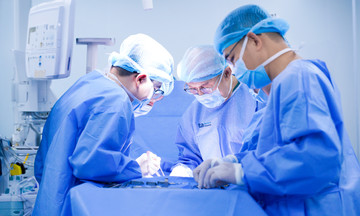
Breast reconstruction surgery helps women maintain breast fullness after mastectomy. The timing of breast reconstruction significantly impacts aesthetic outcomes, safety, and recovery. Currently, medical practice offers three options: immediate, delayed, or semi-delayed reconstruction.
Immediate reconstruction is performed during the same mastectomy surgery. The surgeon removes the tumor and reconstructs the breast shape simultaneously. This approach helps patients maintain a natural breast shape, promotes psychological stability, reduces the number of surgeries and costs, and does not delay adjuvant treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. However, surgery time is longer, post-operative tissue monitoring can be challenging, and scarring is more likely.
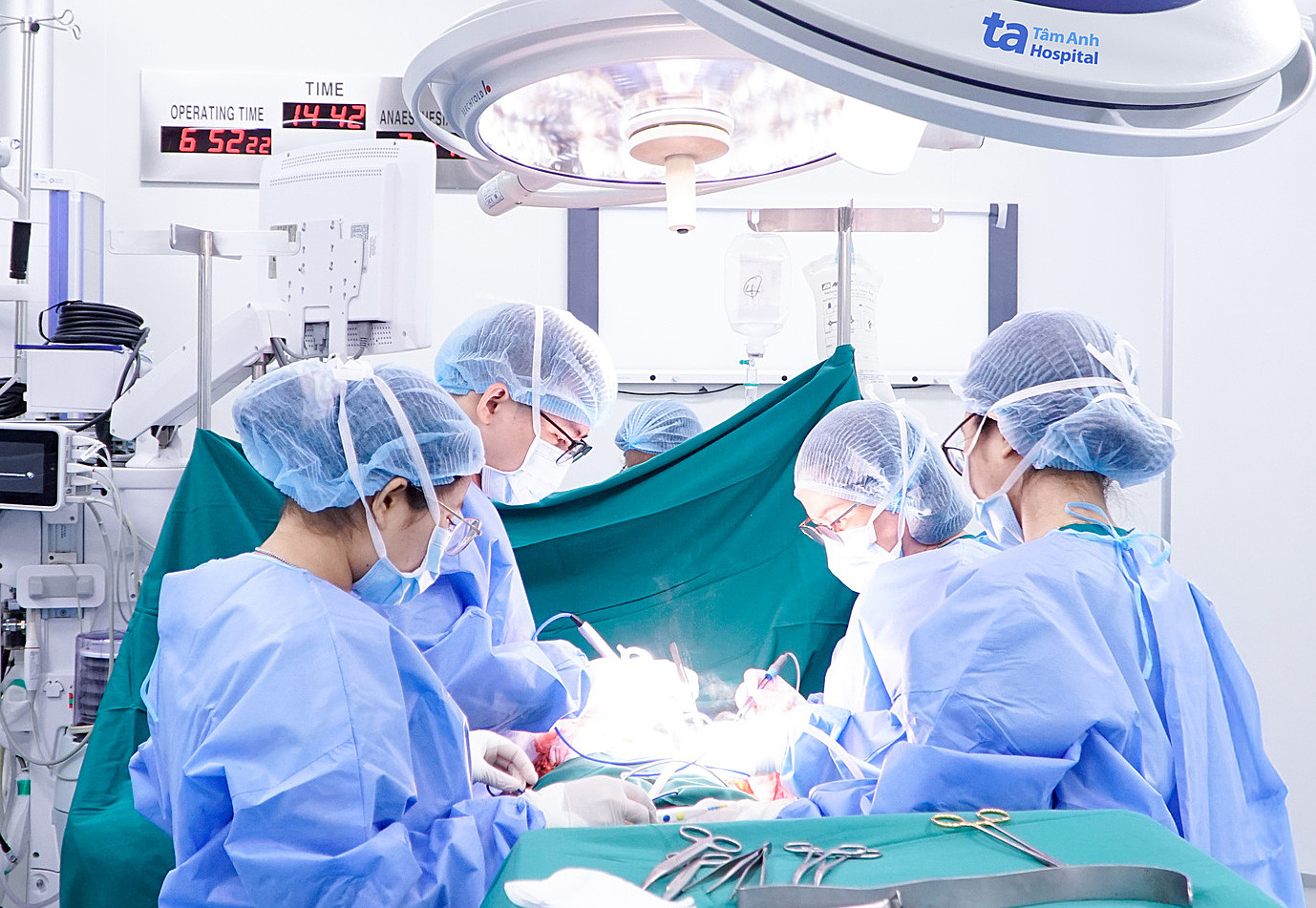 |
Doctors perform mastectomy combined with immediate breast reconstruction for breast cancer patients. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital. |
Delayed reconstruction is performed after the patient completes cancer treatment, typically several months to several years after mastectomy. This option is suitable for patients who require post-operative radiation therapy or are not yet ready physically or psychologically. A disadvantage is that the skin in the breast area may contract and scar, making reconstruction more difficult and less natural.
Semi-delayed reconstruction is an intermediate option between the two methods mentioned above. During mastectomy, the doctor places a temporary tissue expander to maintain breast shape. If pathology results indicate no need for radiation therapy, the patient undergoes definitive reconstruction after one to two weeks. If radiation therapy is required, the expander remains until treatment concludes. This method helps preserve skin and breast shape, yielding good aesthetic results, but it is more expensive and may involve complications related to the tissue expander.
The decision regarding breast reconstruction timing should be based on the stage and characteristics of the breast cancer, the risk of needing post-operative radiation or chemotherapy, the patient's overall health and comorbidities, and their preferences and circumstances. You should discuss with your treating doctor to plan the most suitable and effective surgical approach.
Master, Doctor Tran Nguyen Nhat Khanh
Department of Breast, Head and Neck Surgery
Tam Anh General Hospital TP HCM
| Readers can ask questions about cancer here for doctors to answer |