|
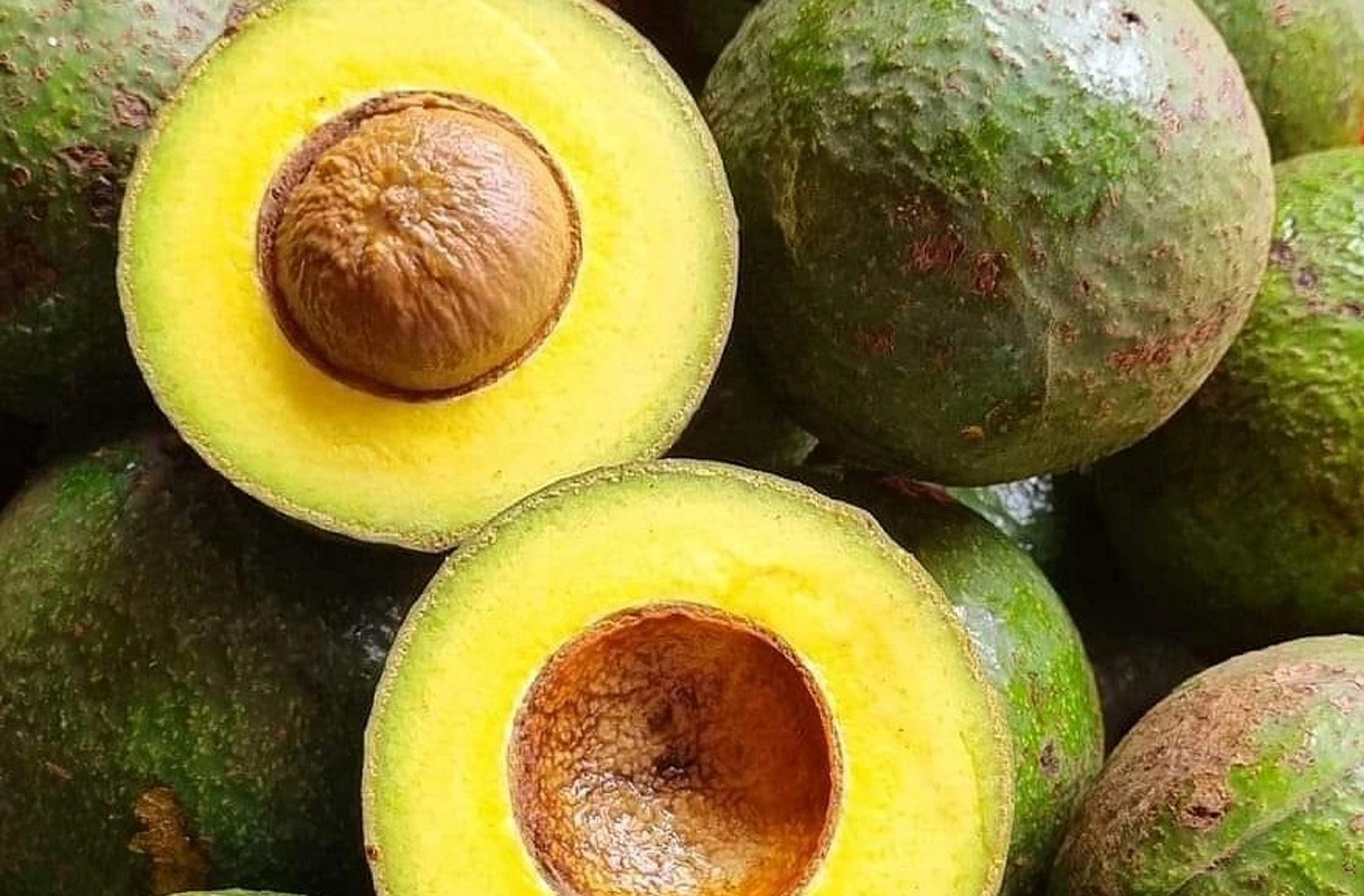
Avocado is rich in potassium and unsaturated fats, supporting muscle recovery and maintaining electrolyte balance. This fruit also provides plant protein, beneficial for heart health and the digestive system. Eating avocado correctly helps manage weight and improves overall health. |
Avocado is a nutrient-dense fruit known for its benefits in muscle recovery. It is rich in potassium and unsaturated fats, which are crucial for maintaining electrolyte balance and supporting the body's post-exercise recuperation. Beyond muscle support, avocado offers plant-based protein, contributing to cardiovascular health and aiding digestion. Proper consumption of this fruit can also assist in weight management and promote general well-being.
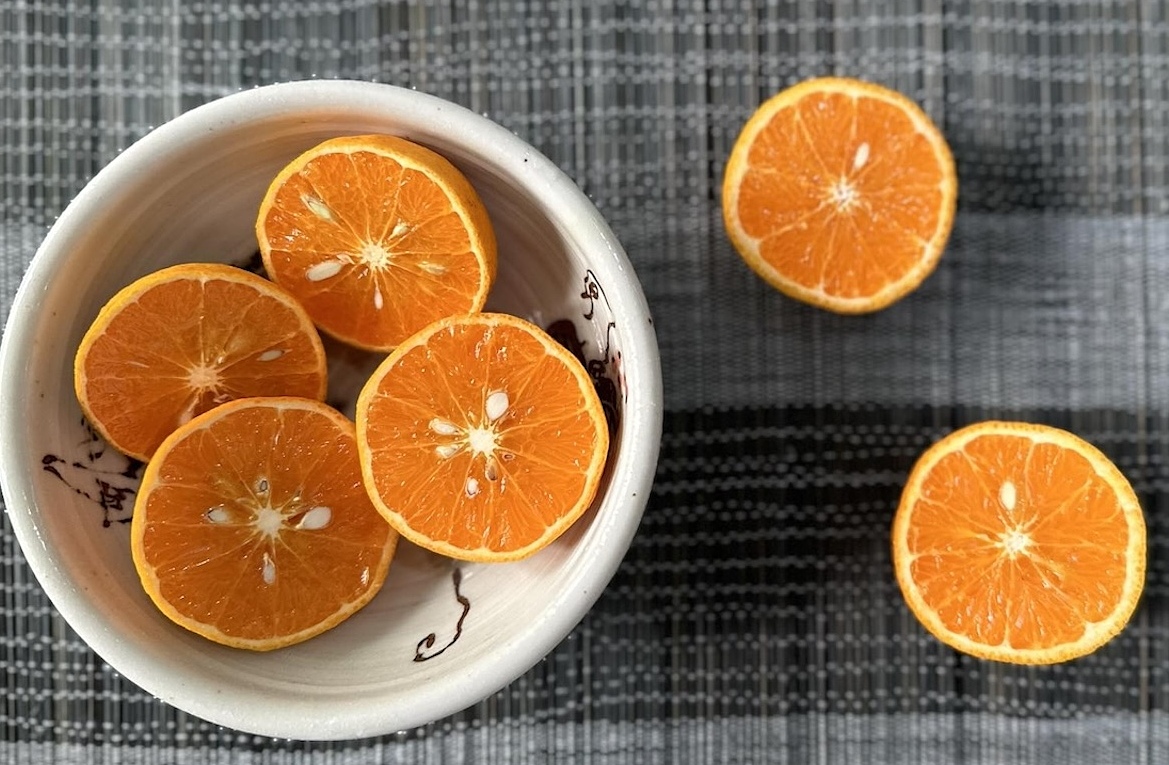 |
Orange is rich in vitamin C - a powerful antioxidant, helping reduce inflammation and promoting muscle tissue repair after training. The natural compound hesperidin in oranges enhances circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients to muscles faster, while replenishing energy and electrolytes after exercise. |
Oranges are an excellent source of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that helps reduce inflammation and promotes muscle tissue repair following workouts. They contain hesperidin, a natural compound that enhances circulation, ensuring faster delivery of oxygen and nutrients to muscles. Additionally, oranges replenish energy and electrolytes lost during physical activity.
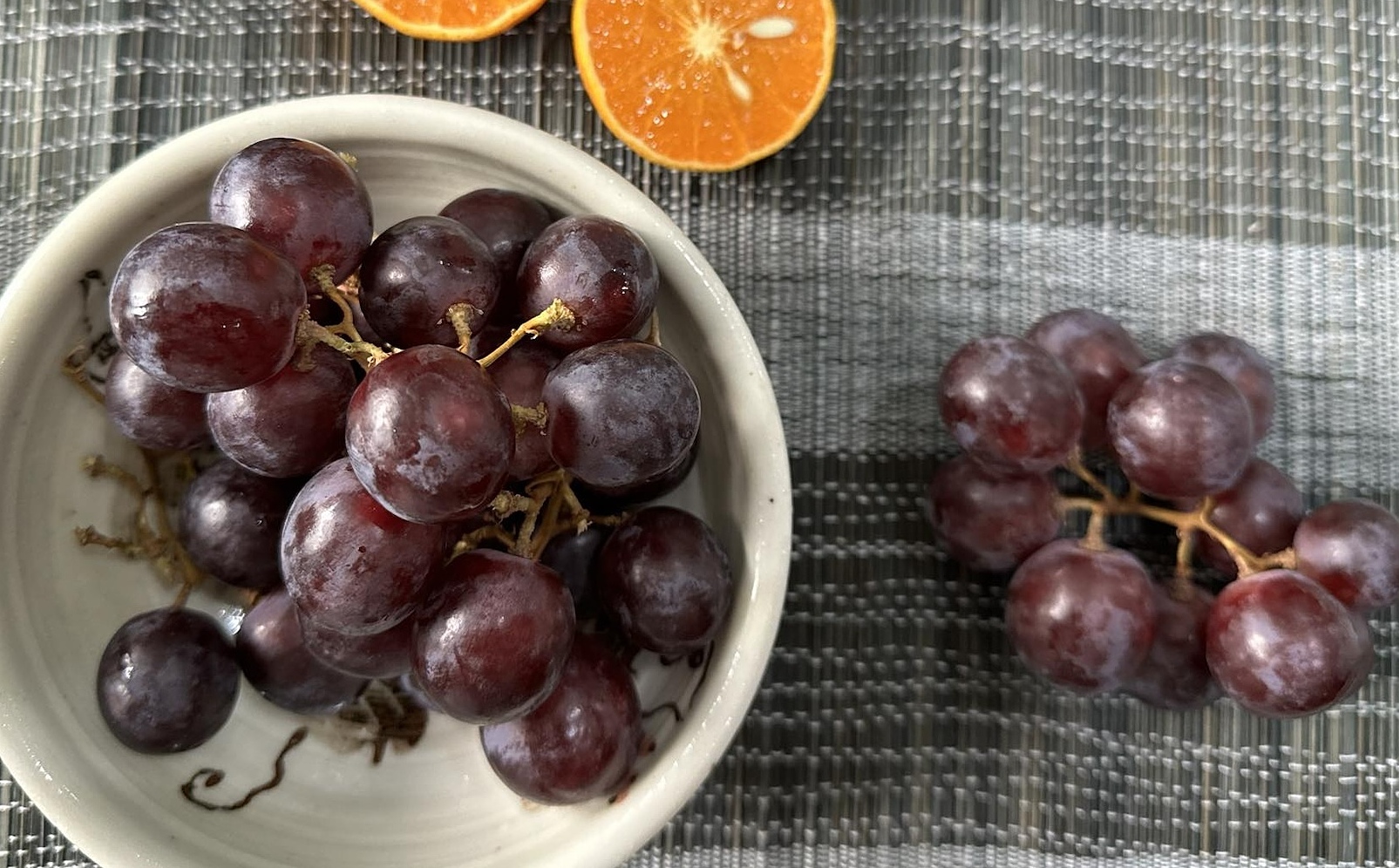 |
Grapes contain low natural sugar, rich in antioxidants like resveratrol, supporting energy maintenance and reducing muscle inflammation. People who want to lose weight and gain muscle can eat grapes before or after training, combined with lean protein meals to enhance effectiveness. |
Grapes are a beneficial fruit for those aiming to build muscle, as they contain low natural sugar and are rich in antioxidants like resveratrol. These compounds help maintain energy levels and reduce muscle inflammation. Individuals focused on weight loss and muscle gain can incorporate grapes into their diet before or after workouts, ideally paired with lean protein meals to maximize results.
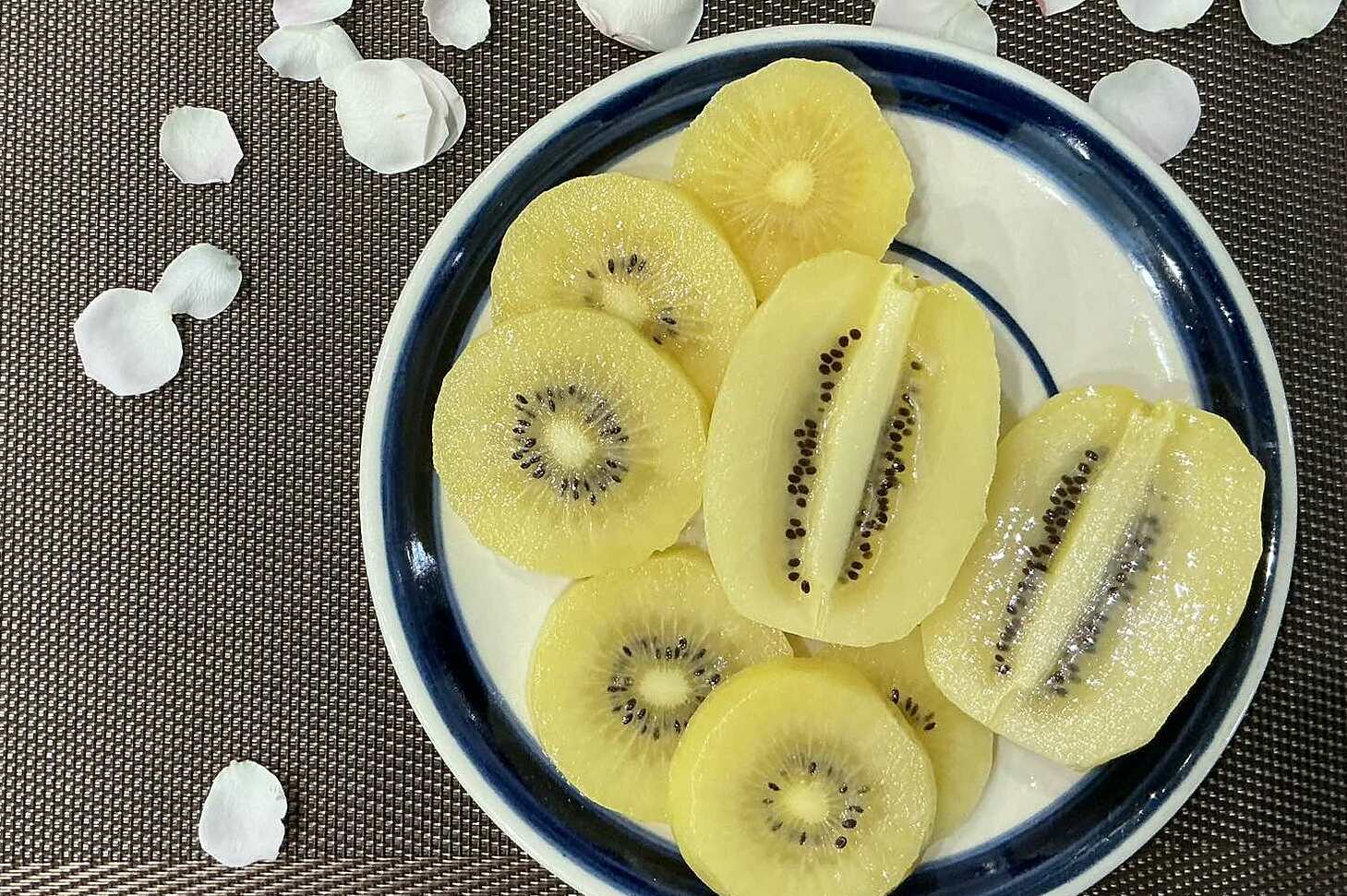 |
Kiwi contains about 2 grams of protein per fruit, and is rich in vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants, promoting collagen production and limiting oxidative stress in muscles. This fruit also brings benefits for cardiovascular health, the digestive system, and boosts immunity. |
Kiwi offers approximately 2 grams of protein per fruit, along with abundant vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants. These nutrients are vital for promoting collagen production and mitigating oxidative stress in muscles. Furthermore, kiwi supports cardiovascular health, aids the digestive system, and boosts the body's immune response.
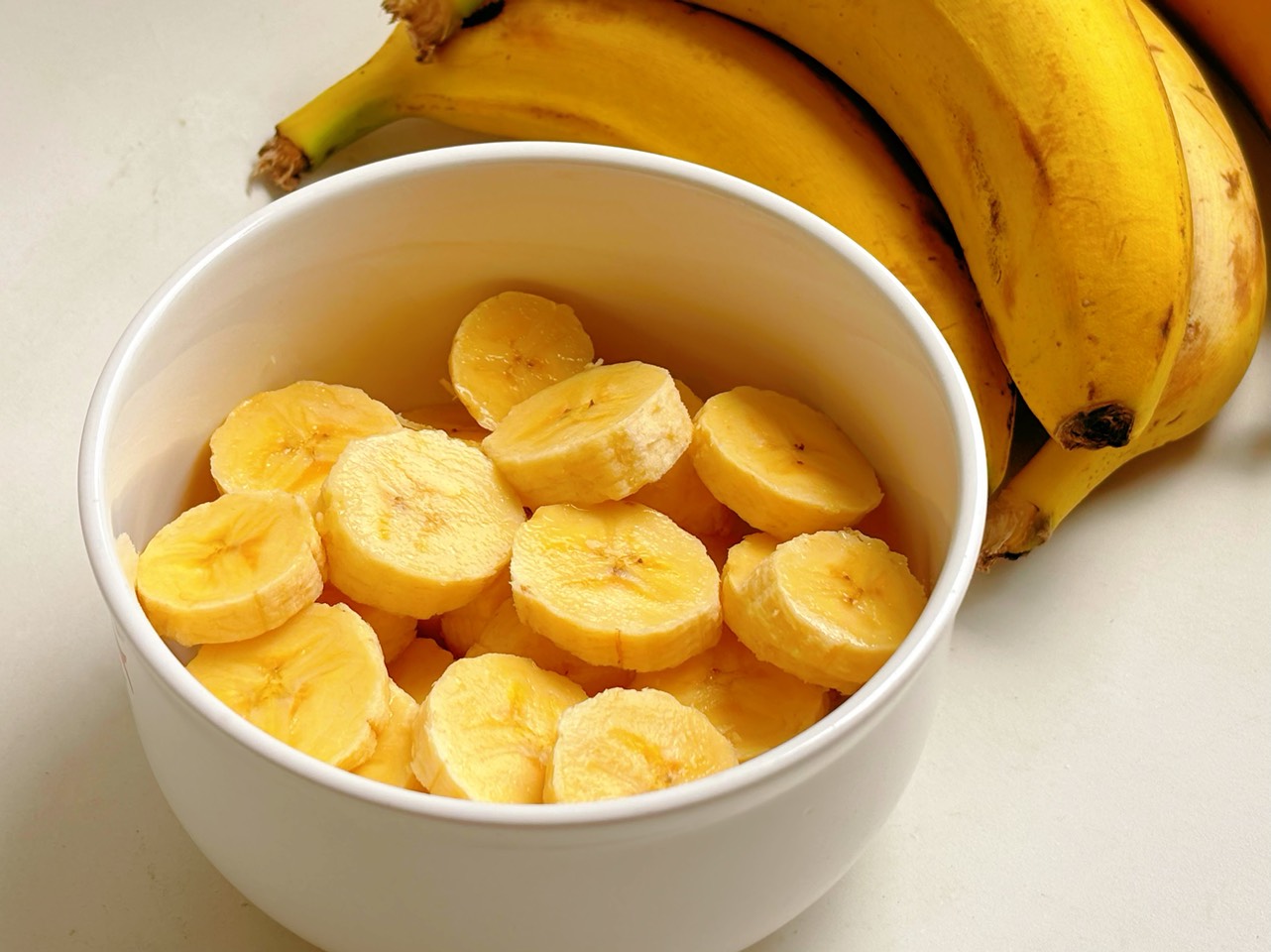 |
Banana is rich in potassium and carbohydrates, replenishing glycogen stores and limiting muscle cramps. Its protein content helps maintain muscle mass, reducing the risk of muscle degradation. Bananas are suitable before meals or as a post-workout snack to boost energy and promote recovery. |
Bananas are an ideal fruit for active individuals, packed with potassium and carbohydrates that replenish glycogen stores and help prevent muscle cramps. Their protein content aids in maintaining muscle mass and reduces the risk of muscle degradation. Bananas are suitable for consumption before meals or as a light snack after exercise, providing an energy boost and promoting recovery.
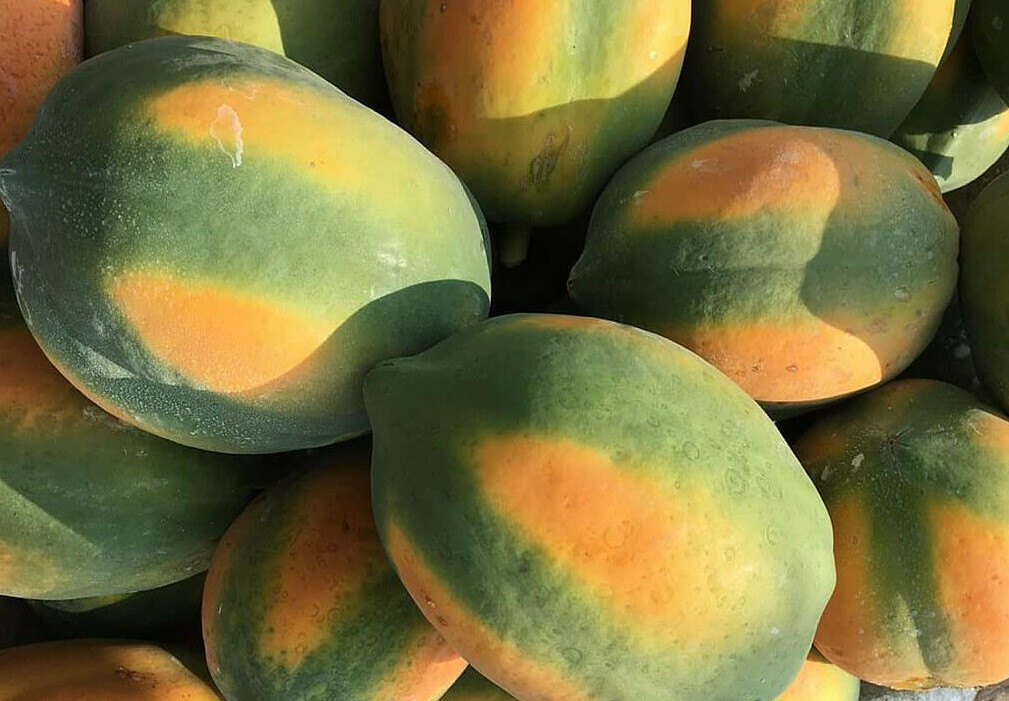 |
Papaya contains papain, an enzyme that aids digestion and protein absorption, thus benefiting muscle synthesis. Vitamin C in papaya can boost the body's immunity to fight illness. |
Papaya is valuable for muscle development due to its papain content, an enzyme that assists in digestion and protein absorption, thereby facilitating muscle synthesis. The vitamin C found in papaya also strengthens the body's immunity, helping to ward off illness.
Anh Chi (According to ETimes, Healthline, WebMD)
Photos: Anh Chi, Bao Bao, AI