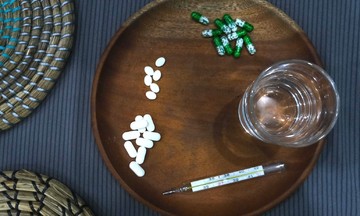Pickled vegetables, commonly made from cucumbers, cabbage, or other greens, are often prepared through fermentation or brining with salt and vinegar. They are typically served with main meals or greasy dishes to balance the richness. Their low-calorie, high-fiber, and probiotic content from fermentation can aid weight management.
For individuals aiming for weight loss, consuming pickled vegetables two to three times per week, with each serving not exceeding 100 g, can be beneficial. It is crucial to control the amount of salt and sugar used during preparation, as excessive intake can lead to high sodium levels, which is detrimental to health.
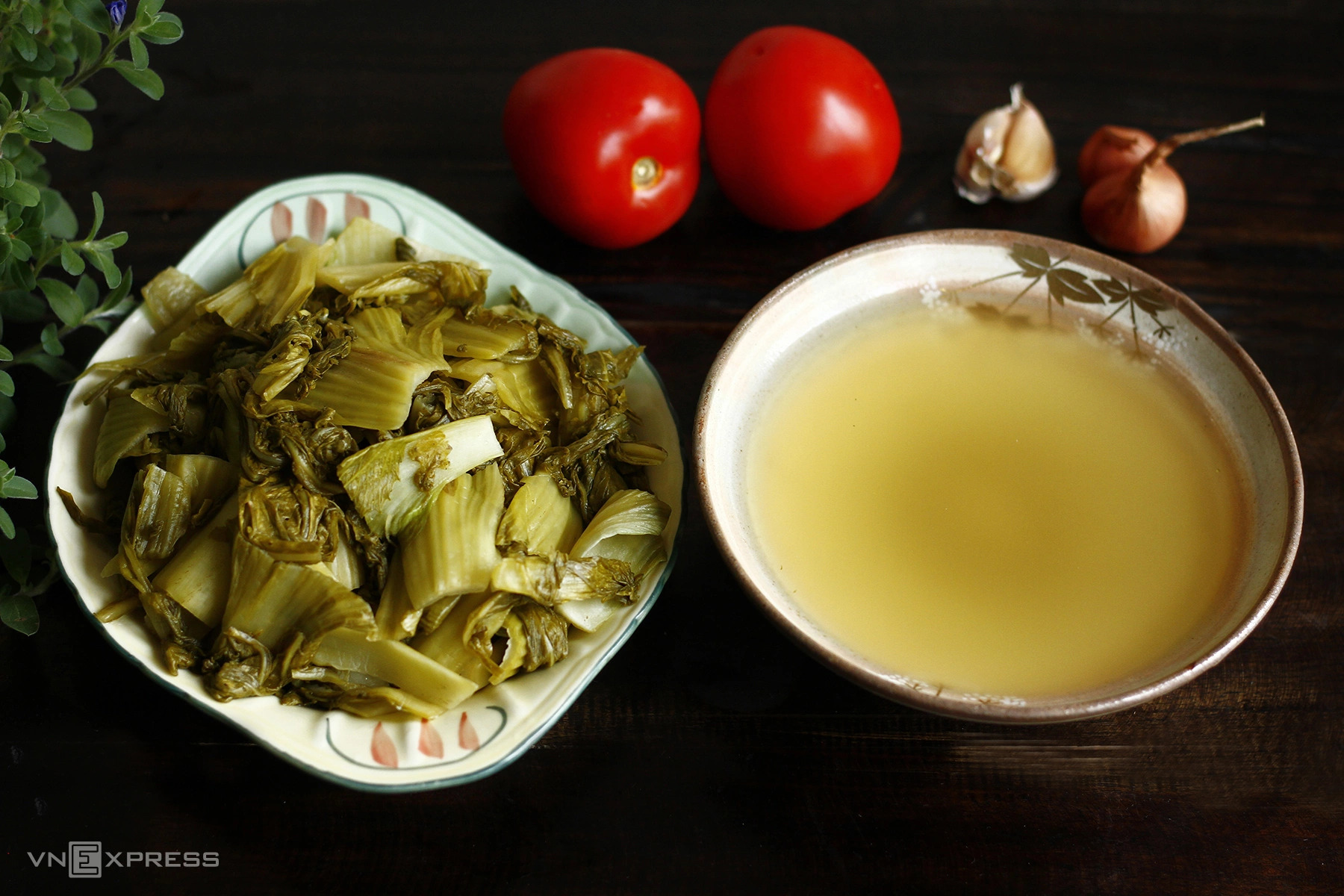 |
Pickled vegetables are rich in fiber and can support weight loss. Photo: Bui Thuy |
Pickled vegetables are rich in fiber and can support weight loss. Photo: Bui Thuy
The distinct sour and salty taste of pickled vegetables stimulates the palate while being low in calories. Their fiber content promotes a feeling of fullness quickly, which helps reduce cravings for high-energy foods like sweets and sugary items.
Pickled vegetables also have a high water content, contributing to the body's hydration. The mild saltiness can stimulate thirst, encouraging greater water intake. This helps maintain fullness and prevents overeating at subsequent meals.
A medium serving of pickled vegetables (approximately 65 g) provides only 5-10 calories. This minimal calorie contribution fits well within a controlled-calorie diet, having little impact on daily energy intake.
Compared to many processed snacks, pickled vegetables are low in sugar. Managing sugar intake is important for weight management and overall health. When consuming pickled vegetables, it is advisable to limit added sugar and check the nutritional labels of canned products.
Beyond their low-calorie profile, pickled vegetables offer antioxidants like beta-carotene (a precursor to vitamin A), which supports vision, immunity, and inflammation prevention. This food also contains vitamin K and beneficial probiotics from the fermentation process, aiding digestion, urinary tract health, and contributing to weight control when consumed judiciously.
Effective weight loss requires a balanced diet alongside maintaining a calorie deficit. This involves reducing fried foods, high-sugar items, and processed meats, while increasing fiber, low-sugar fruits, and lean protein. Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, jogging, cycling, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), helps increase energy expenditure. Adequate sleep and stress management also play a role in hormone regulation, supporting metabolism and sustainable weight loss.
Anh Chi (According to Very Well Health)
| Readers can submit questions about endocrine diseases here for doctors to answer. |