Answer:
Joint pain is a common symptom of osteoarthritis, arthritis, or mild uric acid disorders. The causes can be related to cartilage damage, inflammation of the soft tissue surrounding the joints, or cold, damp weather increasing the sensitivity of sensory nerve endings.
People with joint pain should limit their consumption of bamboo shoots, especially fresh and pickled bamboo shoots, as they can negatively affect joint inflammation and pain. Bamboo shoots contain oxalic acid, which can combine with calcium in the body to form calcium oxalate. This can precipitate and deposit in soft tissues, joints, or kidneys, increasing the risk of arthritis, kidney stones, and worsening pain.
Some bamboo shoots also contain natural cyanide. This is a potential toxin if not properly cooked and can cause fatigue, headaches, or mild poisoning. Pickled bamboo shoots often contain high levels of salt, which can cause water retention, increasing pressure on joints, and is especially harmful to those with osteoarthritis or metabolic disorders.
Individuals with joint problems don't need to completely avoid bamboo shoots but should limit consumption to about once a week, with no more than 100-150 g per serving. Boil the bamboo shoots thoroughly, changing the water several times to remove toxins and reduce oxalate levels.
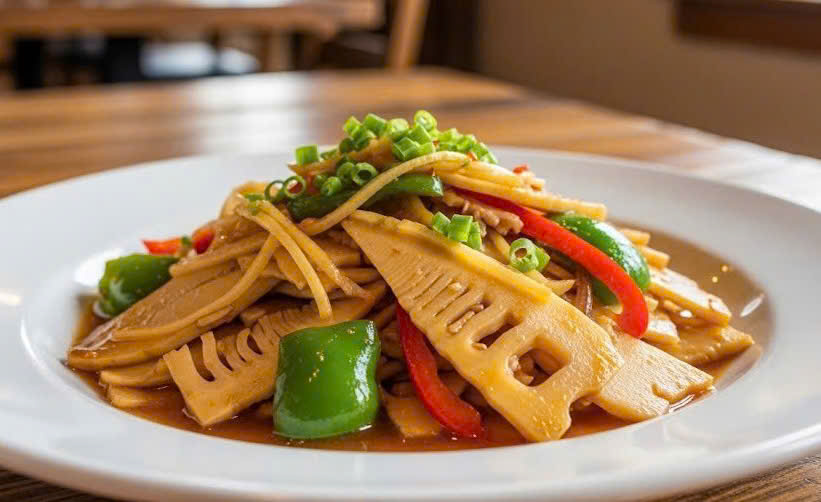 |
People with joint pain should limit their consumption of bamboo shoots. Photo: Trong Nghia |
People with joint pain should limit their consumption of bamboo shoots. Photo: Trong Nghia
Those with joint pain should also limit foods high in purines, such as organ meats, red meat, seafood, fried foods high in oil, carbonated soft drinks, and alcohol. These can worsen inflammation and increase joint pain.
A good diet for joints should prioritize dark green vegetables (spinach, kale), fatty fish (salmon, tuna), fruits rich in vitamin C (oranges, kiwi, guava), nuts, low-fat milk, and foods rich in natural collagen. Drinking enough water, light exercise, and avoiding putting heavy loads on joints are also helpful in improving symptoms.
Those experiencing joint pain should consult a musculoskeletal specialist to determine the specific cause and receive advice on a suitable diet and exercise plan. Monitoring inflammation and degeneration indicators is also recommended if an underlying condition is suspected. Supplements like eggshell membrane, chondroitin sulfate (a major component of the extracellular matrix), turmeric root extract, undenatured type II collagen, and hydrolyzed collagen peptides can help reduce pain, lubricate joints, nourish cartilage, and increase joint flexibility.
MSc. Dr. Nguyen Anh Duy Tung
Nutrihome Nutrition Center
| Readers can submit nutrition questions here for answers from doctors. |