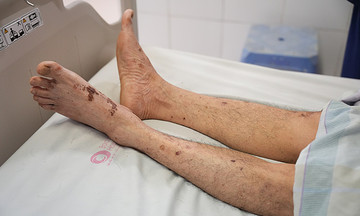
The Chikungunya virus, part of the alphavirus genus in the Togaviridae family, causes Chikungunya fever. This infectious disease can lead to high fever, severe joint pain, rash, fatigue, and even multiple organ failure and death. Typically transmitted through mosquito bites, it's usually found in tropical regions like South America and India. However, climate change is altering its epidemiology.
On 8/7, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) reported that this year's Chikungunya outbreak in France started earlier than usual, indicating increased mosquito breeding in the area. France has recorded 8 cases in various locations. Authorities are urging residents and visitors to take precautions against mosquito bites to limit the spread of this and other mosquito-borne diseases.
This warning comes just weeks after the UK suspended the use of a newly approved Chikungunya vaccine for people over 65, following two deaths and 21 serious adverse reactions.
Beyond Chikungunya, Europe has seen an alarming increase in other mosquito-borne illnesses. For example, dengue fever cases this year reached 304, double the number in 2023 and four times the 2022 figure.
West Nile virus, another mosquito-borne illness, has also appeared in the UK this year. In 2024, Europe reported 1,436 cases across 212 areas in 19 countries, a significant rise from 713 cases in 123 areas in 2023.
The ECDC recommends preventative measures for travelers, such as using mosquito repellent on exposed skin, wearing long sleeves and pants during peak mosquito hours (early morning and evening), and sleeping under mosquito nets or in air-conditioned rooms whenever possible.
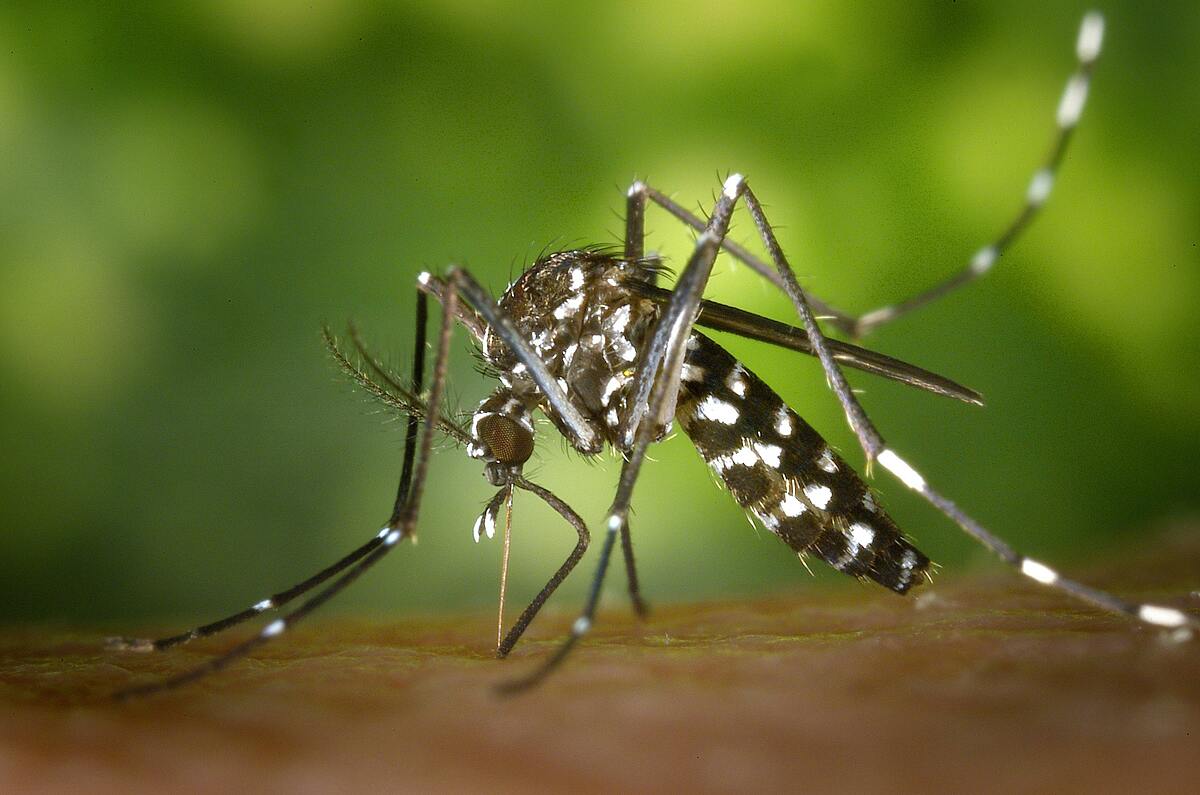 |
Tiger mosquitoes can transmit various diseases. Photo: Pexel. |
Tiger mosquitoes can transmit various diseases. Photo: Pexel.
In France, public health agencies are advising people to eliminate mosquito breeding grounds. This includes covering or emptying standing water in containers. Belgium has issued similar warnings after observing an increase in tropical mosquitoes.
Experts explain that most mosquito-borne diseases aren't directly transmitted between people. However, an infected person can be bitten by a mosquito, which then carries the disease to new areas, creating clusters of infection within communities and among travelers.
Thuc Linh (Daily Mail, Nature)