Answer:
A fungal ear infection, or otomycosis, is a condition where fungi infect the outer ear canal. Many different types of fungi cause ear infections, but aspergillus and candida are the most common. Symptoms can be obvious, but some cases progress silently, only becoming apparent during an ear, nose, and throat examination. In the early stage, patients often experience mild itching in the outer ear canal, which gradually worsens. During an endoscopy, doctors observe redness of the ear canal skin. The condition also causes tinnitus, pain, discharge, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and hearing loss.
Individuals with weakened immunity (such as those with diabetes or prolonged corticosteroid use), eczema, chronic skin conditions, or those who frequently participate in water activities face a higher risk of fungal ear infections. Water entering the ear and improper cleaning, along with prolonged humidity, create favorable conditions for fungal growth. Earwax removal at barbershops or hair salons also carries a risk of cross-contamination with fungi.
Fungi penetrate the ear and adhere to the ear canal lining, causing inflammation and irritation. The body responds by increasing earwax production to protect itself and expel the harmful agents. Fungi also consume the keratin layer, leading to significant flaking of the ear canal skin. A fungal ear canal environment is often moist with altered pH levels, which further promotes fungal growth and leads to greater earwax accumulation.
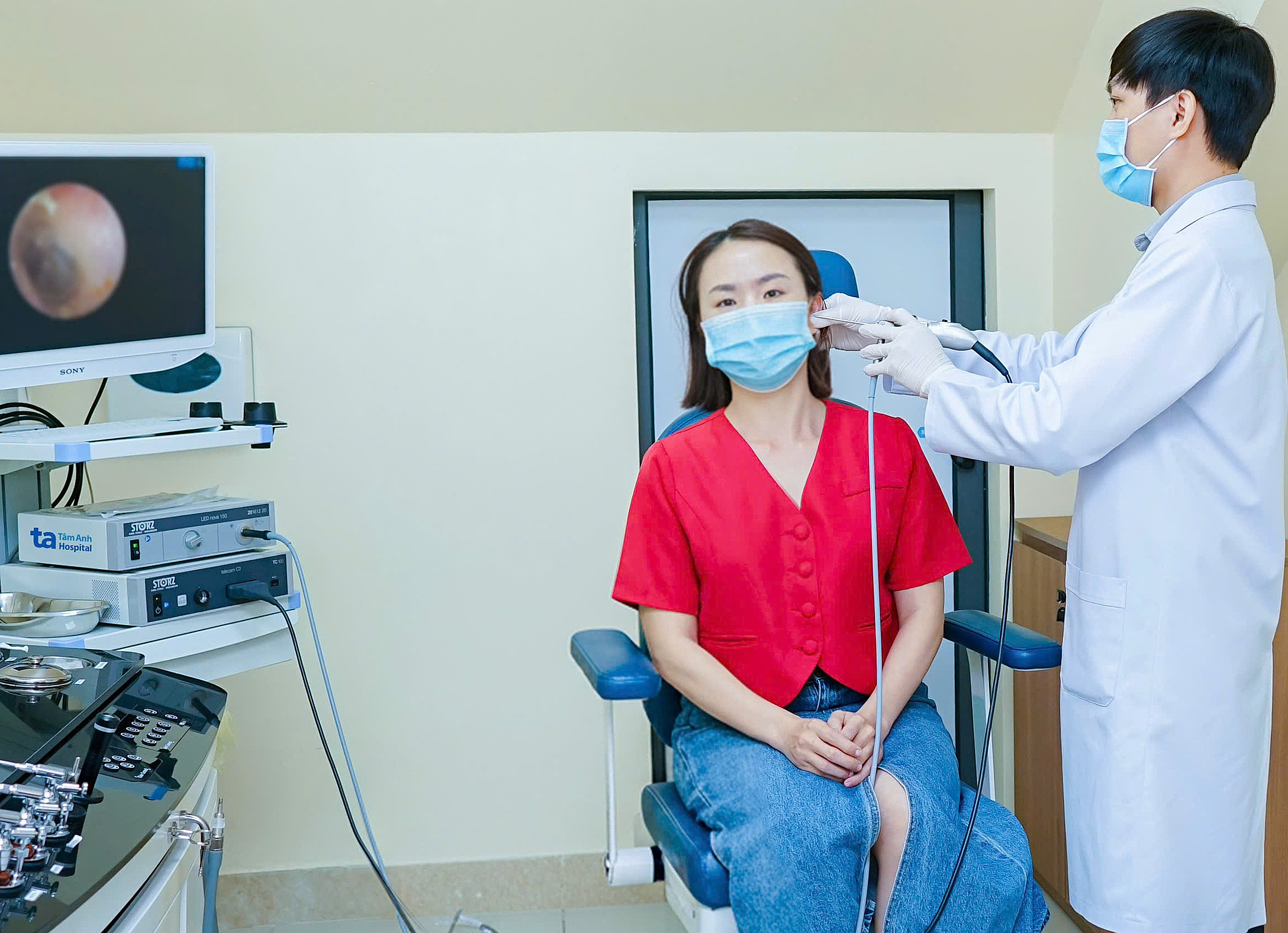 |
Doctor Minh performs an ear endoscopy for a patient. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
To diagnose a fungal ear infection, doctors typically take a patient's medical history, perform an ear endoscopy to examine the ear canal and eardrum, and treat by thoroughly cleaning earwax, sanitizing the ear, and prescribing medication. Alongside prescribed medication, patients must keep their ears dry and avoid getting water in them, as moisture creates a favorable environment for fungal recurrence. Limit swimming in public places and avoid using cotton swabs to clean ears.
If not diagnosed and treated promptly, a fungal ear infection can lead to otitis media, external otitis, or a perforated eardrum. If you experience frequent ear itching, tinnitus, excessive earwax, or hearing loss, consult an ear, nose, and throat specialist for timely diagnosis and treatment.
MSc. Doctor Huynh Hoang Minh
Ear, Nose, and Throat Center
Tam Anh General Hospital, TP HCM
| Readers can ask questions about ear, nose, and throat conditions here for a doctor's answers. |