The incidence of kidney disease is increasing due to neglected warning symptoms, infrequent health check-ups, and unhealthy lifestyles, according to Doctor of Medicine II Ho Tan Thong, from the Nephrology - Dialysis Unit at Tam Anh General Clinic District 7. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for preventing severe progression that could necessitate dialysis. Below are seven key indicators of weakened kidneys, often appearing with advanced kidney disease.
Changes in urination habits and foamy urine
The earliest warning signs of kidney damage include nocturia (frequent urination at night) and increased urination frequency and volume. These symptoms typically appear in the early stages of chronic kidney disease as the kidneys gradually lose their ability to concentrate urine. In advanced stages of acute kidney injury or end-stage chronic kidney failure, urine output may decrease, leading to oliguria or anuria.
Foamy urine also serves as an early warning sign of kidney disease, especially when the white foam is abundant, thick, and slow to dissipate, resembling soap suds, or when tiny, persistent bubbles appear. This can indicate the presence of protein in the urine (proteinuria). Dark urine, resembling black tea, also warrants attention.
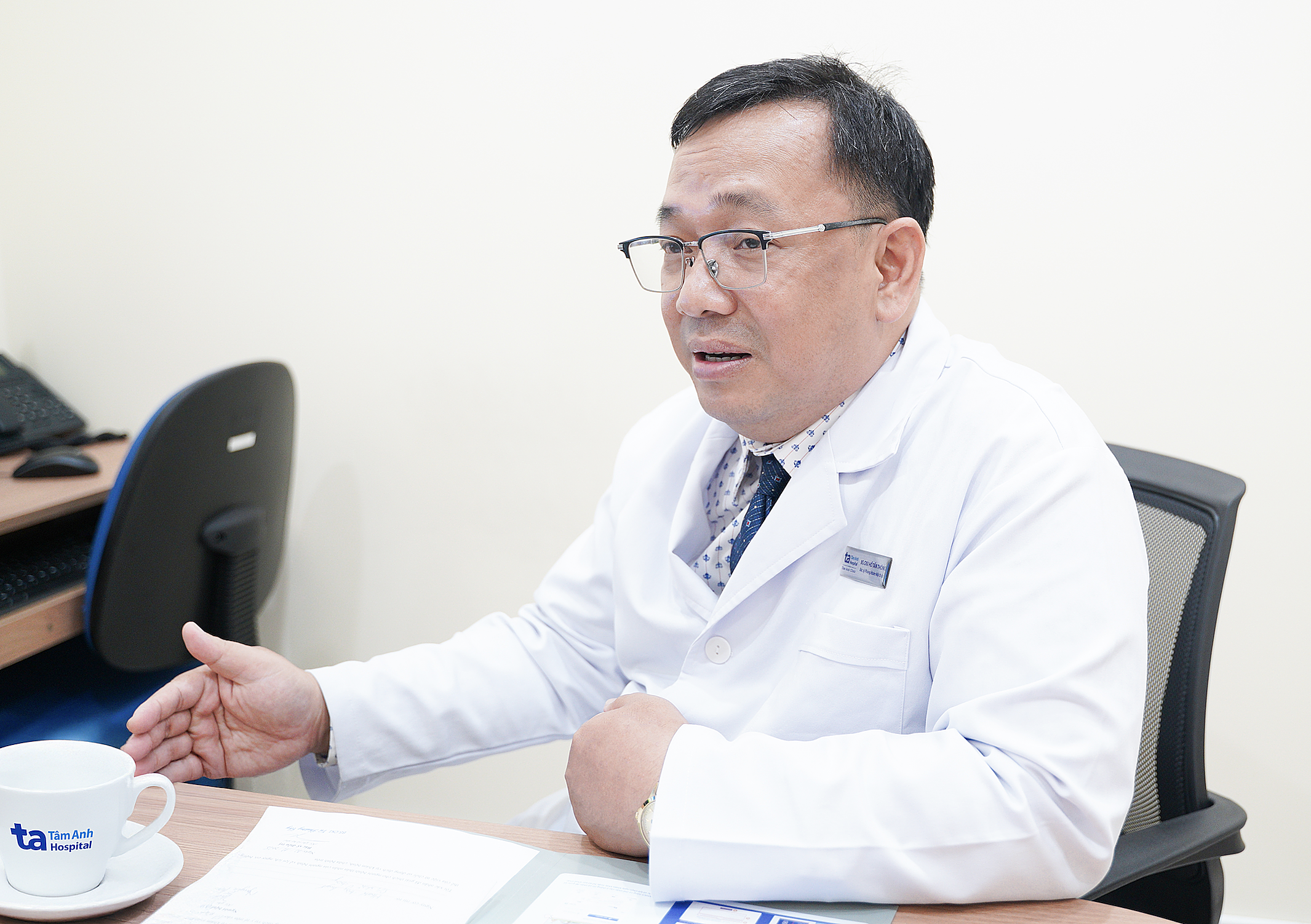 |
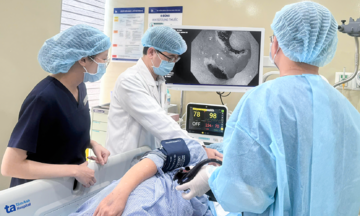
Doctor Thong advises a patient. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Prolonged, unexplained swelling
Swelling in the feet and ankles, making shoes feel tighter or leaving sock marks, can be a warning symptom of kidney disease. This is because the kidneys are responsible for regulating the body's salt balance; if this process is disrupted, it can cause edema (swelling). In more severe stages, patients may experience swelling around the face, eyes, neck, and abdomen, also known as generalized edema, due to the kidneys excreting too much protein.
Ammonia breath and metallic taste in mouth
Breath smelling like urine or ammonia, along with a metallic taste in the mouth causing loss of appetite and weight loss, indicates advanced kidney disease. However, this sign is often overlooked as patients may confuse it with bad breath.
Skin color changes
Kidney dysfunction can lead to changes in skin pigmentation because the kidneys fail to properly filter out toxins, causing an accumulation of toxins or certain electrolytes.
Unusual fatigue and sleep apnea
The kidneys are responsible for producing erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells. When kidney function declines, erythropoietin levels decrease, leading to insufficient red blood cell production and resulting in anemia due to kidney failure, which causes unusual fatigue — a common condition in chronic kidney disease.
If the body accumulates too much fluid, failing to excrete water and salt, it can lead to fluid retention and swelling, narrowing the airway during sleep. Consequently, some individuals with chronic kidney disease are prone to sleep apnea, manifesting as loud snoring, interrupted breathing, restless sleep, and daytime fatigue.
Rashes and itchy skin
When kidneys fail, excess toxins and electrolytes accumulate in the blood, causing skin irritation, leading to persistent itching and rashes. Patients may scratch continuously, even to the point of skin abrasions and tears.
Uncontrolled high blood pressure
The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating blood pressure by balancing salt and water and through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). When the kidneys are damaged, their ability to excrete salt and water decreases, and this hormonal system functions abnormally, leading to elevated blood pressure.
Doctor Thong emphasizes that patients with mild kidney disease often have no symptoms or easily confuse them with other conditions. Therefore, regular kidney function checks can help detect kidney disease early and ensure timely treatment.
Ha Thanh