Headaches are a common neurological symptom, affecting people of all ages. The pain can be diffuse or localized, dull or severe, lasting for a few minutes or several days. It can occur in episodes or be continuous, affecting the head and face.
Dr. Nguyen Huu Khanh, from the Department of Neurology at Tam Anh General Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City, explains that non-serious headaches usually improve with rest. However, in some cases, headaches can be a warning sign of dangerous conditions like brain aneurysms, strokes, brain tumors, or meningitis. These require prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. Dr. Khanh highlights the following warning signs.
Sudden and severe headaches: A sudden, severe headache, described as a "thunderclap" and reaching its peak within seconds or minutes, could indicate a subarachnoid hemorrhage, ruptured brain aneurysm, or stroke. These headaches are often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, altered consciousness, and potentially coma if not treated promptly.
Persistent, unrelieved headaches: A dull or throbbing headache lasting for days and unresponsive to pain medication may signal a brain tumor, temporal arteritis, or a chronic disorder of the central nervous system. Headaches that occur regularly at night or when lying down could indicate increased intracranial pressure.
Headaches with fever, stiff neck, or rash: According to Dr. Khanh, a headache accompanied by high fever, stiff neck, sensitivity to light, nausea, and rash often suggests meningitis or a central nervous system infection. These conditions require hospitalization and prompt treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent serious neurological complications.
Headaches after trauma: If you experience a headache after a traffic accident, fall, or any significant head injury, even if the headache appears hours or days later, seek immediate medical attention. This could indicate a subdural hematoma, brain hemorrhage, or closed head injury, requiring a CT or MRI scan for assessment.
Headaches with other neurological symptoms: Headaches accompanied by numbness or weakness in the limbs, loss of balance, dizziness, difficulty speaking, or vision changes such as double vision, blurred vision, or blind spots, warn of potential damage to the motor or visual areas of the brain. These symptoms are often associated with strokes, brain tumors, or central nervous system disorders.
To accurately diagnose the cause of a headache, doctors may order imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to detect brain or blood vessel damage, Doppler ultrasound, or EEG. For chronic migraines or neurological disorders, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is often recommended. TMS uses magnetic pulses to regulate brain activity in pain-related areas, helping to alleviate headaches.
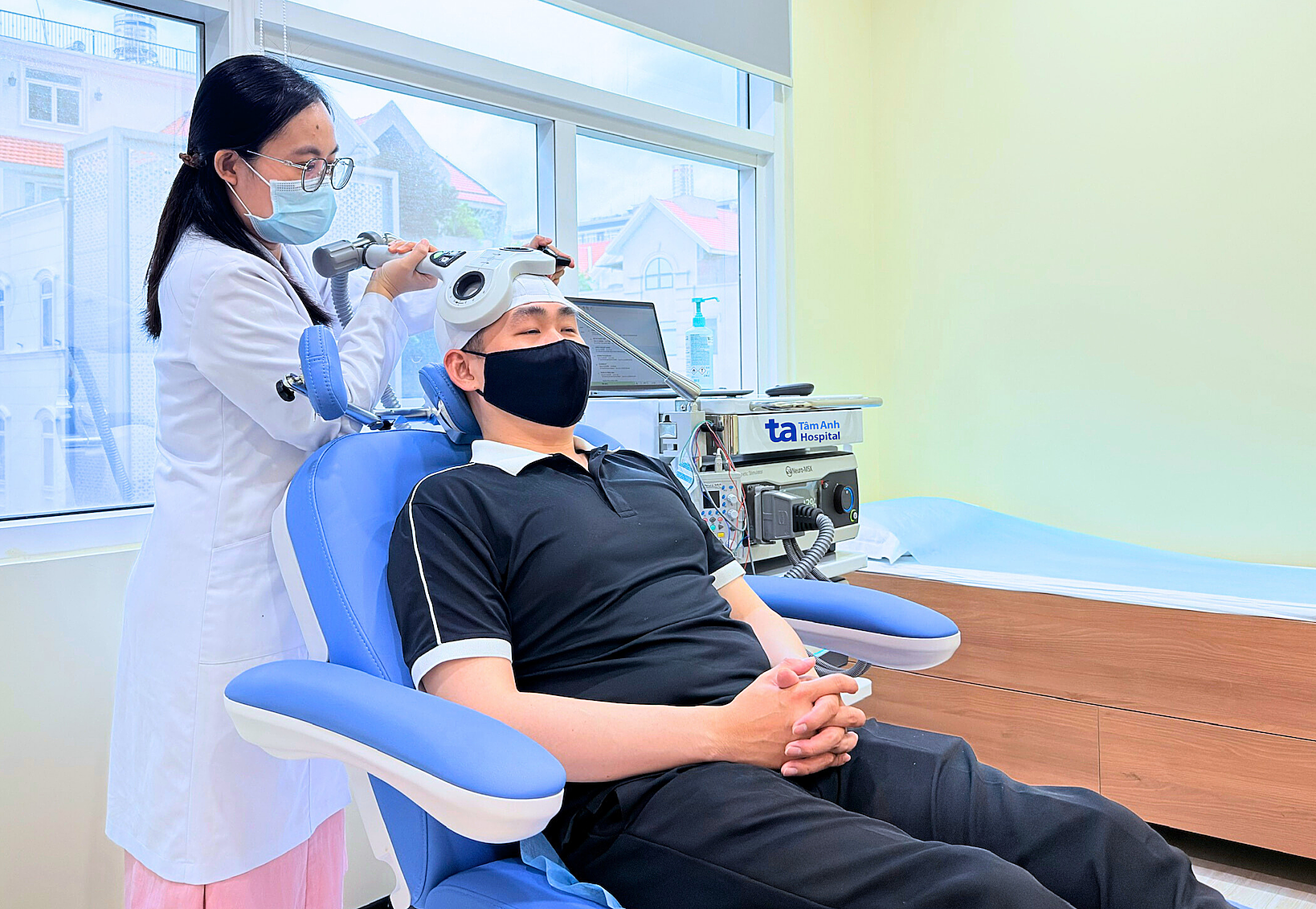 |
A patient undergoing transcranial magnetic stimulation for headache treatment. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
A patient undergoing transcranial magnetic stimulation for headache treatment. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
Dr. Khanh advises against prolonged use of pain relievers, as this can lead to medication overuse headaches, tolerance, and potential damage to the liver, kidneys, and nervous system. Effective headache treatment relies on accurate diagnosis, combined with lifestyle adjustments, physical therapy, psychotherapy, or medication prescribed by a doctor.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, getting enough sleep, reducing stress, limiting alcohol consumption, and regularly monitoring blood pressure are recommended. Older adults or those with chronic underlying conditions should manage their conditions to prevent dangerous neurological complications.
Phuong Thy
| Readers can submit questions about neurological conditions here for expert answers. |