|
The BXL.01 UAV, designed and manufactured by Z131 Factory, General Department of Defense Industry, is a suicide UAV carrying a shaped-charge warhead capable of destroying stationary targets with armor thickness under 250 mm. It has a maximum takeoff weight of 10 kg, carries a 1.2 kg warhead, a service ceiling of 1,000 m, a flight speed of 100-120 km/h, and an operational range of 10 km. |
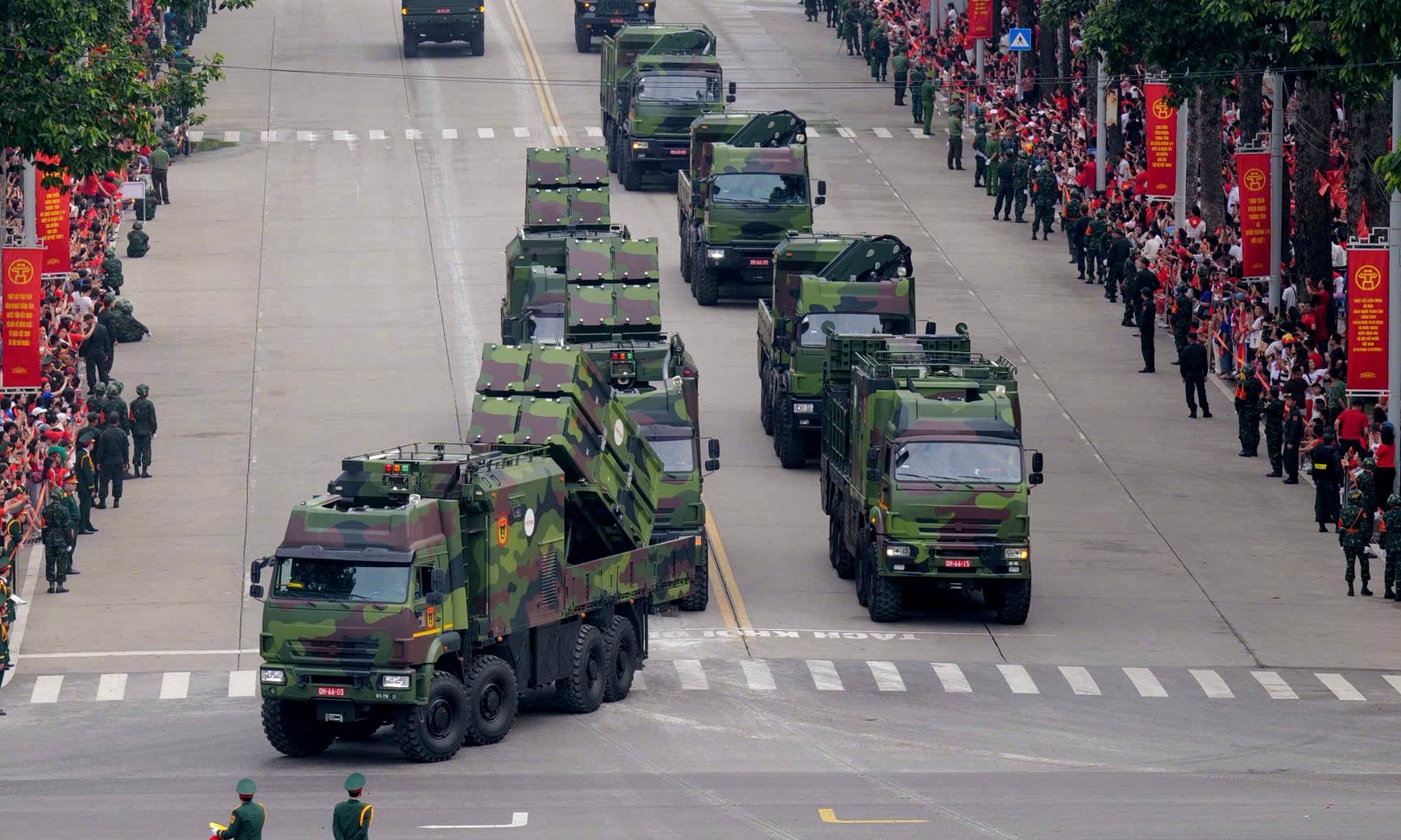
Over 16,000 personnel from the army, air force, navy, and mechanized units participated in the air, sea, and ground parade on 2/9, commemorating the 80th anniversary of Vietnam's National Day.
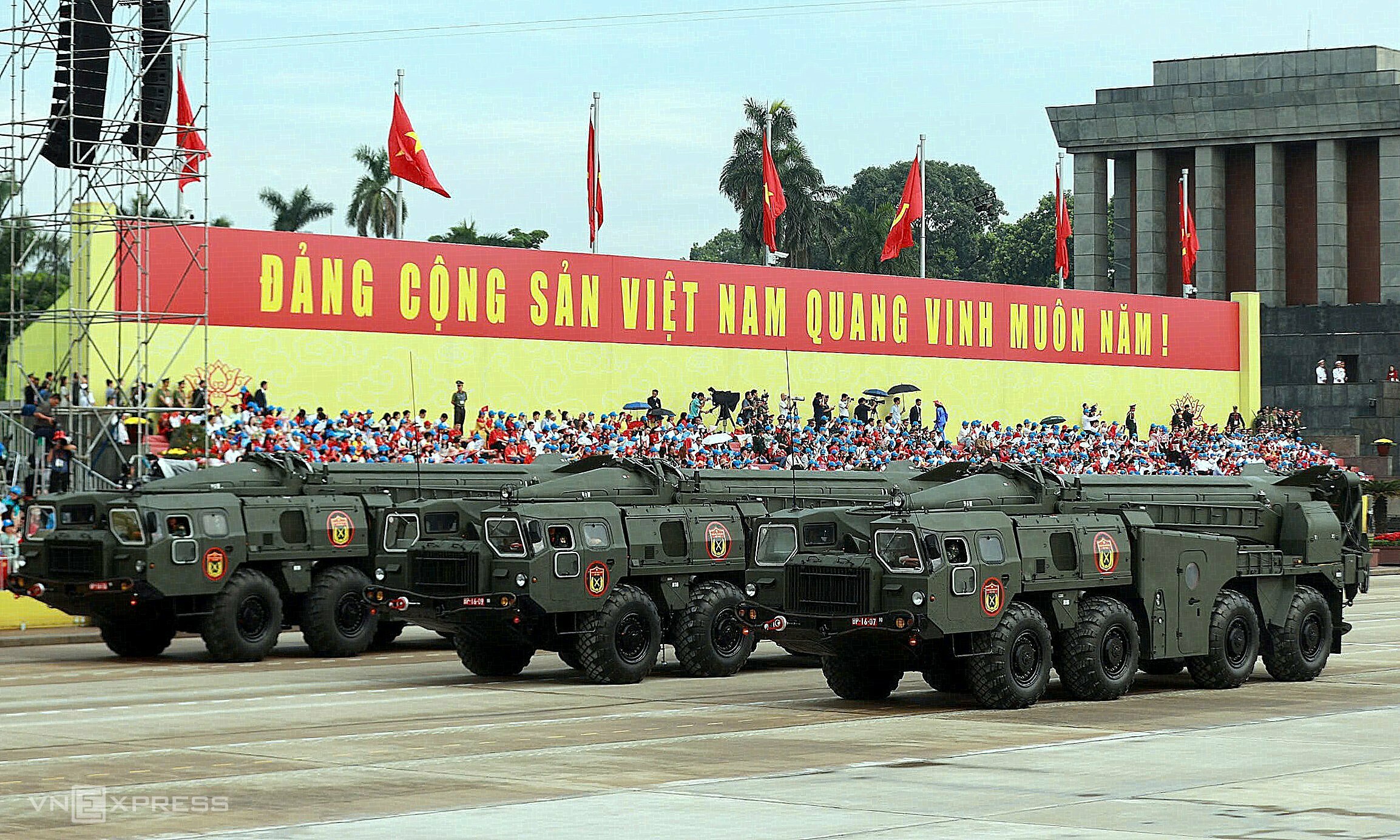
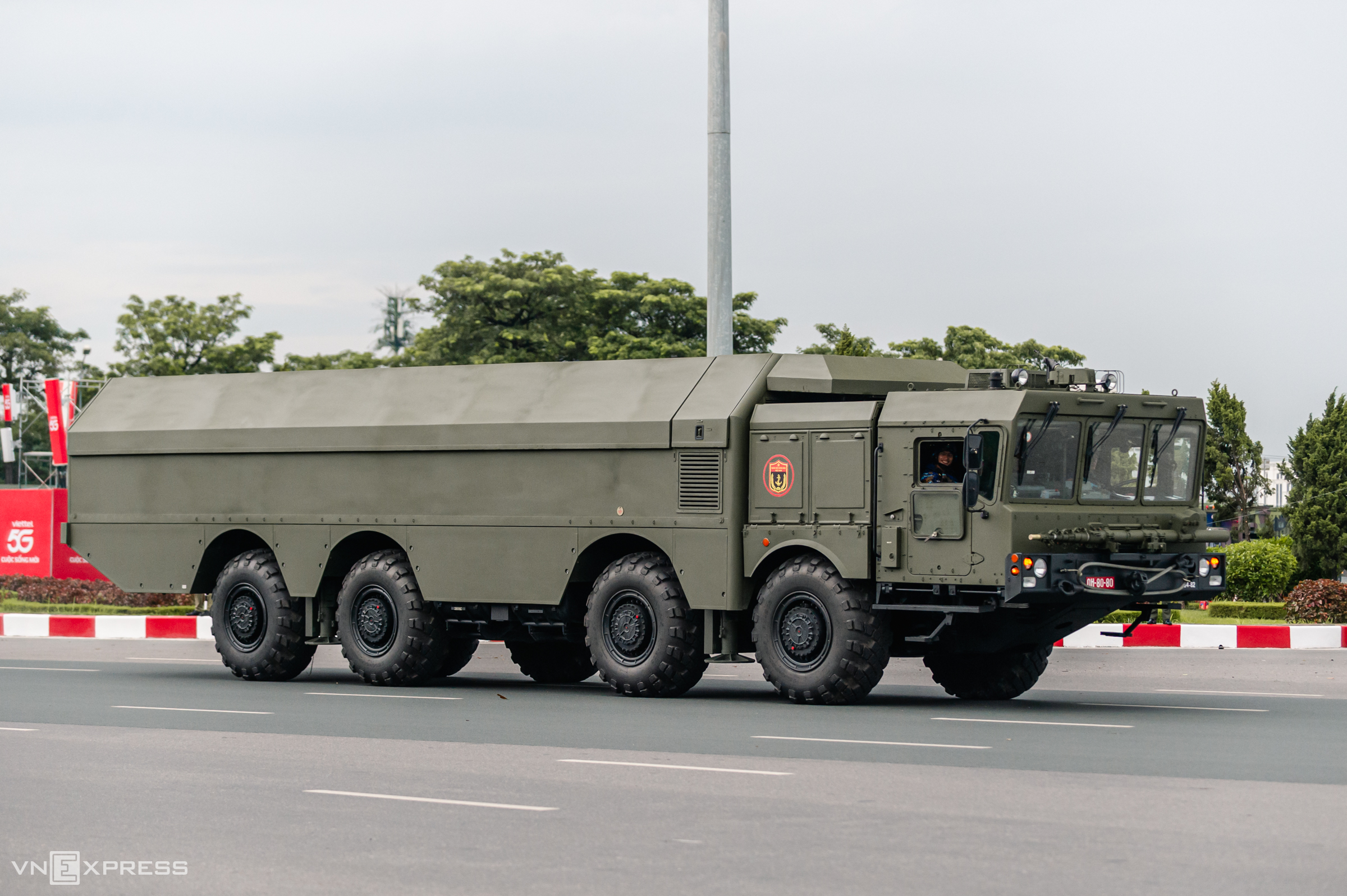
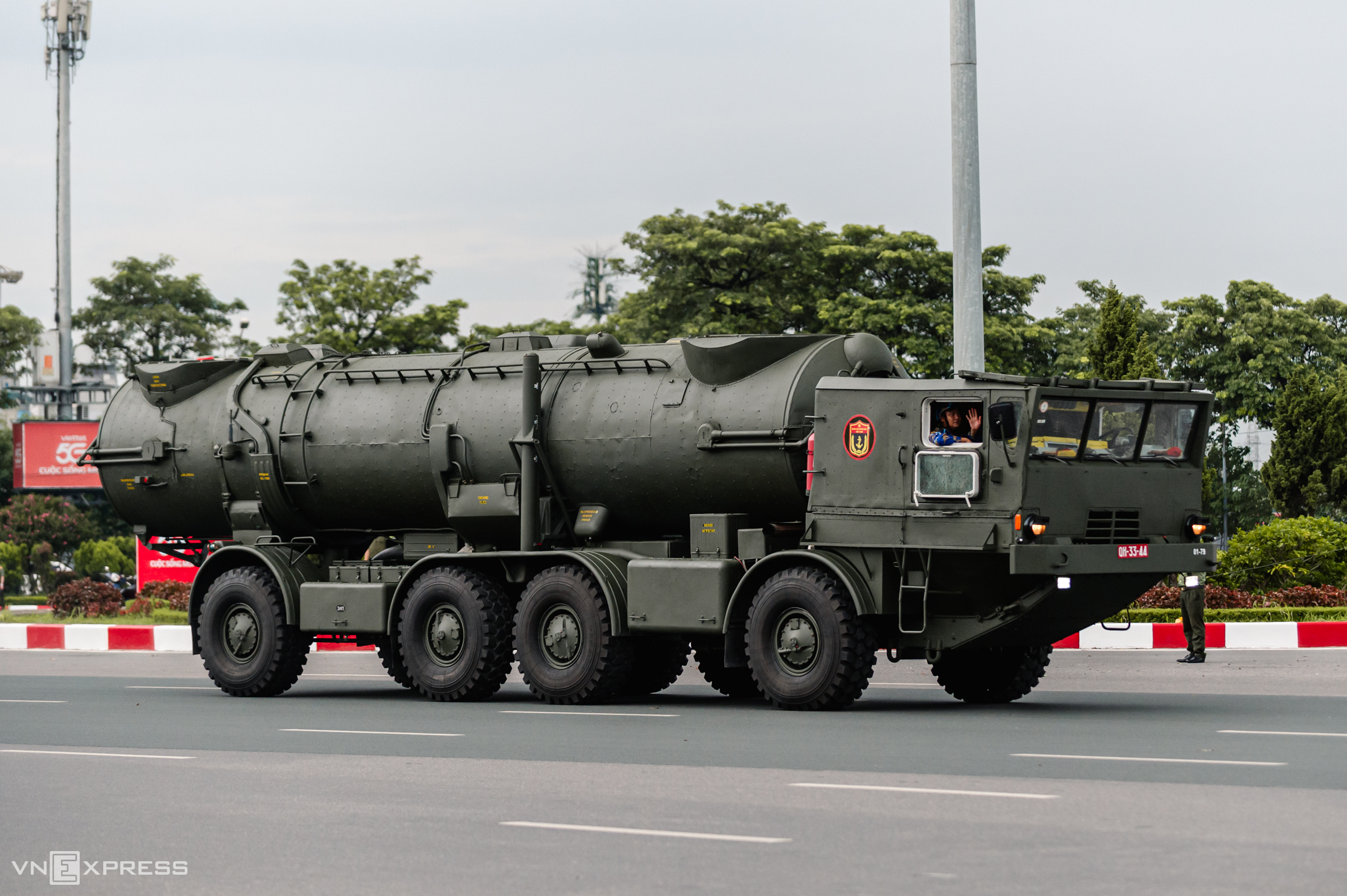
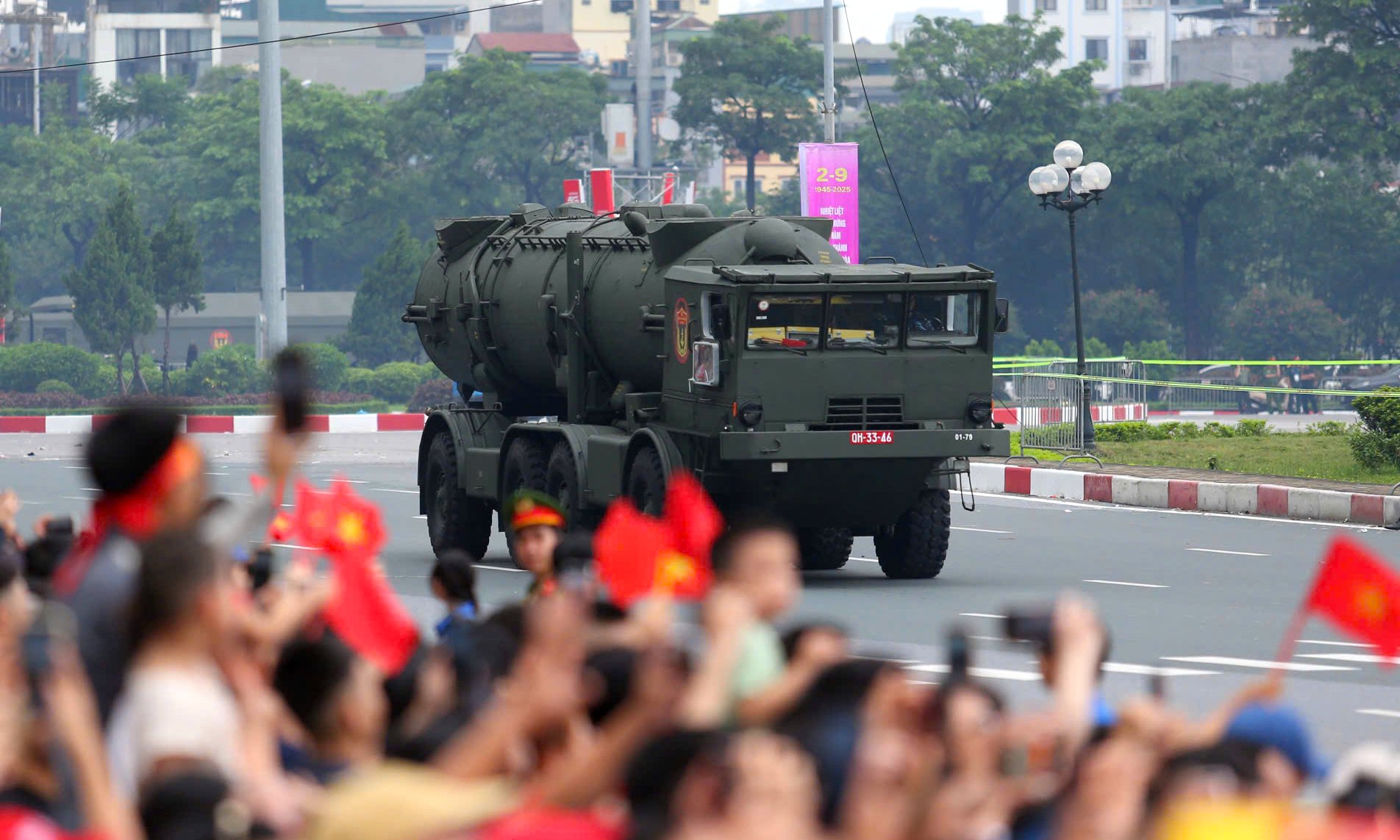
The photo shows a transporter erector launcher (TEL) of the R-17E ballistic missile system passing the reviewing stand on the morning of 2/9.
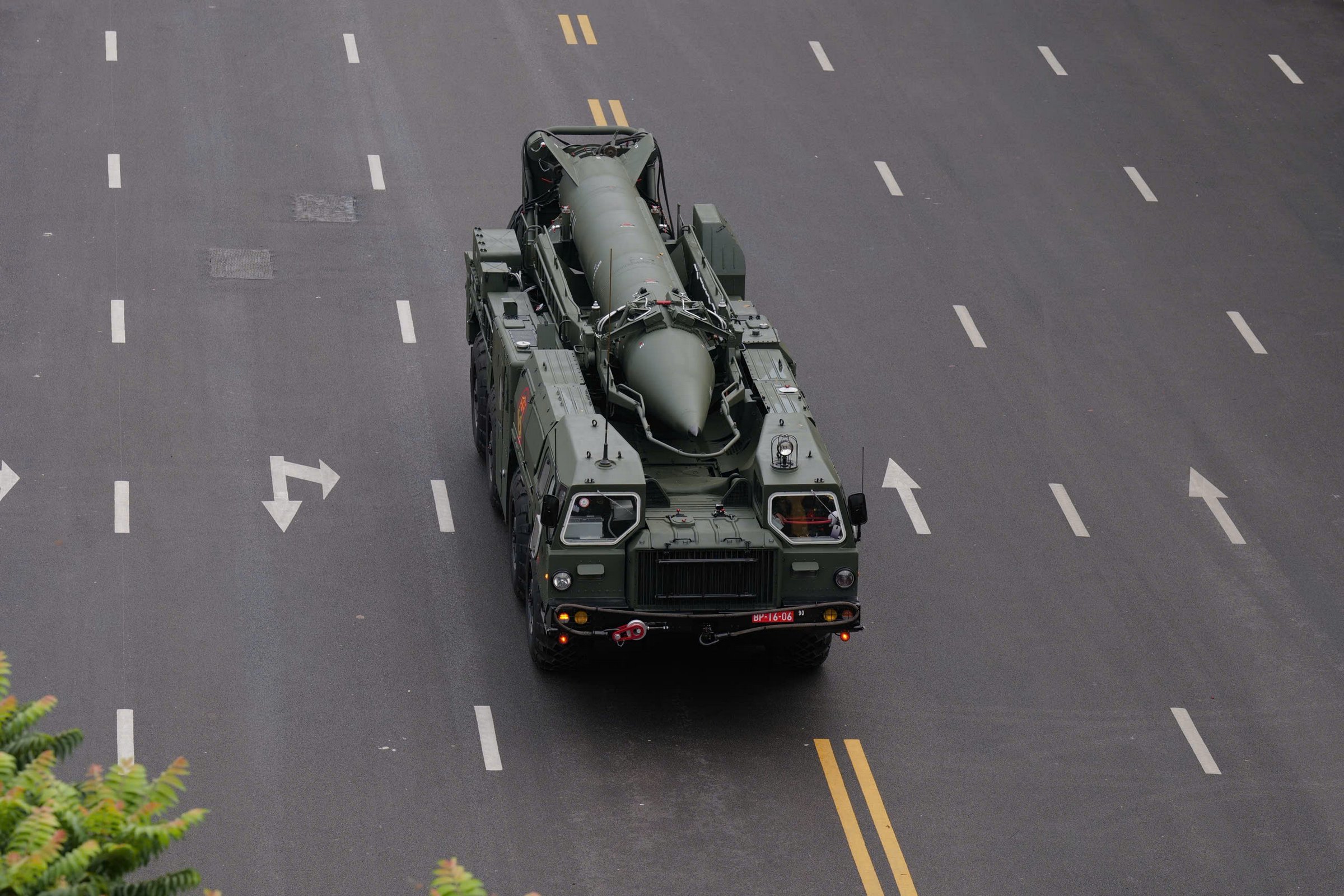 |
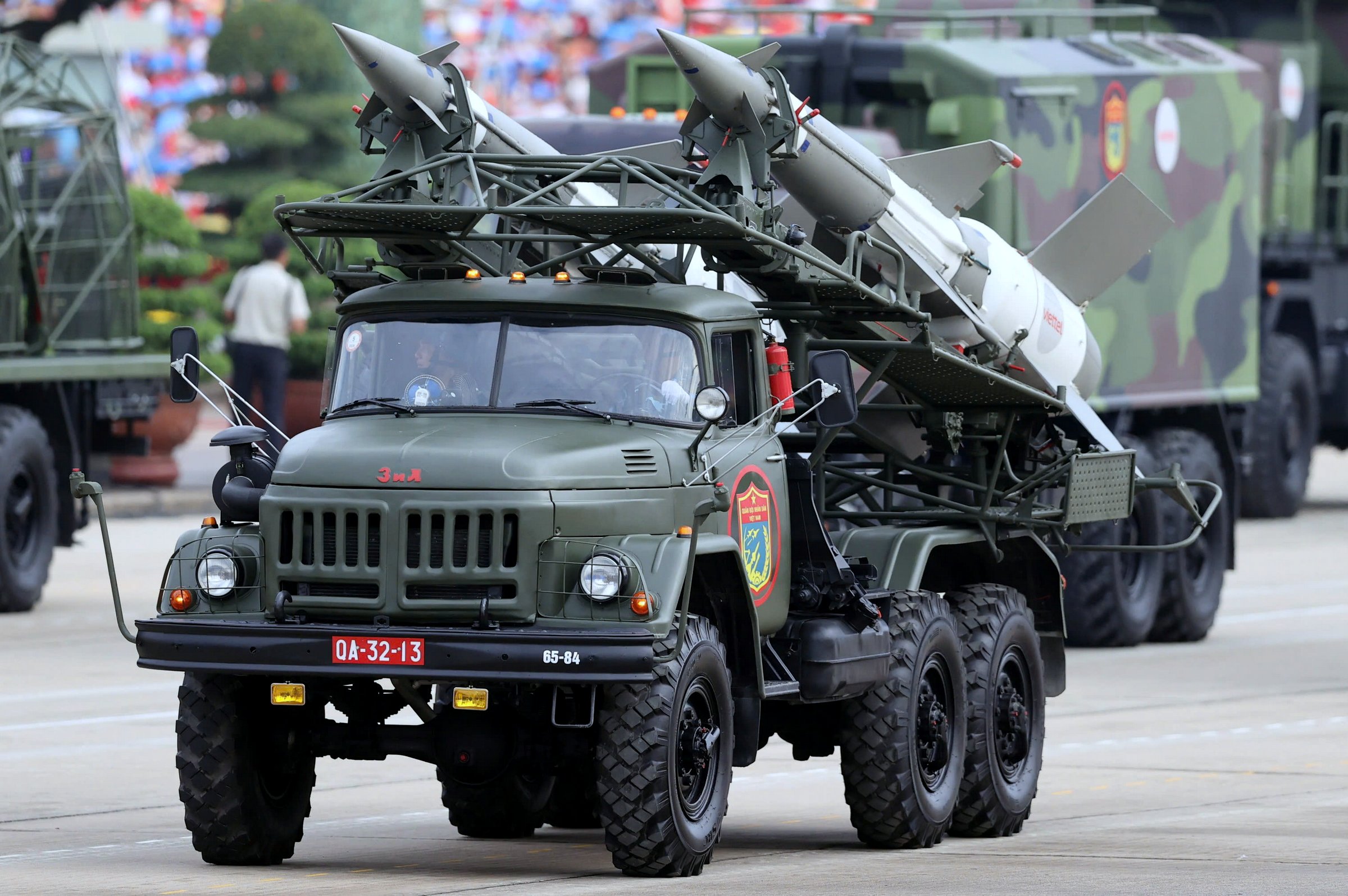
The R-17E tactical ballistic missile is the export variant of the R-17 Elbrus, designated Scud-B by NATO. Developed by the Soviet Union in the 1970s, the R-17 has a maximum range of 300 km and carries a warhead weighing approximately one ton.
Vietnam incorporated the Scud-B system into its long-range strategic ground forces in the 1980s, making it the first Southeast Asian nation to possess ballistic missiles. Indonesia has since acquired the Turkish-developed KHAN missile with a range of 280 km.
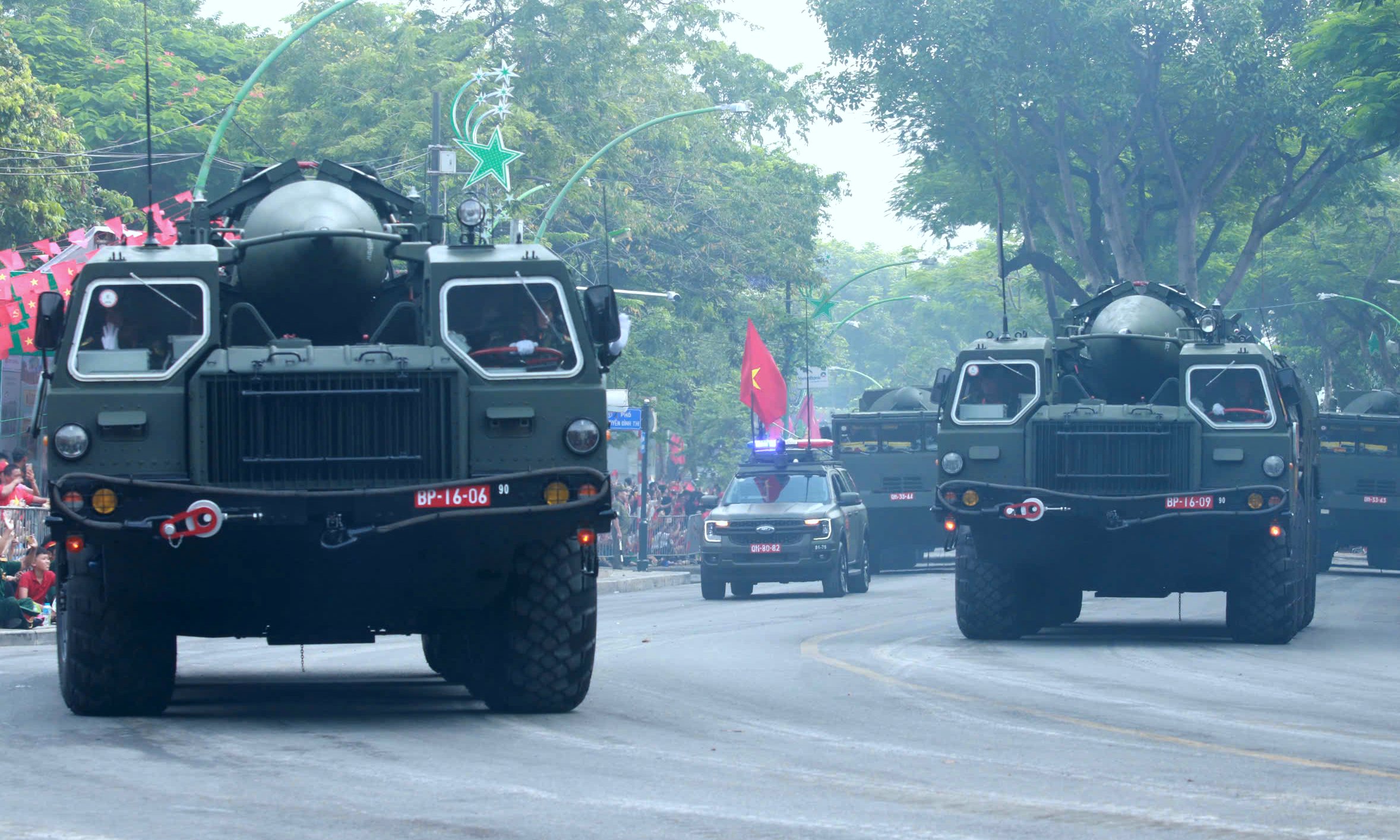 |
Vietnam first unveiled the Scud-B system in December 2019 during the 30th anniversary of National Defense Day and the 75th anniversary of the Vietnam People's Army. The A80 event marked the system's first appearance in a parade.
The photo shows Scud-B TELs moving at the end of Thanh Nien Road on the morning of 2/9.
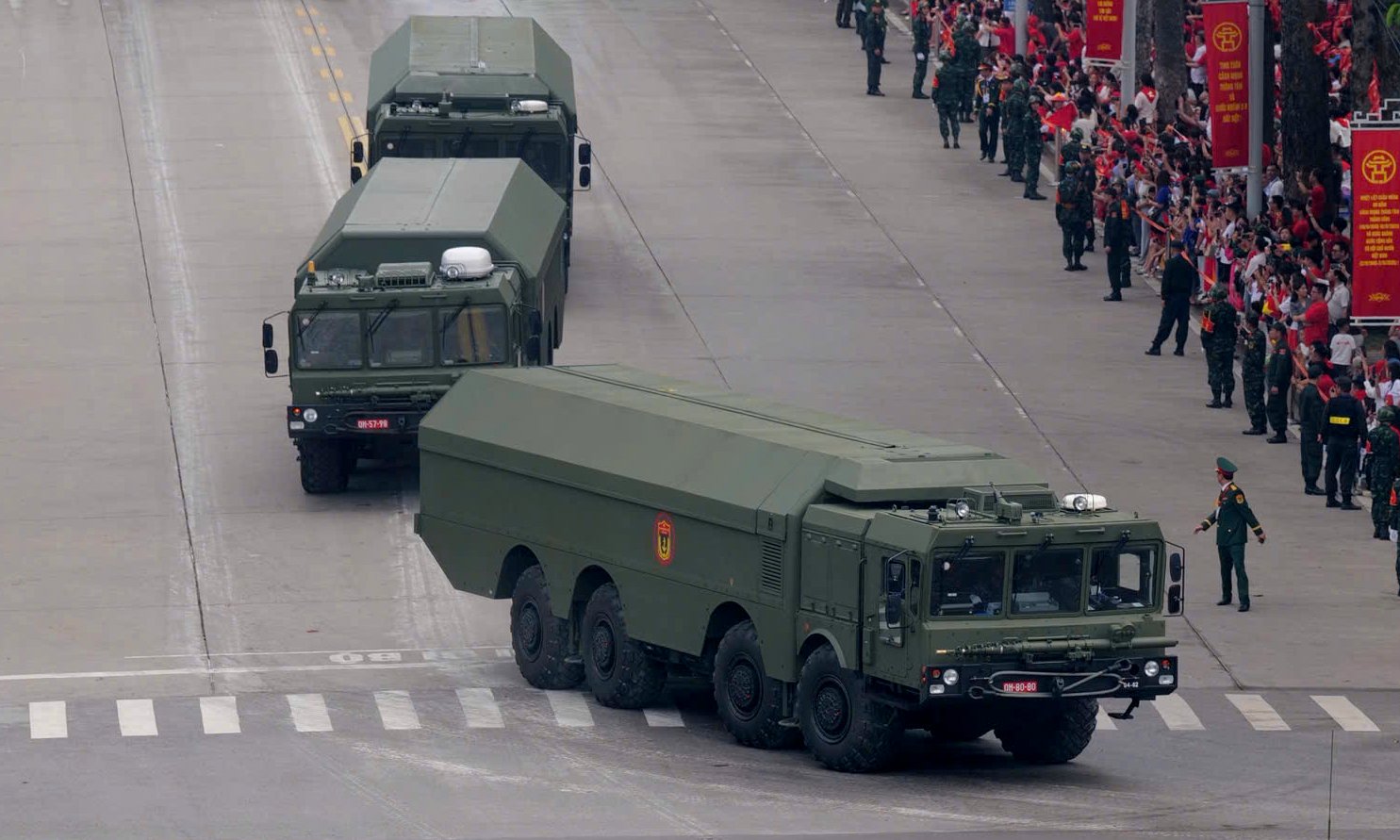 |
TELs of the K-300P Bastion-P coastal defense missile system are seen moving at the end of Hung Vuong Road. Developed by Russia and in service since 2011, the Bastion-P has only been exported to Vietnam and Syria. It's considered one of the most modern and powerful coastal missile systems in the world.
Each system typically includes one or two command vehicles, a support vehicle, 4 TELs, and 4 reloading vehicles. The launchers can be positioned up to 25 km from the command post to minimize the risk of detection and damage during enemy attacks.
The Bastion-P can transition from travel to combat-ready mode in 5 minutes, firing missiles at intervals of 2 to 5 seconds.
 |
Each TEL carries two P-800 Oniks supersonic missiles with a range of 600-800 km, while the export variant, Yakhont, has a maximum range of 120-300 km depending on the flight altitude. The Oniks missile is equipped with a 300 kg warhead, while the Yakhont carries a 200 kg warhead. Both Oniks and Yakhont missiles reach a cruising speed of 3,200 km/h, which is 2.9 times the speed of sound.
The Bastion-P's primary mission is coastal defense, engaging surface vessels such as carrier strike groups, transport ships, and landing ships. It can also strike ground targets.
The P-800 is equipped with inertial guidance and activates an active radar seeker in the terminal phase to home in on the target. For ground attacks, it can use the GLONASS satellite navigation system to strike pre-determined coordinates or use radar to acquire targets with high contrast against the surrounding environment.
 |
A TEL of the 4K44 Redut-M coastal missile system is seen at the F1 racetrack.
Developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War, the Redut-M's missiles are still in service with Russia as part of the Utyos system. Vietnam received the Redut-M system along with dozens of missiles in 1980. The entire system is currently assigned to the 679th Brigade of the 1st Naval Region.
The main components of the Redut-M system include the Skala-E ground control station, a command post, and 3 TELs, each carrying one missile in a launch tube. All components are mounted on wheeled chassis for increased mobility.
 |
The P-28 missile of the Redut-M system has a range of 300 km, a maximum altitude of 7 km, and a speed of nearly 1,400 km/h. In a salvo launch, one missile can fly at a higher altitude for target acquisition and share data with lower-flying missiles.
During the terminal phase, the P-28 descends to an altitude of 25-100 m to evade air defense radar, minimizing reaction time and the enemy's interception capabilities. The missile carries a 560 kg warhead, capable of destroying various warships, including aircraft carriers and heavy landing ships, if it hits its target.
 |
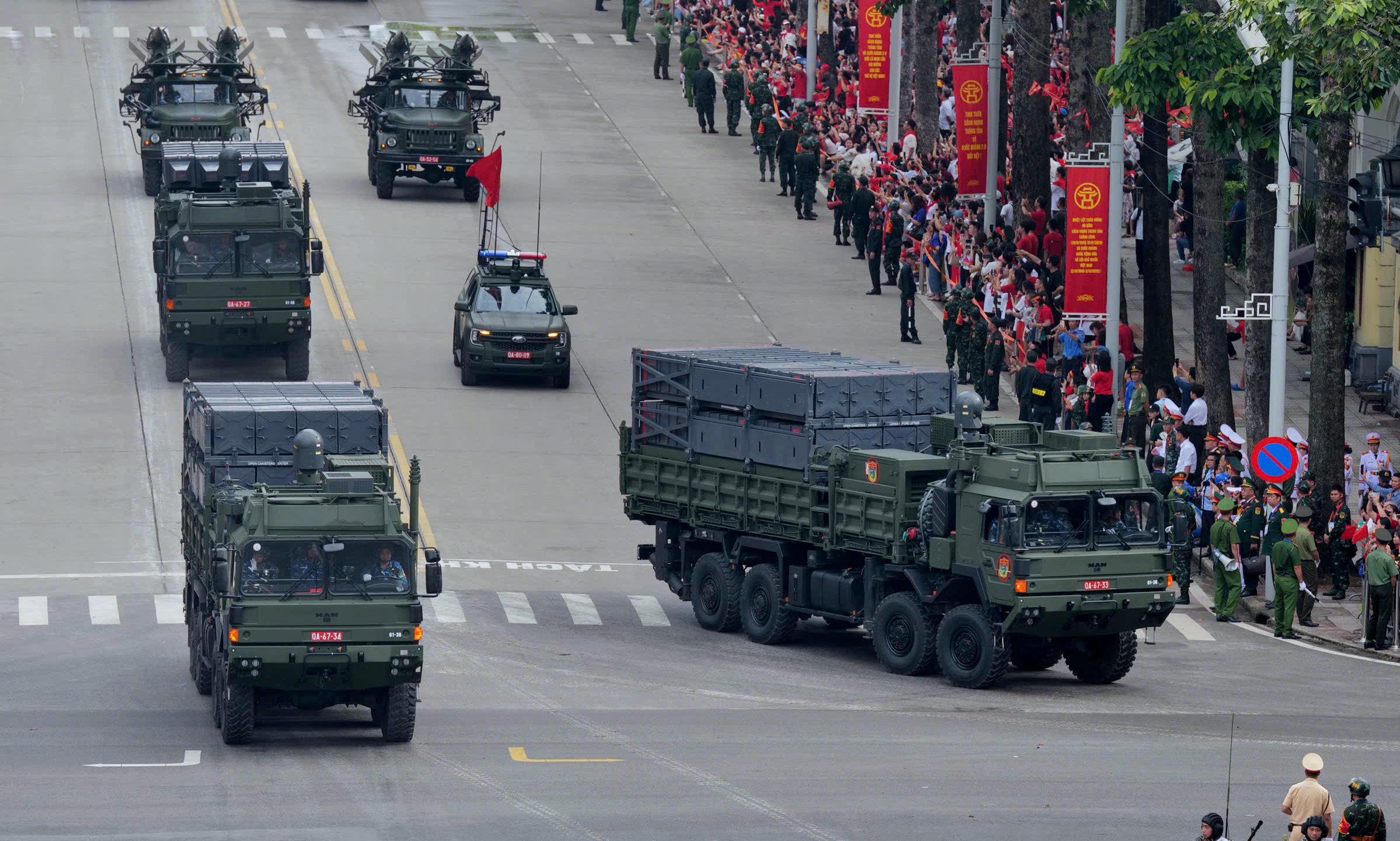
Radar and TEL vehicles of the Truong Son anti-ship and land-attack missile system, developed by Vietnam, are displayed. The system uses the Song Hong missile with a range of approximately 80 km, flying low and following the wave tops in the final phase to evade enemy defenses.
Each Truong Son system includes a command vehicle that can control 8 launchers with up to 32 missiles ready for combat, a fire control radar, transport vehicles, and reloading vehicles. The Truong Son radar has a range of about 200 km.
 |
The SPYDER-MR (front) medium-range and SPYDER-SR short-range air defense systems, developed by Israel and introduced in 2005, can be mounted on various wheeled chassis, including the RMMV HX with a top speed of 100 km/h and a range of up to 800 km.
Both versions use the same type of missile, but the SPYDER-MR missiles have a booster stage for increased range. The ready-to-fire missile count on each SPYDER-MR launcher is also doubled compared to the SPYDER-SR, from 4 to 8 missiles.
The SPYDER-MR version uses the Python-5 infrared-guided missile with a range of 40 km and a ceiling of 9,000 m, along with the radar-guided Derby missile with a range of 80 km and a ceiling of 16,000 m.
The SPYDER system utilizes the EL/M-2084 multi-role active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar, capable of detecting targets at a distance of 250 km and processing up to 1,200 targets in air surveillance mode.
 |
Reloading vehicles for the S-125-VT system pass the reviewing stand.
The S-125 medium-range air defense system was developed by the Soviet Union to complement the S-75 Dvina and S-25 Berkut missiles. The original S-125 used the V-600 missile weighing over 950 kg with a 60 kg warhead, a range of 35 km, and a ceiling of 18,000 m.
The S-125-VT has been upgraded to improve hit probability and significantly reduce deployment and recovery time to 20 minutes, compared to 90 minutes for the original S-125.
The UNV-VT radar of the S-125-VT has been significantly improved, enabling operation in high-intensity electronic warfare environments with a range of up to 90 km. The S-125-VT also includes an electro-optical sensor system for detecting and locking onto low-flying targets when the radar is completely jammed.
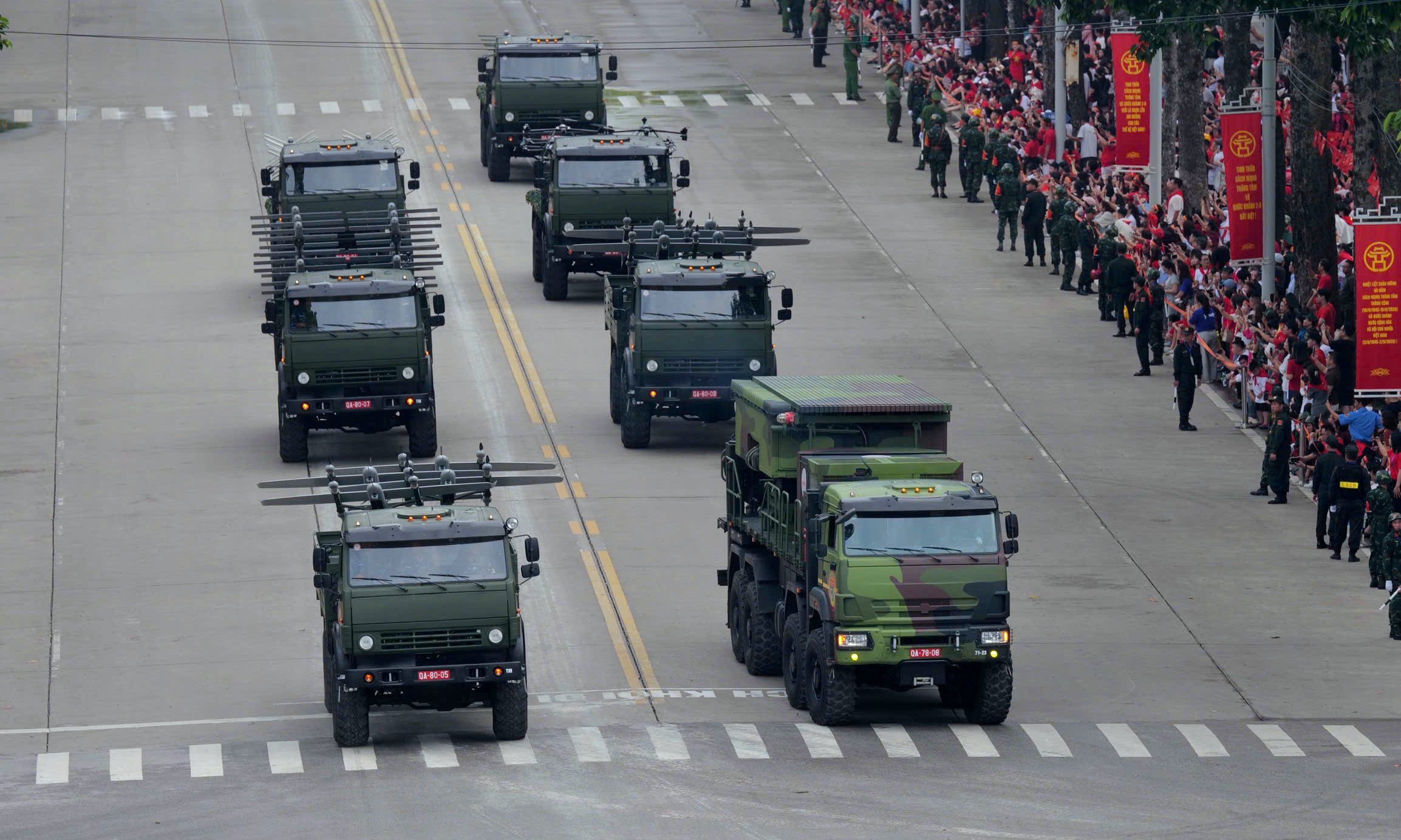 |
A group of domestically developed and manufactured unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), led by a command vehicle, is showcased.
The products manufactured by Viettel include reconnaissance UAVs capable of operating day and night with high-precision target detection and identification, and tactical combat UAVs capable of attacking ground targets such as infantry and light armored vehicles.
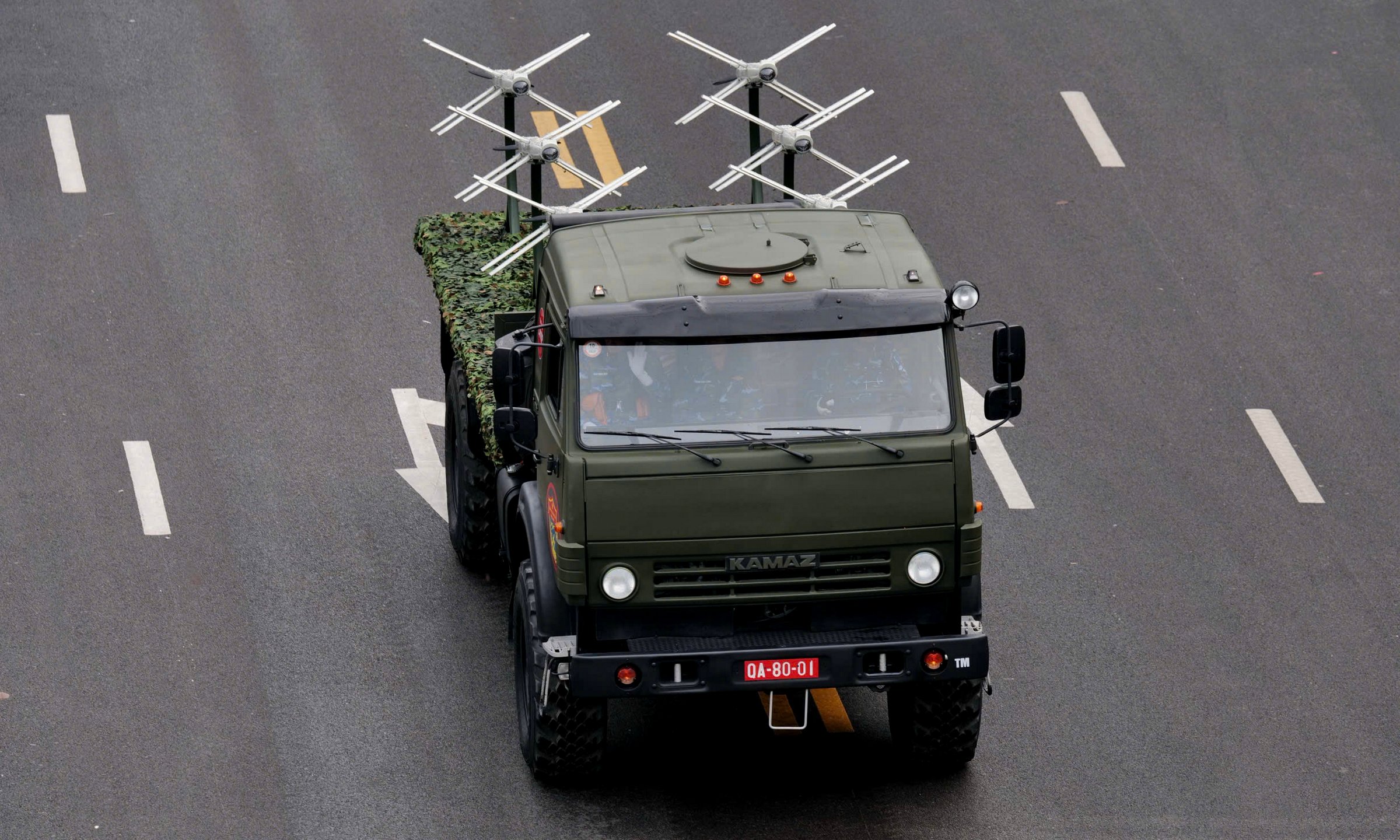 |
Photo: Ngoc Thanh - Duc Dong - Pham Chieu - Vo Hai