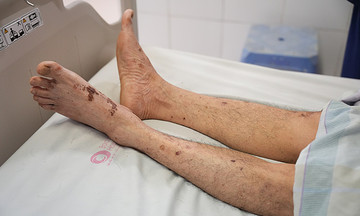
On 5/7, a representative of the Hanoi Hospital of Andrology and Infertility reported that upon arrival, the patient experienced intense pain, subcutaneous hematoma and bruising, penile swelling, and deformity. Doctor Trinh Kien Cuong, specializing in andrology, performed an ultrasound and determined a tear in the tunica albuginea of the left corpus cavernosum while erect. This caused blood to leak from the corpus cavernosum into the subcutaneous layer of the genital area, leading to significant hematoma, swelling, and deformity.
The doctor ordered emergency surgery. The operation lasted about an hour, with the surgical team removing the hematoma and suturing the tunica albuginea. Post-surgery, the patient's condition stabilized, and he is currently under observation at the hospital.
 |
The doctor performs surgery on the patient. Photo: Hospital provided |
According to Doctor Cuong, anatomically, the penis does not have bones but is composed of three cylindrical tubes. Two corpora cavernosa are located above and one corpus spongiosum below, between the groove of the two corpora cavernosa. These three tubes are encased in layers of connective tissue, forming the complete structure of the penis, enabling its erectile function. Therefore, the term "penile fracture" actually refers to a tear in the tunica albuginea of the corpus cavernosum while the penis is erect, not a bone fracture as many mistakenly believe.
Penile fractures often occur at the base of the penis, characterized by immediate loss of erection, sharp intense pain, widespread bruising, bleeding, and swelling of the scrotum and genital area. Some common causes include sexual intercourse in difficult positions, trauma to the erect penis, or improper bending of the penis.
The doctor warned that penile fracture is a condition requiring surgical emergency. If not treated promptly, it can lead to complications affecting sexual and reproductive function, as well as urination in men. Delayed treatment can cause the hematoma to become infected, necrotic, and leave permanent consequences such as corporal fibrosis, curvature or bulging of the penis, pain during erection, erectile dysfunction, and urethral stricture causing difficulty urinating.
Men should not apply strong force to the penis, especially when erect, and should break the habit of self-bending. During sexual intercourse, safe positions should be chosen, limiting strong impacts and avoiding uncontrolled actions. In cases of swelling, pain, or bleeding, immediately seek medical attention at a specialized facility for timely examination.
Thuy Quynh