Liver enzymes are proteins produced by liver cells. Elevated enzyme levels indicate inflammation or damage to these cells, often signaling underlying liver conditions. Master, Doctor Doan Vinh Binh, from the Medical Information Center at Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, states that alongside medical treatments, an appropriate diet plays a crucial role in managing liver disease and stabilizing enzyme levels. The following outlines several food categories that individuals with elevated liver enzymes should avoid:
Alcohol consumption increases the liver's workload, forcing it to metabolize and eliminate alcohol and harmful chemicals. This process generates acetaldehyde, which damages liver cells, potentially leading to cirrhosis and cancer over time.
Foods rich in unhealthy fats, such as animal fat, red meat, butter, cheese, organ meats, poultry skin, and snack foods, contain high levels of saturated and trans fats. These can increase low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, disrupt blood lipid levels, promote fat accumulation, and stimulate inflammatory responses, thereby raising liver enzyme levels.
Foods and beverages high in sugar and refined starches, including candies, soft drinks, dried fruits, or sweet fruits like durian, ripe mango, longan, lychee, and jackfruit, increase blood sugar and contribute to excess energy storage in the body. This excess energy is converted into fat, which accumulates in the liver, exacerbating fatty liver inflammation and raising liver enzymes.
Raw or undercooked foods pose a risk of containing bacteria and parasites, such as toxoplasma, e.coli, listeria, salmonella, vibrio vulnificus, and tapeworms. Upon entering the body, these pathogens can travel through the bloodstream or digestive tract to the liver and bile ducts, causing prolonged inflammation, elevated liver enzymes, and impaired organ function.
Processed foods, including sausages, bacon, and instant noodles, often contain numerous preservatives, artificial colors, flavorings, and high levels of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. These substances increase the metabolic burden on the liver, producing toxins that cause inflammation and increase fat accumulation.
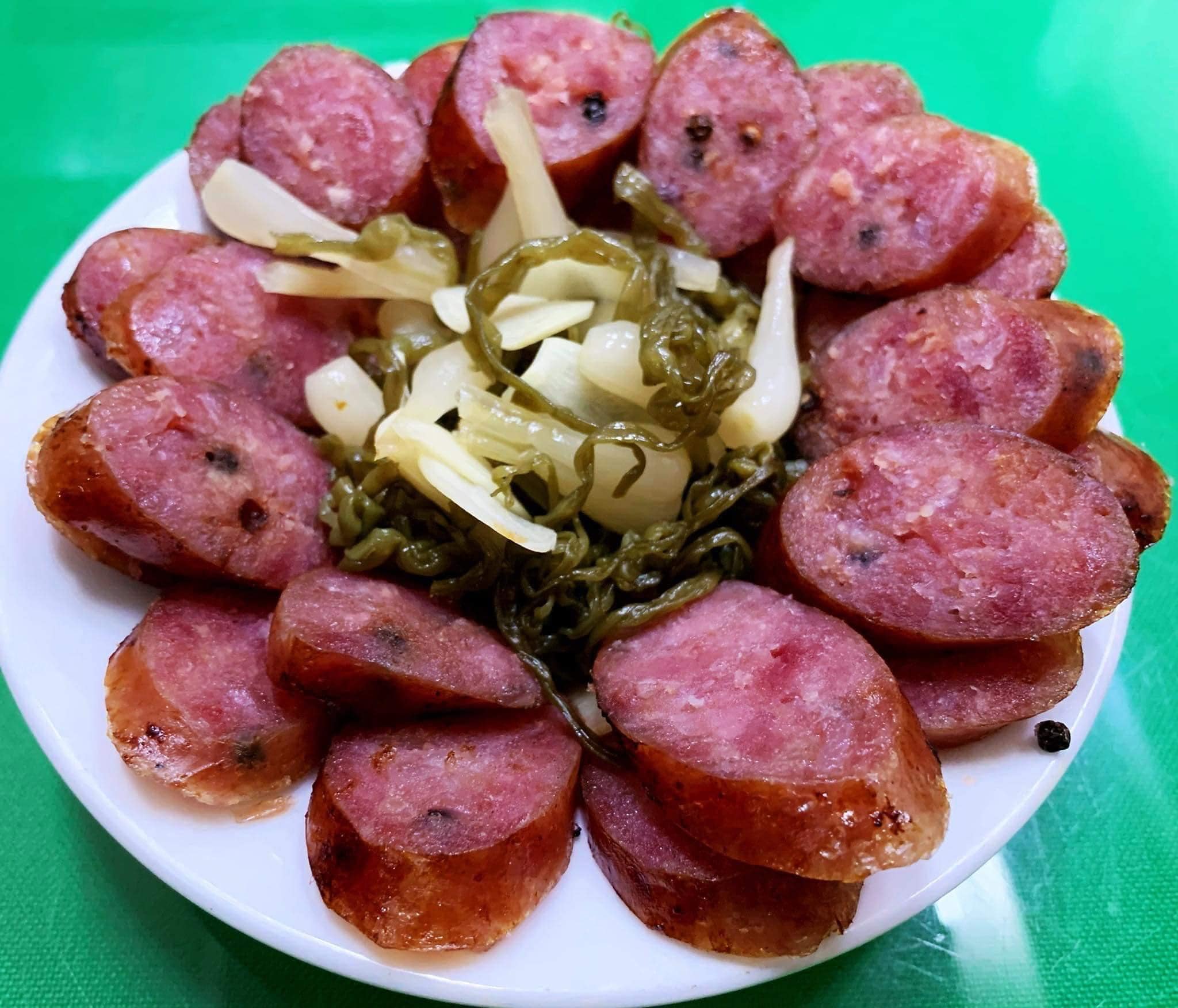 |
Processed foods, high in fat and chemicals, are detrimental to individuals with elevated liver enzymes. Photo: Dinh Dieu |
Processed foods, high in fat and chemicals, are detrimental to individuals with elevated liver enzymes. Photo: Dinh Dieu
Moldy foods, commonly found in grains, nuts, dried fruits, and pickled vegetables, can produce aflatoxins. These toxins not only damage the liver but also increase the risk of cancer. Molds can also generate other harmful toxins like amatoxins and orellanine, posing further health risks.
Spicy foods with excessive seasoning stimulate digestive fluid secretion and irritate the digestive tract, increasing pressure on the liver and impairing its function.
Grilled foods, when cooked at high temperatures, can produce harmful compounds such as heterocyclic amines (HCAs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). These substances have inflammatory potential and can contribute to elevated liver enzymes.
Doctor Binh advises patients to maintain regular physical activity, manage weight, ensure adequate sleep, and minimize stress to support better liver recovery. Regular health check-ups once every six months help monitor liver enzyme levels. Individuals experiencing persistent fatigue or jaundice should seek early medical evaluation and timely treatment. Consistent supplementation with natural essences like wasabia and s.marianum is recommended to help protect liver cells from harmful agents and stabilize liver enzymes.
Dinh Dieu
| Readers can submit questions about digestive diseases here for a doctor's response |