Dr. Nguyen Nhu Duy, an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist at Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, performed an ear endoscopy on Han. The examination revealed a foreign object in her left ear, a congested eardrum, and pus in the ear canal. Her right ear had an earwax plug, preventing observation of the eardrum. Han was crying due to the foreign objects being pushed deep into her ears, causing severe pain, which necessitated anesthesia for their removal. The endoscopy confirmed that the foreign objects in both ears were two green beans that had split their shells and sprouted.
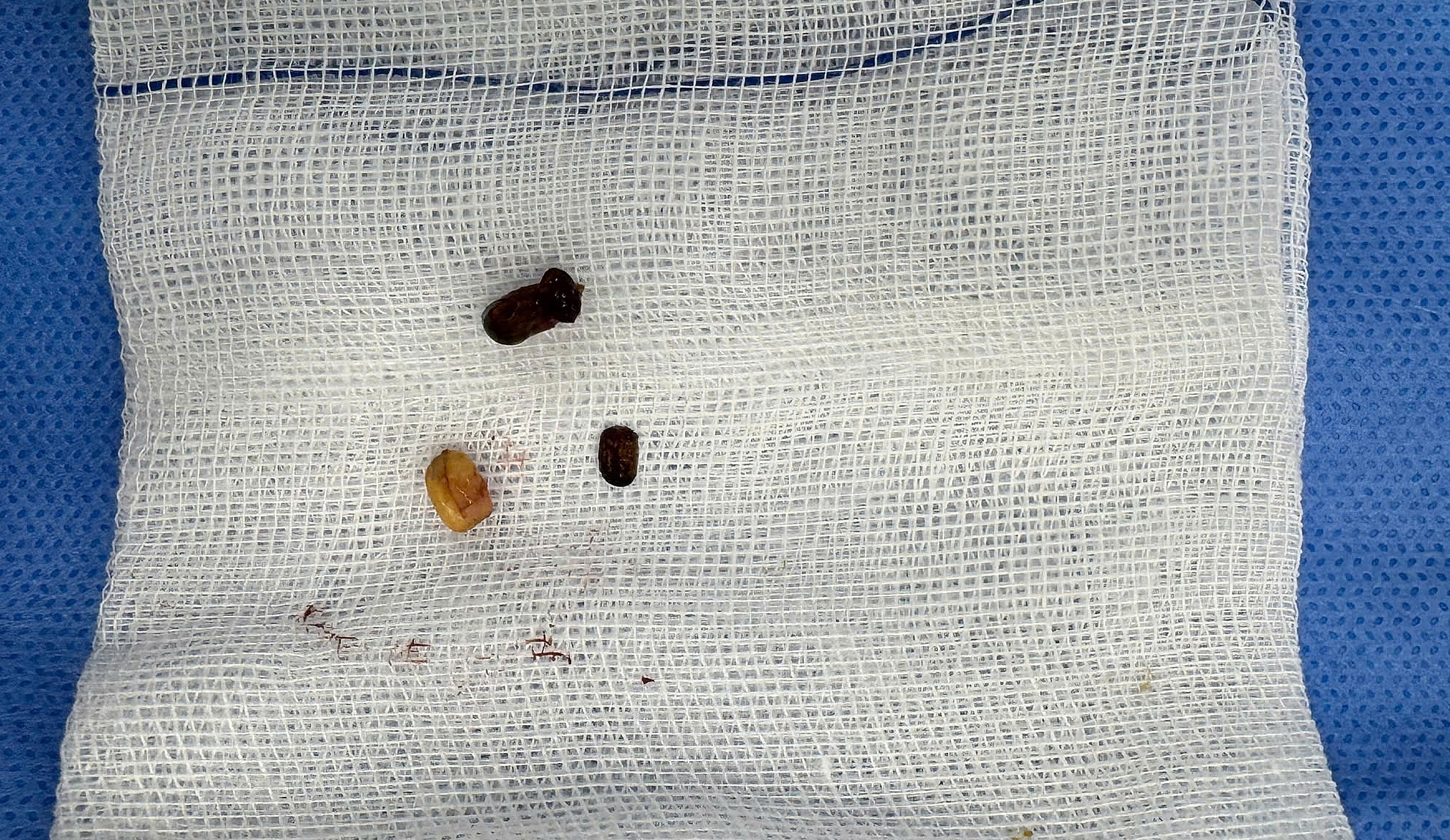 |
Two shelled green beans removed from Han's ears. *Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital* |
"The beans likely lodged in the child's ears for a prolonged period. The warm, moist environment in the ear canal provided ideal conditions for the beans to absorb water, swell, and sprout," Dr. Duy explained. He added that when the beans absorbed excessive moisture, their outer shells split, causing pain, tinnitus, and damage to the ear canal.
Using microsurgical forceps, the doctor carefully removed the two beans and their shells from Han's ears. After confirming both ear canals were clear, Han was discharged the same day.
 |
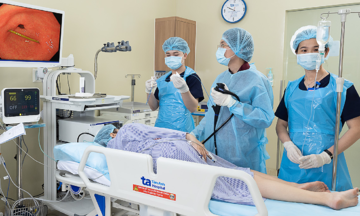
Dr. Nhu Duy performs an endoscopic follow-up examination for Han. *Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital* |
Children are naturally curious and often unaware of potential dangers, leading them to insert small items like toy pieces, school supplies, modeling clay, batteries, or magnets into their ears, nose, or throat. Dr. Duy emphasized that if foreign bodies in a child's ear are not detected and treated promptly, they can lead to hearing impairment, tinnitus, outer and middle ear infections, and eardrum perforation. Objects such as batteries or magnets can trigger chemical reactions inside the ear, resulting in inflammation, bleeding, and infection. Sharp objects pose a risk of piercing the eardrum, which can significantly reduce hearing.
Parents should be vigilant for symptoms such as ear itching, a tickling sensation inside the ear, rubbing or scratching the ear, earache, or rustling sounds. If any of these signs appear, it is crucial to take the child to an ENT specialist immediately for timely intervention.
To prevent children from inserting foreign objects into their ears, adults should avoid leaving children unsupervised and monitor them frequently. It is important to teach children not to place objects into their ears, nose, or throat. Parents should also limit children's access to small items that are easily inserted into these areas, such as Lego bricks, sharp objects, coins, buttons, and batteries.
Uyen Trinh
*Patient's name has been changed.