Answer:
Sinuses are hollow, air-filled cavities located within the bones of the face. Sinusitis is a condition where the mucous membrane lining the sinuses becomes inflamed and swollen, producing excess mucus due to viruses, bacteria, fungi, allergies, or blocked sinus openings.
Stagnant fluid from blockage creates a breeding ground for bacteria, leading sinusitis to develop into a sinus infection. Symptoms then worsen, including thick white, yellow, or green mucus draining from the nose down the back of the throat, bad breath, nasal congestion, pain and swelling around the eyes and face, reduced sense of smell and taste, fatigue, fever, earache, and headache.
Acute sinusitis lasts less than 4 weeks, usually improving after 7-10 days. Symptoms lasting over 12 weeks or recurring frequently are considered chronic. Anyone can get a sinus infection, but those with a history of allergies or asthma are at higher risk. Other risk factors include exposure to cigarette smoke, nasal polyps, and pressure changes (from flying or scuba diving). Sinus infections can also be caused by anatomical abnormalities like a deviated septum or enlarged turbinates.
Prolonged or improperly treated infections can lead to dangerous complications. One common complication is the spread of infection to the eye and surrounding structures, causing cellulitis, dacryocystitis, or orbital cellulitis. Patients may also develop orbital abscesses, eyelid abscesses, or optic neuritis behind the eyeball, leading to impaired vision or blindness.
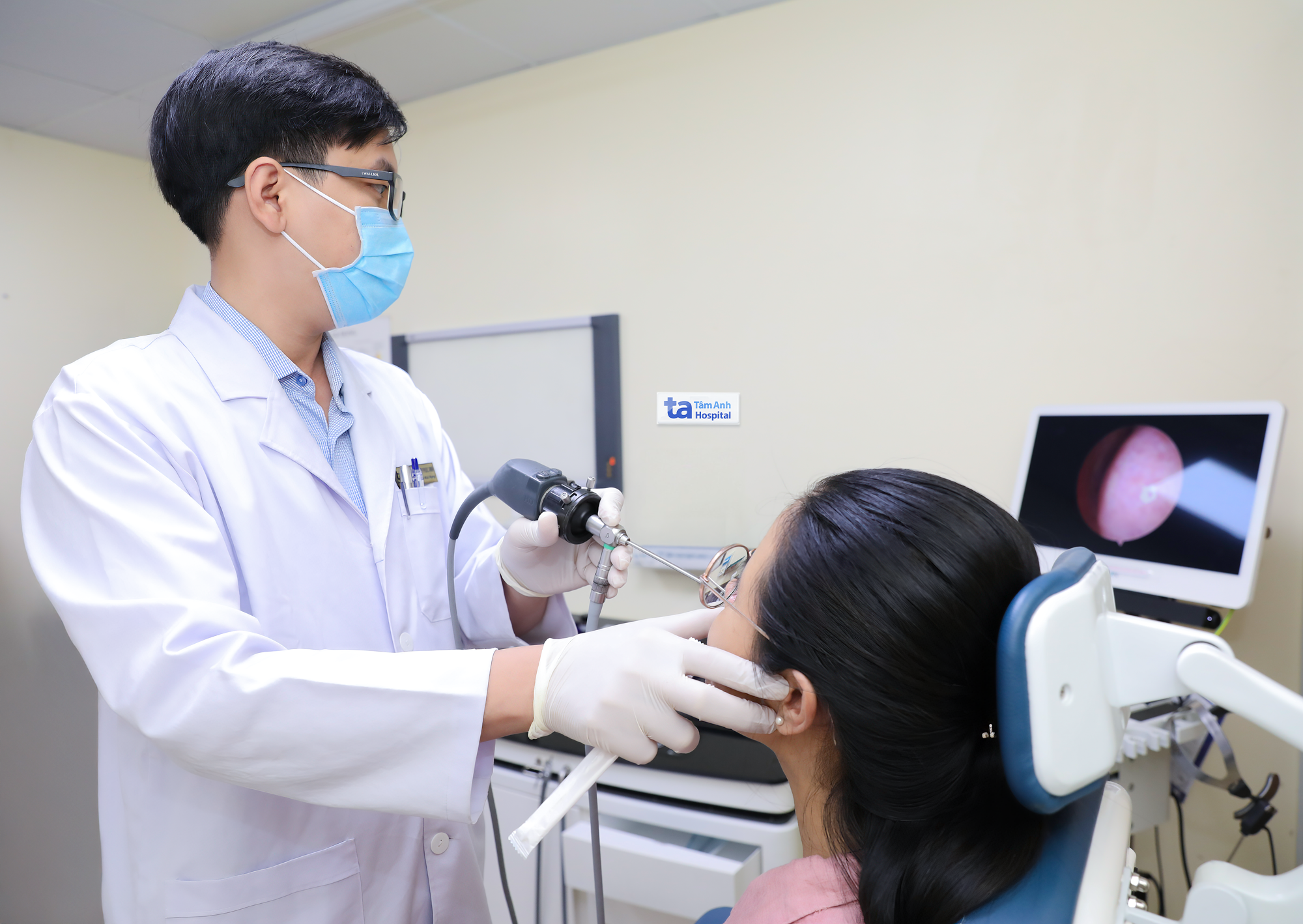 |
Doctor Phuc Anh performs a nasal endoscopy on a patient. Photo illustration: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Bacterial or fungal sinus infections can spread to the skull bones (osteomyelitis) and into the brain, causing meningitis, brain abscesses, or hydrocephalus, leading to hemiplegia, cognitive impairment, cranial nerve palsy, vision loss, and hearing loss. The infection can also cause complications in the ear, such as otitis media, which is common in children due to their shorter, horizontal Eustachian tubes. Continuous mucus drainage down the throat can cause chronic pharyngitis and tonsillitis. A rare but serious complication of sinus infection is cavernous sinus thrombosis, which can have long-term effects like ophthalmoplegia, blindness, and hypopituitarism.
Sinus infections are initially treated with medication. If the infection recurs frequently, has caused complications, or doesn't respond to medical treatment and is accompanied by a deviated septum or nasal polyps, surgery may be recommended.
To prevent sinus infections, limit contact with people who have colds or respiratory infections. Avoid allergens like pet dander and pollen, and don't smoke or be exposed to secondhand smoke. Wear a mask when going out to avoid polluted air and fine dust, and consider using a humidifier.
If you experience fever, nasal congestion, sore throat, foul-smelling nasal discharge, forehead or eye swelling, or blurred vision, consult an ENT specialist immediately for diagnosis and treatment to limit potential complications.
MSc. MD. CKI Diep Phuc Anh
ENT Center
Tam Anh General Hospital TP HCM
| Readers can submit questions about ENT diseases here for doctors to answer. |