Dr. Tong Thi Ngoc Cam, Deputy Medical Director of the Northern Region for VNVC Vaccination System, stated that cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, with approximately 10 million deaths annually. In Vietnam, cancer is a significant burden, with 180,480 new cases and 120,184 deaths in 2022, according to the Global Cancer Organization (GLOBOCAN).
According to Dr. Cam, in addition to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes abstaining from smoking, eating a balanced diet, and increasing physical activity, vaccinations can also help prevent agents that cause the following cancers:
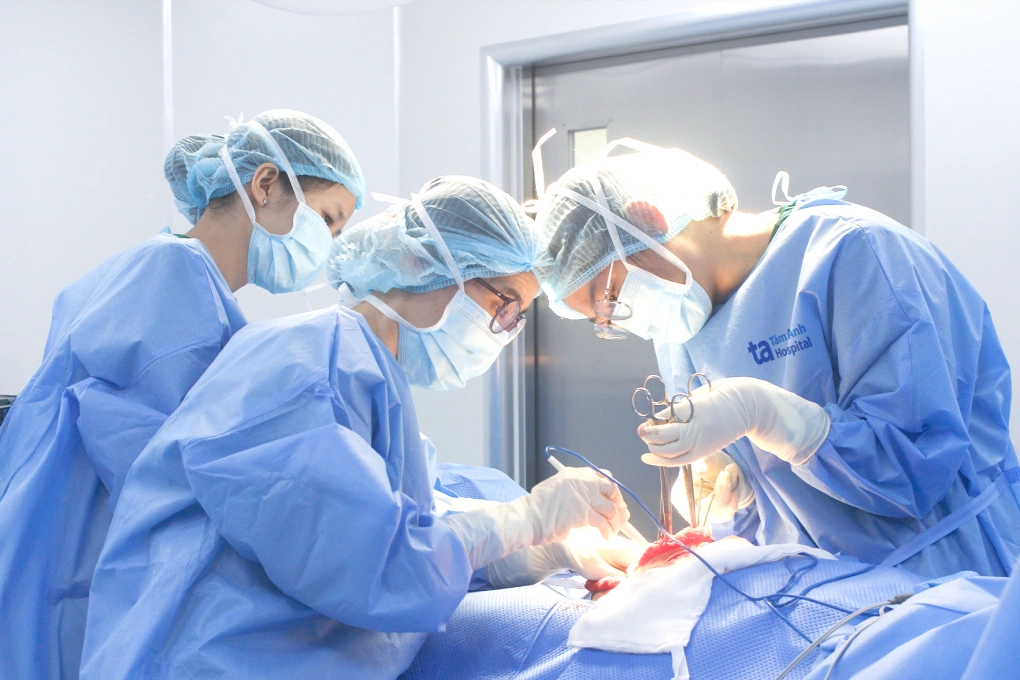 |
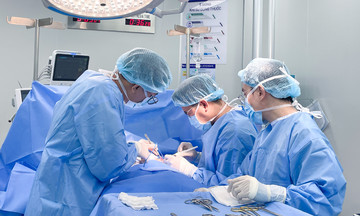
Surgeons operate on a cervical cancer patient. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital, TP HCM. * |
Liver cancer
Liver cancer currently has high incidence and mortality rates in Vietnam, especially among those under 30. The disease progresses silently, and symptoms such as jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, nausea, liver pain, and loss of appetite may only appear in the later stages. Most patients seek medical attention when the disease is advanced, with an average survival time of less than a year. 60% arrive at the hospital in intermediate or advanced stages, and the rate of early detection is very low.
Liver cancer has many causes, including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, an unhealthy diet, environmental pollution, late nights, and lack of exercise. Among these, the main causative agents are the hepatitis B and C viruses, accounting for about 80% of liver cancer cases.
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a common disease in women, with about 6,200 cases diagnosed and over 2,500 deaths annually in Vietnam, according to Globocan 2022. The disease progresses silently. In the early stages, it is difficult to detect because cancer cells have not multiplied significantly, and the tumor is small on the surface of the cervical mucosa, without causing warning symptoms. Some cases may have signs easily mistaken for other gynecological issues, such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, menstrual disorders, pain during intercourse, vaginal discharge with an odor, and pelvic pain. Patients only seek medical attention and cancer screening when symptoms become severe in the later stages. This leads to difficult and expensive treatment and a high mortality rate.
Infection with one or more high-risk HPV types is confirmed as the primary cause of cervical cancer. Eight common carcinogenic types – 16, 18, 45, 33, 51, 58, 31, 52, and 35 – are responsible for approximately 96.1% of cervical cancer cases.
Throat cancer
In addition to causing cervical cancer, the HPV virus is also linked to about 60-70% of throat cancer cases. This cancer has a high incidence in Vietnam, affecting approximately 12% of the population. However, symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, sore throat, hoarseness, tinnitus, persistent cough, ear pain, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck are easily mistaken for other respiratory illnesses, leading to late detection, difficult treatment, and a high mortality rate.
Nasal cavity cancer
Nasal cavity cancer is a tumor that forms inside the nasal cavity or sinuses, more common in men. The disease causes symptoms such as frequent unilateral blockage, reduced sense of smell, nasal congestion, and mucus discharge from the nose. However, these symptoms are easily confused with the common cold or sinusitis, leading many to ignore them. This results in late detection, making treatment challenging.
According to Dr. Cam, in addition to factors such as smoking, air pollution, and inhaling chemicals or wood dust, about 30% of nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancer cases are caused by HPV infection. Recently, Tam Anh General Hospital in TP HCM recorded a case of a 35-year-old man with a nasal cavity tumor also due to HPV type 6.
HPV also causes anal cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer, penile cancer, and genital warts, which have high incidence and transmission rates.
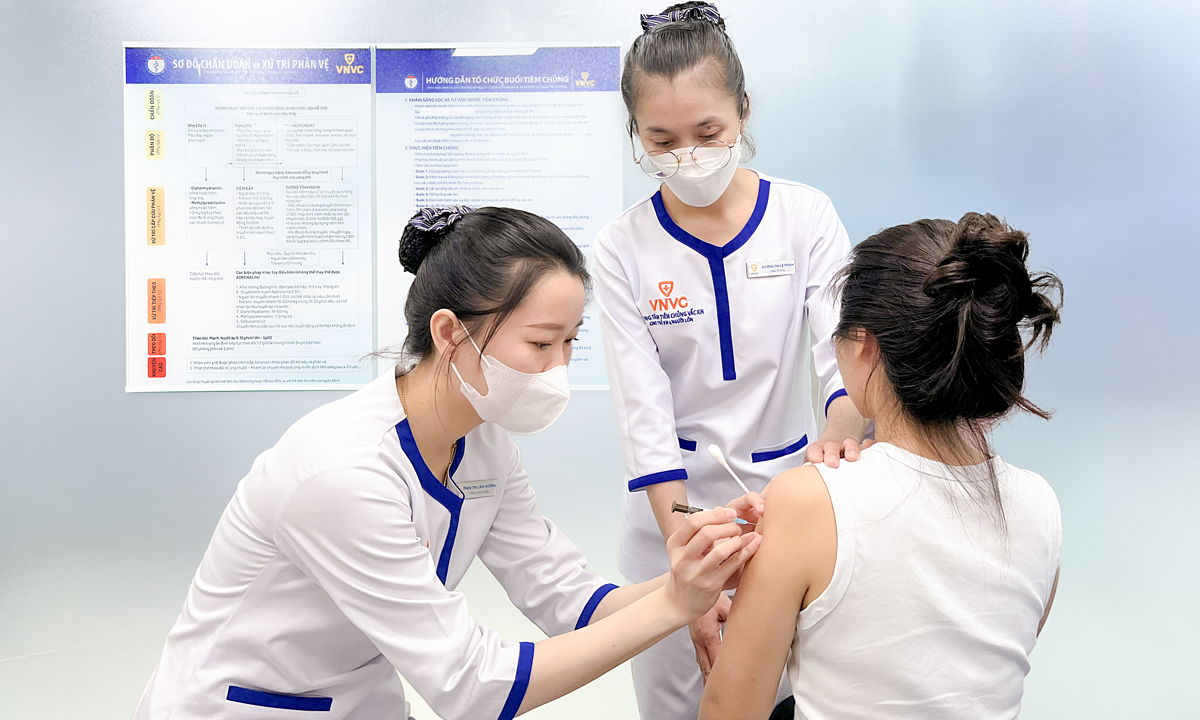 |
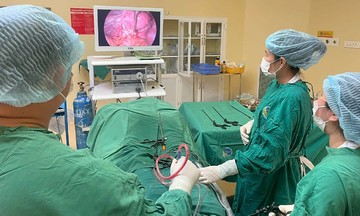
Adults receive vaccines against cancers caused by the HPV virus. Photo: Dieu Thuan.* |
Vaccines that help prevent disease
One strategy for preventing liver cancer and other diseases caused by hepatitis viruses is vaccination. Currently, there is no vaccine for hepatitis C, but there is one for hepatitis B, such as the 5-in-1 and 6-in-1 vaccines for children; Heberbiovac HB (Cuba), Gene Hbvax (Vietnam), and Twinrix (Belgium) prevent hepatitis A and B for children and adults.
Adults should get tested for hepatitis B before getting a booster shot, which is administered when antibodies decrease. Children should be vaccinated within 24 hours of birth, followed by the 5-in-1 or 6-in-1 vaccination schedule.
For HPV, Vietnam currently has two vaccines: Gardasil and Gardasil 9. Gardasil protects against 4 types (6, 11, 16, and 18) and is indicated for females aged 9-26. Gardasil 9 protects against 9 types (6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58) and is indicated for males and females aged 9-45, with over 90% efficacy. The 9-14 age group receives two doses at least six months apart. Those aged 15-45 receive three doses within six months. Individuals who miss or are late for their scheduled vaccination do not need to restart the series but will continue with the appropriate schedule.
In addition to vaccines, to avoid cancer, people should adopt a healthy lifestyle, limit alcohol and tobacco use, maintain good oral hygiene, practice safe sex, and avoid sharing personal items.
Thao Nguyen