Liver cancer involves malignant tumors forming in the liver, destroying liver cells and impeding the organ's normal function. According to Master, Doctor Nguyen Tien Sy from the Oncology Department, Tam Anh General Hospital TP HCM, several treatment methods are available for liver cancer patients.
Surgery is an effective treatment for liver cancer in patients with good liver function or early-stage cancer. Doctors may recommend resection of a liver segment. After removing the part of the liver containing the tumor, the remaining liver can function normally. Within a few weeks to several months, the liver can regenerate and return to its normal size. However, if the patient has advanced cirrhosis, even a small tumor, surgical resection is not indicated because it does not address the underlying disease.
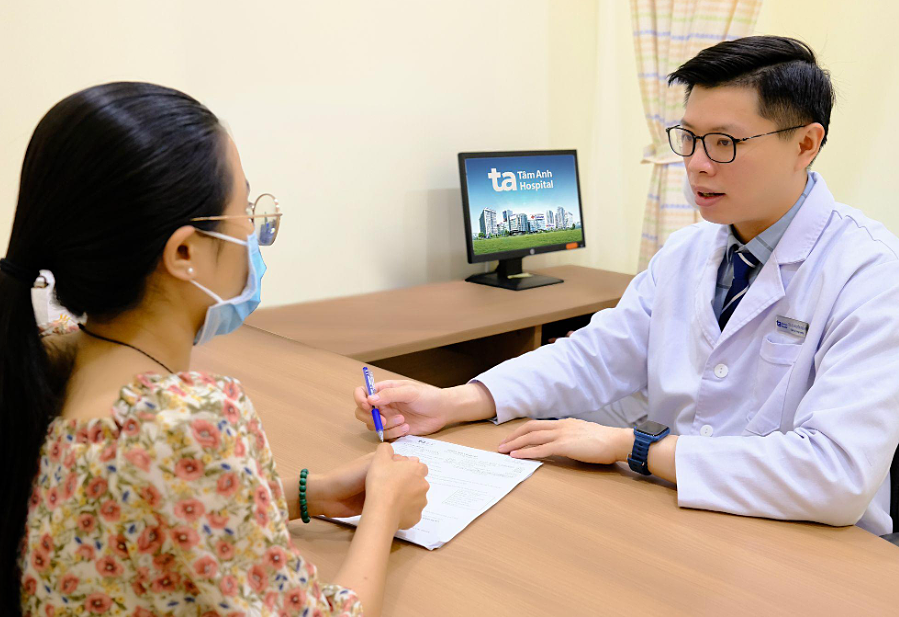 |
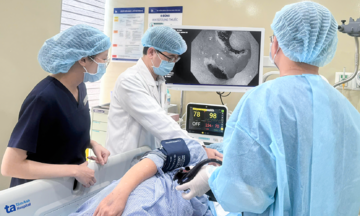
Doctor Sy consults a patient. Illustration: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Liver transplant involves removing the entire liver and replacing it with healthy liver tissue from a donor. This method is indicated when the damage is localized within the liver and has not metastasized beyond the liver. Patients may undergo a liver transplant if they meet specific criteria, including tumor size, number, affected area, and compatibility of the donated tissue.
Local treatments directly target cancer cells or the tissue surrounding the tumor. These include tumor ablation, cryoablation, alcohol injection, hepatic artery chemoembolization, and radioembolization.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is used when tumors are difficult to surgically remove and are smaller than 3 cm. This is a common technique where doctors insert one or more needle electrodes directly into the tumor, heating it to 60-100 degrees Celsius.
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) helps cut off the blood supply to the tumor and destroy it. This minimally invasive procedure selectively targets the hepatic artery, preserving healthy liver tissue and helping the patient maintain essential liver function. Doctors inject chemotherapy drugs (which are cytotoxic and block blood flow) into the malignant liver tumor via a catheter.
Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation to destroy cancer cells. For liver cancer, techniques such as stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) may be used.
Chemotherapy involves taking medication orally or via intravenous injection to find and destroy cancer cells. However, chemotherapy can also kill healthy cells and cause side effects. This method is indicated for advanced liver cancer that has invaded blood vessels, regional lymph nodes, or metastasized. Currently, chemotherapy is less frequently used due to the availability of systemic treatment alternatives with fewer side effects.
Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target certain genes or proteins in cancer cells, blocking blood vessel formation and inhibiting the growth and spread of cancer cells to surrounding tissues. This method is often used for patients with unresectable liver tumors.
Immunotherapy leverages the body's immune system to fight cancer. This therapy helps quickly detect foreign cells, activating the immune system's ability to attack and eliminate cancer cells. Experts create substances in the laboratory to enhance, guide, and restore the body's natural defenses against cancer cells.
Nguyen Tram
| Readers can send questions about cancer here for doctors to answer. |