Do Thi Lan, a nutrition specialist from the Department of Nutrition at Tam Anh General Hospital in Hanoi, states that vitamin D is a vital micronutrient essential for bone metabolism, immune function, and cardiovascular health. Prolonged deficiency can increase the risk of osteoporosis, muscle aches, respiratory infections, and immune disorders. Here are ways to ensure children get enough vitamin D.
Proper sun exposure
During the cold season, children are more prone to vitamin D deficiency because sunlight intensity decreases, outdoor time is shorter, and they wear more layers of clothing that cover their skin. For effective sun exposure, parents should let children sunbathe later in the day, after 9-10 AM, rather than early morning. Sun exposure might need to be longer to absorb sufficient sunlight, typically 15 to 30 minutes, depending on skin type and clothing coverage. Avoid sunbathing behind glass, as UVB rays do not penetrate it.
Eating vitamin D-rich foods
Egg yolks, beef liver, cod liver oil, and fatty fish like salmon, herring, mackerel, and sardines contain vitamin D. Children who consume marine fish two to three meals per week also get omega-3, which supports cardiovascular health and immunity. Milk and dairy products also provide a certain amount of vitamin D. According to specialist Lan, a glass of vitamin D-fortified milk can supply 15-25% of the daily requirement, enough to help a child's body maintain stable levels when sunlight significantly decreases.
Certain mushrooms, such as shiitake, portobello, and maitake, can significantly increase their vitamin D2 content when exposed to sunlight for about 30 to 60 minutes. This mechanism is similar to how human skin synthesizes vitamin D upon exposure to UVB rays. Although vitamin D2 is not as potent as vitamin D3, supplementing through mushrooms remains a healthy option.
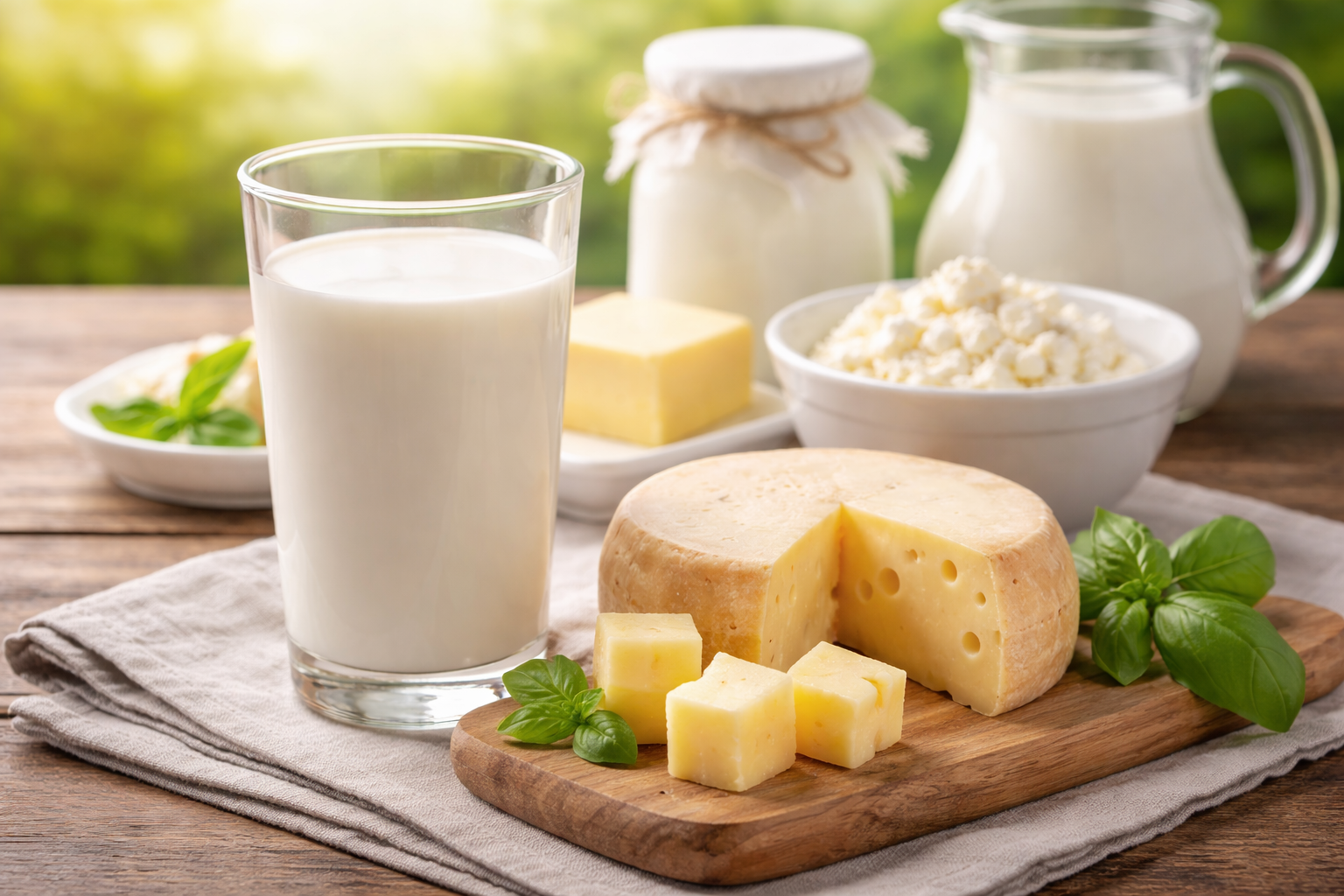 |
Milk and cheese can provide vitamin D for children during the cold season. Image generated by AI |
Combine with healthy fats
According to specialist Lan, to enhance vitamin D absorption from food, parents should combine it with healthy fat sources in each meal for their child. Vitamin D requires fat to dissolve and be absorbed through the small intestine. When vitamin D-rich foods (fatty fish, eggs) are consumed with healthy fats (olive oil, avocado), the body absorbs more vitamin D, utilizing it better than if consumed separately.
Increase physical activity
Increasing physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight also optimize vitamin D absorption. Outdoor physical activity around noon, when UVB rays are strongest, allows the skin to receive more natural light while promoting energy metabolism. This habit also reduces excess fat accumulation. Overweight and obese children often have lower vitamin D levels.
Specialist Lan notes that many children remain at high risk of deficiency even after supplementing vitamin D through natural methods, particularly those who are inactive, have darker skin, are overweight or obese, and young children. This group should have their 25(OH)D blood levels tested at the beginning of the cold season or if they show symptoms like fatigue, muscle aches, frequent illness, or poor sleep. If test results indicate low vitamin D, a doctor may prescribe oral supplements at an appropriate dosage. Self-administering high doses is not recommended, as excess vitamin D can cause toxicity, leading to hypercalcemia, which affects the cardiovascular system and kidneys.
Trinh Mai
| Readers can submit questions about infant and newborn care here for doctors to answer. |