The order of eating can enhance satiety, prevent post-meal blood sugar spikes, and provide stable energy for the body. People with diabetes should begin their meals with a plate of vegetables (comprising 1/2 of the portion) to help manage blood sugar levels. Vegetables offer numerous benefits, from increasing meal volume to providing fiber and water.
Reduced calories
When starting a meal with vegetables, individuals consume low-calorie, fiber-rich foods, which helps reduce subsequent food intake. Non-starchy vegetables increase meal volume, slowing both eating speed and food digestion, thereby preventing rapid blood sugar increases. You can eat a bowl of stir-fried, soup, or boiled vegetables first, followed by meat, fish, eggs, and finally starches.
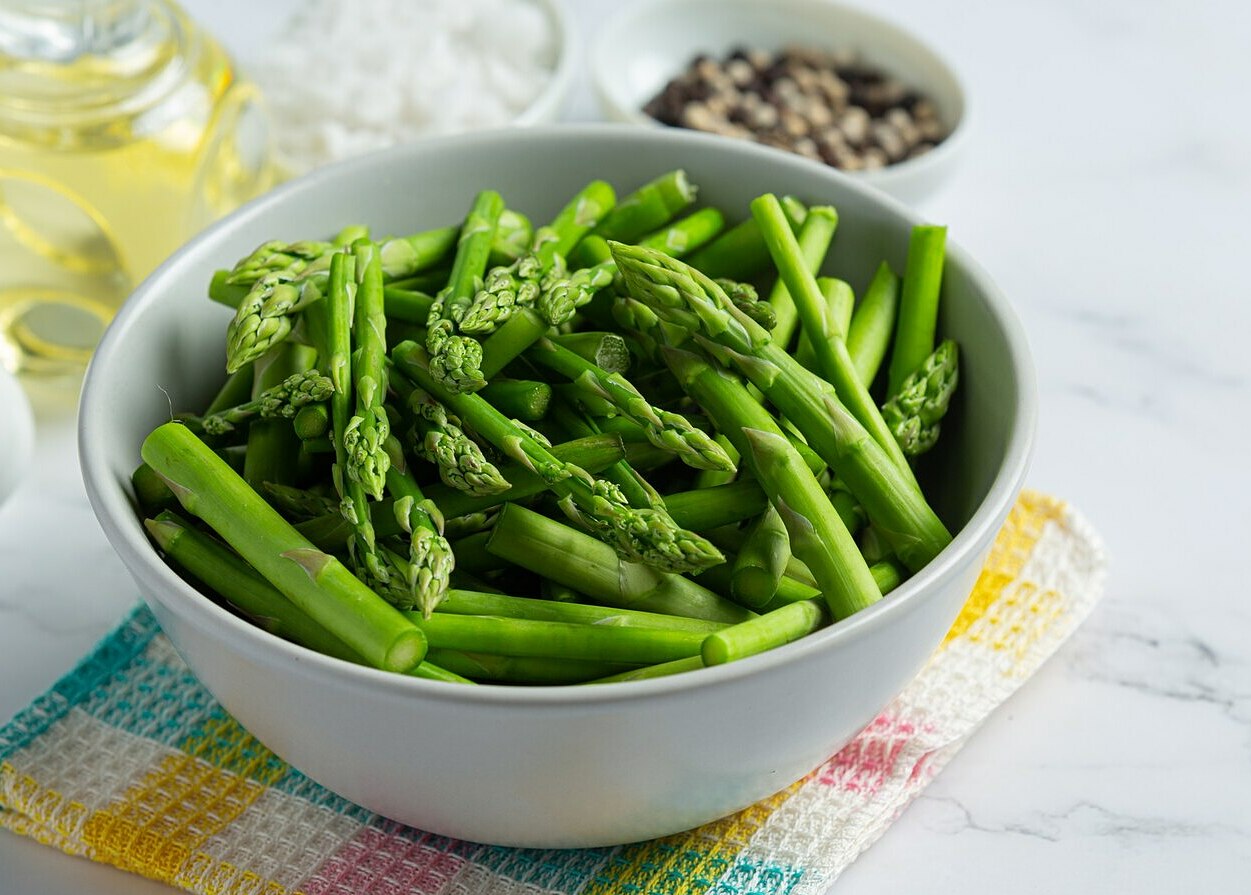 |
Green vegetables enhance satiety with minimal impact on blood sugar. *AI-generated image* |
Increased fiber intake
Fiber is an essential nutrient that helps balance blood sugar. It slows the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing post-meal blood sugar spikes. Starting meals with fiber-rich vegetables like leafy greens in salads, raw or boiled broccoli, or vegetable soup helps stabilize blood sugar. Avoid starting with starchy vegetables such as potatoes or pumpkin due to their high carb content and glycemic index.
Hydration
Water is crucial for people with diabetes and overall health. Vegetables, especially when eaten raw, steamed, or boiled, have a high natural water content, promoting faster satiety. Drinking water before meals can slow digestion, reducing the impact of blood sugar on the meal. Vegetables do not replace drinking water for daily fluid needs. Therefore, individuals should eat plenty of vegetables and drink 2 liters of water daily.
People with diabetes should vary their vegetable menu regularly to prevent boredom. Some suggested dishes include:
Vegetables: Raw vegetables like bell peppers, cherry tomatoes, sliced cucumbers, or green peas can be paired with dips such as soy sauce or sesame salt.
Simple salad: A quick green salad with mixed greens, shredded carrots, and diced cucumbers helps provide fiber and water. Adding healthy fats from olive oil or nuts contributes to stable blood sugar maintenance.
Soup: Starting a meal with vegetable soup made from bone broth or vegetable stock helps increase satiety and slows digestion, balancing blood sugar. Consider using lentils, kidney beans, or black beans in your soup to boost fiber and protein.
People with diabetes should maintain moderate portion sizes, avoiding overeating, which can lead to sudden blood sugar spikes. The "palm-sized plate" method is recommended, consisting of 1/2 non-starchy vegetables, 1/4 lean protein, and 1/4 whole grains or starches from brown rice or whole-wheat bread.
Beyond diet, short walks of 10-15 minutes after meals, ample water intake, sufficient sleep, and stress reduction are advisable. Avoid sugary drinks and highly seasoned processed foods.
Anh Chi (*According to Eating Well*)