|
Ginger
Ginger contains bioactive compounds such as gingerol and shogaol. These compounds offer anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits, helping to alleviate acute airway muscle spasms and lung inflammation. Adults can consume about two to four grams of fresh ginger daily, roughly a small, thumb-sized piece.
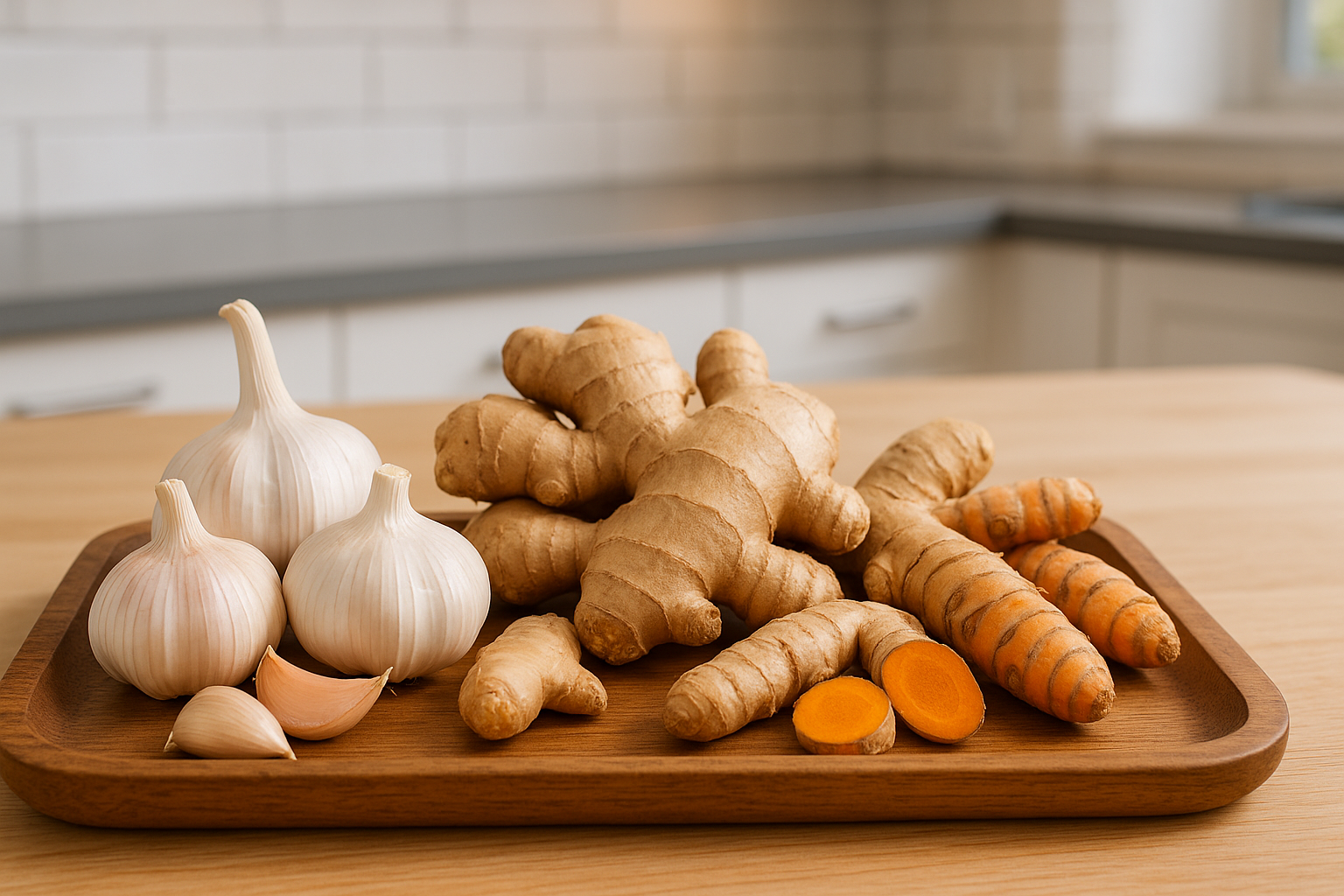 |
Turmeric
This spice is rich in curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, contributing to the protection of lung tissue from oxidative stress caused by pollution. A safe dosage of turmeric is 0-3 mg of curcumin per kilogram of body weight per day, which is about 5 grams of turmeric powder for a 50 kg person daily.
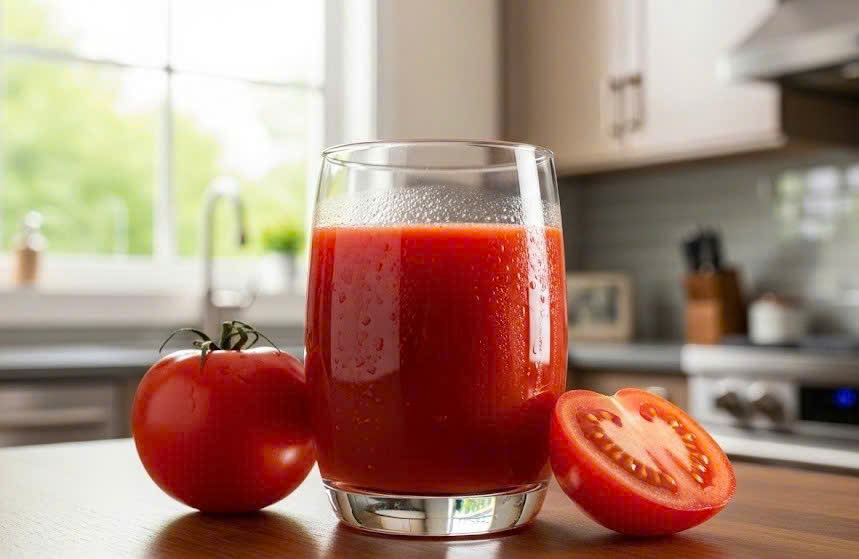 |
Tomatoes
Tomatoes provide the antioxidant lycopene, which supports respiratory health and reduces oxidative stress associated with air pollution. Cooking tomatoes increases lycopene absorption.
 |
Green Vegetables
Green leafy vegetables are rich in glucoraphanin. This compound converts into sulforaphane, activating enzymes that help detoxify and eliminate pollutants, also reducing inflammation. These vegetables are versatile and can be stir-fried, steamed, boiled, or blended into smoothies.
 |
Vitamin C-rich Fruits
Vitamin C is a water-soluble antioxidant capable of neutralizing free radicals generated by pollutants in the lungs. Guava, kiwi, bell peppers, and oranges are rich in this vitamin. You can chop these foods to make salads or eat them individually.
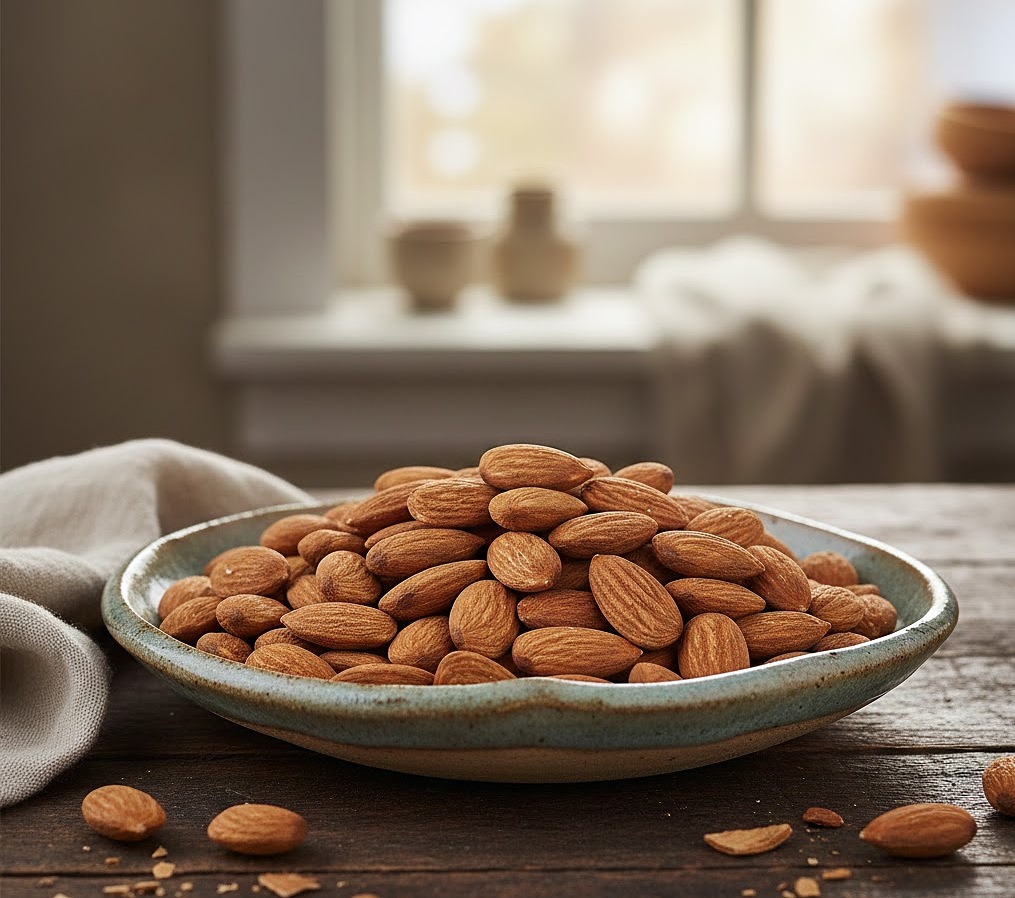 |
Almonds
Almonds are rich in vitamin E, a fat-soluble antioxidant that protects lung cell membranes from oxidative damage caused by pollutants. A small handful of almonds (about 28 grams) daily can enhance overall health. For an improved taste, consider eating them with yogurt.
Le Nguyen (According to Economic Times, Hindustan Times)
Photo: AI